A patriarch is a male leader, often the head of a family, tribe, or community, holding significant authority and influence across generations. This role is deeply rooted in cultural, religious, and historical contexts, shaping social structures and traditions. Discover how the concept of patriarchs impacts societies worldwide by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
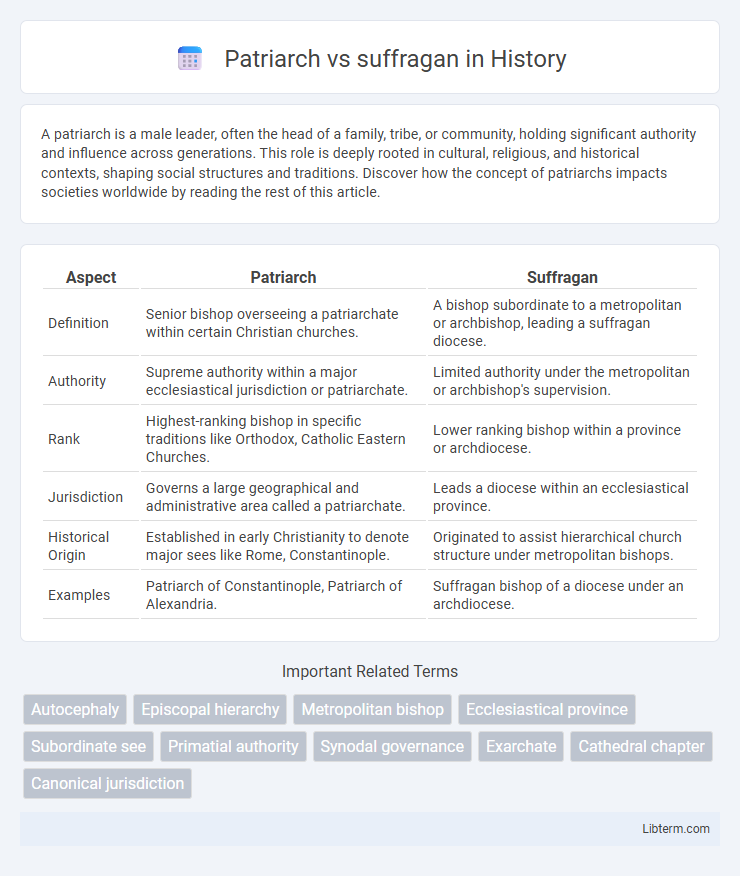
| Aspect | Patriarch | Suffragan |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Senior bishop overseeing a patriarchate within certain Christian churches. | A bishop subordinate to a metropolitan or archbishop, leading a suffragan diocese. |
| Authority | Supreme authority within a major ecclesiastical jurisdiction or patriarchate. | Limited authority under the metropolitan or archbishop's supervision. |
| Rank | Highest-ranking bishop in specific traditions like Orthodox, Catholic Eastern Churches. | Lower ranking bishop within a province or archdiocese. |
| Jurisdiction | Governs a large geographical and administrative area called a patriarchate. | Leads a diocese within an ecclesiastical province. |
| Historical Origin | Established in early Christianity to denote major sees like Rome, Constantinople. | Originated to assist hierarchical church structure under metropolitan bishops. |
| Examples | Patriarch of Constantinople, Patriarch of Alexandria. | Suffragan bishop of a diocese under an archdiocese. |
Understanding the Hierarchy: Patriarch vs Suffragan
The hierarchy within certain Christian churches distinguishes a patriarch as the highest-ranking bishop overseeing an entire autonomous church or large geographical region, wielding significant authority and spiritual leadership. In contrast, a suffragan bishop serves under a metropolitan or patriarch, managing a specific diocese or subdivision without independent jurisdiction. Understanding this distinction clarifies the organizational structure, where the patriarch holds overarching governance while suffragan bishops support localized administration.
Historical Origins of Patriarchs and Suffragans
Patriarchs originated in early Christianity as senior bishops holding authority over large regions, especially in the Roman, Byzantine, and Eastern Orthodox traditions, serving as pivotal leaders in defining doctrine and church governance. Suffragan bishops emerged later as subordinate bishops appointed to assist a metropolitan or archbishop within a diocese, reflecting the church's administrative expansion in the medieval period. The historical distinction centers on patriarchs as primary ecclesiastical authorities with broad jurisdiction, while suffragans function as auxiliary figures with limited regional oversight.
Key Differences Between Patriarchs and Suffragans
Patriarchs are the highest-ranking bishops in certain Christian churches, holding authority over entire patriarchates and possessing significant administrative and spiritual leadership. Suffragan bishops serve under a metropolitan or archbishop, overseeing dioceses within a province but lacking the autonomous authority held by patriarchs. The key differences lie in hierarchical rank, scope of jurisdiction, and degree of ecclesiastical authority.
Roles and Responsibilities of a Patriarch
A Patriarch holds the highest ecclesiastical authority within certain Christian denominations, overseeing multiple dioceses or provinces and providing spiritual leadership, doctrinal guidance, and administrative oversight. Unlike a suffragan bishop who assists a diocesan bishop without independent jurisdiction, the Patriarch exercises autonomous governance over the church's hierarchy, liturgical practices, and canonical legislation. This role includes convening synods, appointing bishops, and representing the church in ecumenical and interfaith dialogues.
Duties and Functions of a Suffragan
A suffragan bishop assists the diocesan bishop by overseeing a specific geographical area or district within the diocese, performing pastoral care, administering sacraments, and supporting local clergy. They carry out confirmations, ordinations, and represent the bishop in various ecclesiastical and community functions. Their duties ensure the smooth administration of the diocese while maintaining close pastoral contact with parishes under their supervision.
Patriarchal Authority: Scope and Influence
Patriarchal authority in ecclesiastical hierarchy holds supreme jurisdiction over significant territorial and spiritual domains, often encompassing entire autocephalous or autonomous churches. This authority includes the power to ordain bishops, define doctrinal stances, and oversee liturgical practices within their patriarchate's extensive influence. In contrast, a suffragan bishop operates under the patriarch's supervision, managing a smaller diocese with limited autonomous authority.
The Significance of Suffragans in Ecclesiastical Structure
Suffragan bishops play a crucial role in the ecclesiastical hierarchy by assisting patriarchs in managing large dioceses and ensuring effective pastoral care. Their authority, while subordinate to patriarchs, enables decentralized governance, facilitating local decision-making and maintaining church unity. This structure enhances administrative efficiency and fosters closer relationships between the clergy and laity within the church.
Patriarch vs Suffragan: Rank and Jurisdiction
A Patriarch holds the highest rank in certain Christian denominations, overseeing a large jurisdiction that often encompasses multiple dioceses or regions, acting as a central ecclesiastical authority. In contrast, a Suffragan is a bishop subordinate to a metropolitan or archbishop, managing a smaller diocese within the larger province without autonomous jurisdiction. The Patriarch's authority typically includes spiritual leadership, administrative control, and ceremonial precedence, while Suffragan bishops primarily execute delegated duties and assist in regional governance.
Modern Examples of Patriarchs and Suffragans
Modern examples of patriarchs include the Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople, who holds a primacy of honor in the Eastern Orthodox Church, and the Coptic Orthodox Patriarch of Alexandria, leading one of the oldest Christian communities in Africa. Suffragan bishops, such as those in the Church of England, serve under diocesan bishops within ecclesiastical provinces, assisting in regional church governance without autonomous authority. Contemporary patriarchs typically oversee entire autocephalous churches, while suffragans function as subordinate bishops within larger diocesan structures.
Impact on Church Governance: Comparing Patriarch and Suffragan
The patriarch holds supreme authority over a major ecclesiastical territory, shaping doctrine, liturgical practices, and church policies with overarching governance power. In contrast, a suffragan bishop operates under the jurisdiction of a metropolitan or patriarch, guiding a specific diocese with limited autonomous decision-making capacity. This hierarchical distinction significantly influences the distribution of power, administrative responsibilities, and the implementation of church directives across various dioceses.
Patriarch Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com