Earl is a noble title historically associated with British and Anglo-Saxon aristocracy, often ranking below a marquess and above a viscount in the peerage system. The title carries a rich heritage and is commonly linked to land ownership, governance, and social prestige throughout history. Discover how the role of an Earl has evolved and its significance in modern times by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
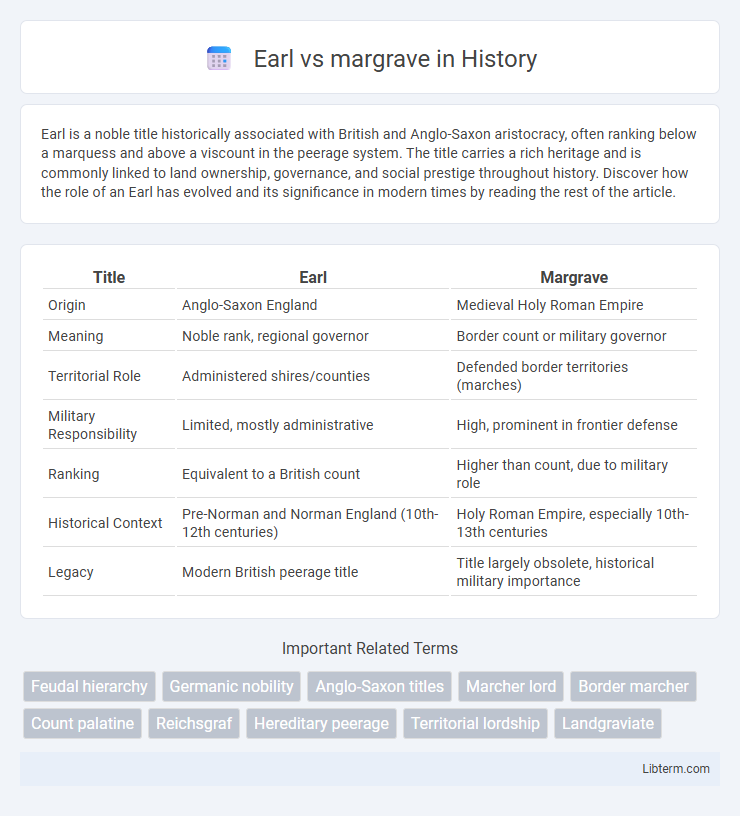
| Title | Earl | Margrave |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Anglo-Saxon England | Medieval Holy Roman Empire |
| Meaning | Noble rank, regional governor | Border count or military governor |
| Territorial Role | Administered shires/counties | Defended border territories (marches) |
| Military Responsibility | Limited, mostly administrative | High, prominent in frontier defense |
| Ranking | Equivalent to a British count | Higher than count, due to military role |
| Historical Context | Pre-Norman and Norman England (10th-12th centuries) | Holy Roman Empire, especially 10th-13th centuries |
| Legacy | Modern British peerage title | Title largely obsolete, historical military importance |
Introduction: Understanding Earl and Margrave
Earl and Margrave are historical European noble titles associated with regional governance and military authority. An Earl, primarily used in England and Ireland, governed a county or shire, often overseeing judicial and administrative functions. A Margrave, derived from the German "Markgraf," ruled border territories known as marches, combining noble rank with military leadership to defend frontier regions.
Historical Origins of Earl and Margrave
The title of Earl originated in Anglo-Saxon England, where it denoted a high-ranking noble appointed by the king to govern a shire or territory, functioning as a regional ruler with administrative and judicial powers. The Margrave, derived from the German "Markgraf," emerged during the medieval Holy Roman Empire as a military governor responsible for defending border provinces, or "marks," with elevated authority to manage frontier security. Both titles reflect the historical necessity of localized governance and defense, with Earls rooted in early English feudal structures and Margraves in the militarized borderlands of Germanic realms.
Nobility Hierarchy: Earl vs Margrave
An Earl ranks as a senior noble in the English peerage, traditionally governing a county, while a Margrave holds a comparable noble title in the Holy Roman Empire and other Germanic regions, responsible for border territories known as marches. The Margrave's role often included military defense duties, reflecting a higher strategic importance despite similar hierarchical status to an Earl. Both titles signify territorial authority but differ in regional jurisdiction and historical military significance within the nobility hierarchy.
Geographic Distribution of Titles
The title of Earl was predominantly used in England and Scotland, signifying a noble rank with administrative and military duties within these kingdoms. Margrave, derived from the German "Markgraf," was commonly found in the Holy Roman Empire and border regions of Central and Eastern Europe, indicating a military governor responsible for frontier territories known as marches. Both titles reflect the geopolitical landscape of medieval Europe, with Earls governing established counties and Margraves defending and managing volatile borderlands.
Roles and Responsibilities
Earls historically governed large territories within a kingdom, managing administration, justice, and defense on behalf of the monarch, often overseeing several counties. Margraves held similar responsibilities but were specifically assigned to border regions, charged with greater military duties to defend frontier areas against external threats. Both titles entailed significant regional authority, but margraves had enhanced military obligations due to their strategic positions along the empire's edges.
Symbolism and Regalia
Earl and margrave titles each carry distinct symbolism and regalia reflecting their historical roles in medieval European nobility. The earl, primarily associated with Anglo-Saxon England, symbolized regional governance and justice, often represented by a sword or ring denoting authority, while the margrave, common in the Holy Roman Empire, signified border defense and military command, with regalia like a distinctive crown or mantle indicating their elevated martial status. These visual and symbolic elements underscored their respective political and military responsibilities within feudal society.
Influence in Medieval Europe
The title of Earl held significant territorial and administrative authority within Anglo-Saxon and Norman England, often governing large counties and commanding armies on behalf of the king. In contrast, a Margrave in the Holy Roman Empire was a military governor tasked with defending border territories known as marches, granting them substantial military influence and autonomy. Both titles wielded considerable power, but while Earls were primarily influential in centralized governance, Margraves played a critical role in regional defense and expansion during Medieval Europe.
Modern Usage and Legacy
The titles Earl and Margrave have distinct origins, with Earl rooted in Anglo-Saxon nobility and Margrave in medieval German frontier governance, yet their modern usage reflects evolving noble hierarchies within British and German contexts. Today, the title Earl remains a prominent rank in the British peerage system, symbolizing historical aristocracy, while Margrave is largely ceremonial or historical in German-speaking regions, replaced by more contemporary noble designations. The legacy of both titles influences cultural heritage and historical studies, underscoring the shift from military and administrative functions to symbolic representation in modern nobility.
Notable Earls and Margraves in History
Notable Earls such as Earl Harold Godwinson of England, who famously fought at the Battle of Hastings in 1066, held significant regional power prior to ascending the throne. Among distinguished Margraves, Margrave Gero of the Holy Roman Empire played a crucial role in the 10th century by consolidating frontier territories against Slavic tribes. These titles, Earl in Anglo-Saxon and English contexts and Margrave in the Holy Roman Empire, both signified noble authority with military and administrative duties on borderlands or significant counties.
Conclusion: Key Differences and Significance
Earls held prominent noble titles in England with administrative and judicial authority over counties, while margraves governed border territories called marches with military responsibilities to defend frontiers. The margrave's role was typically more militarized and strategic due to frontier defense, whereas earls managed internal regions with broader civil duties. Understanding these distinctions highlights the varied governance structures in medieval Europe and their impact on territorial control and defense.
Earl Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com