Understanding political history reveals the roots of current governance systems, power dynamics, and societal changes that have shaped nations over time. This knowledge allows you to critically analyze the decisions, conflicts, and alliances that influenced political landscapes worldwide. Explore the article to uncover key events and figures that defined political history.
Table of Comparison
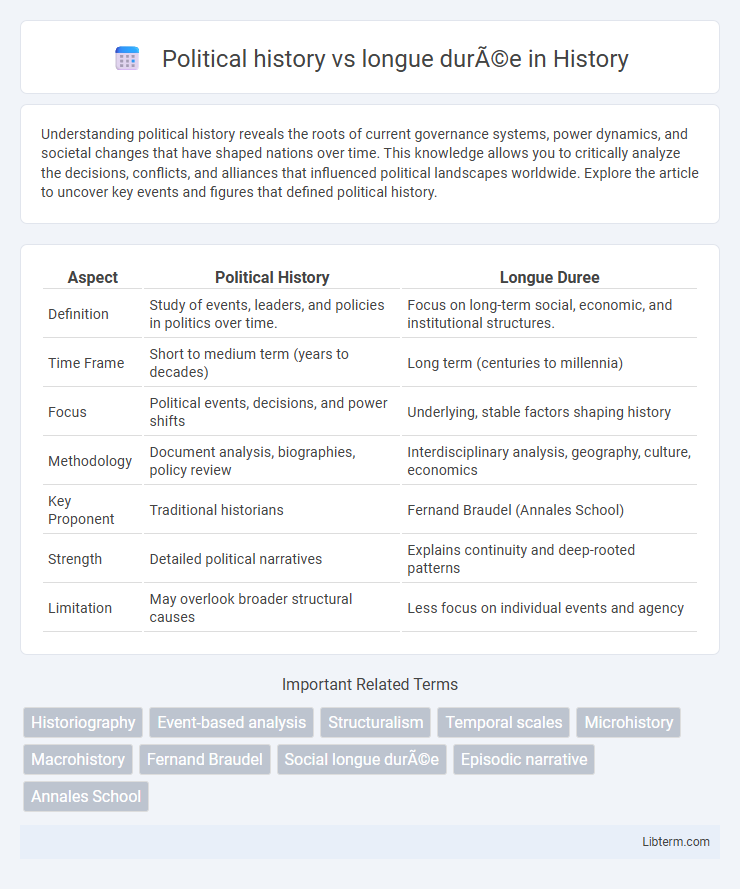
| Aspect | Political History | Longue Duree |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of events, leaders, and policies in politics over time. | Focus on long-term social, economic, and institutional structures. |
| Time Frame | Short to medium term (years to decades) | Long term (centuries to millennia) |
| Focus | Political events, decisions, and power shifts | Underlying, stable factors shaping history |
| Methodology | Document analysis, biographies, policy review | Interdisciplinary analysis, geography, culture, economics |
| Key Proponent | Traditional historians | Fernand Braudel (Annales School) |
| Strength | Detailed political narratives | Explains continuity and deep-rooted patterns |
| Limitation | May overlook broader structural causes | Less focus on individual events and agency |
Defining Political History: Scope and Focus
Political history examines the chronological sequence of events, key figures, policies, and institutions shaping governance and power dynamics over time. It focuses on wars, revolutions, leadership, legislation, and political movements within specific periods. Unlike the longue duree approach, it emphasizes immediate causes and effects rather than long-term structural factors or cultural frameworks spanning centuries.
Understanding the Longue Durée Approach
The longue duree approach emphasizes the analysis of historical structures and social, economic, and cultural patterns that persist over centuries, contrasting with the often event-focused perspective of traditional political history. It prioritizes long-term trends such as demographic shifts, geographical influences, and institutional continuity in shaping political outcomes. Understanding this method allows scholars to uncover deeper causal relationships and broader temporal contexts beyond isolated political events.
Key Scholars and Theoretical Foundations
Political history traditionally examines events, leaders, and institutions with emphasis on chronological narratives and power struggles, shaped by scholars like E.H. Carr and Arthur M. Schlesinger Jr. The longue duree approach, pioneered by Fernand Braudel, prioritizes long-term social, economic, and environmental structures over ephemeral political episodes, integrating interdisciplinary methods from geography, sociology, and economics. Key theoretical foundations contrast the episodic focus of political history with the systemic, deep-time analysis of longue duree, highlighting differences in temporal scale and scope in historical interpretation.
Methodological Differences: Political History vs Longue Durée
Political history emphasizes short-term events, decisions, and individual actions, often relying on archival documents and narrative analysis to understand government policies and power shifts. Longue duree methodology prioritizes long-term social, economic, and cultural structures, employing interdisciplinary data and quantitative methods to reveal deep-rooted patterns beyond immediate political episodes. The contrast lies in political history's event-centric approach versus longue duree's structural and temporal depth in historical interpretation.
Chronology and Temporal Scales in Historical Analysis
Political history traditionally emphasizes discrete events and leadership transitions within defined chronologies, enabling detailed analysis of cause and effect in governance changes. The longue duree approach expands temporal scales by examining underlying social, economic, and environmental structures that persist over centuries, revealing slow-moving forces shaping political contexts. Integrating both methods enhances historical analysis by correlating immediate political actions with broader, enduring historical patterns.
Case Studies: Political Events vs Long-term Structures
Case studies in political history often emphasize specific political events such as revolutions, elections, or treaties, highlighting immediate causes and consequences within a defined timeframe. In contrast, the longue duree approach examines long-term structures like social hierarchies, economic systems, and institutional frameworks that shape political developments over centuries. Combining both perspectives enriches understanding by linking discrete political episodes to enduring structural forces that influence the trajectory of political change.
Interplay between Agency and Structure
Political history emphasizes individual agency by examining the decisions and actions of key political figures and events, while the longue duree approach analyzes the enduring structural forces such as social, economic, and institutional frameworks shaping political outcomes over centuries. The interplay between agency and structure reveals how personal choices and immediate events emerge within, respond to, and sometimes transform deep-rooted systemic conditions. Understanding this dynamic provides a comprehensive perspective on political change by linking short-term actions to long-term historical patterns.
Strengths and Limitations of Each Perspective
Political history excels in analyzing specific events, key actors, and power dynamics, offering detailed insights into decisions and their immediate consequences. The longue duree approach emphasizes long-term structures and enduring social, economic, and environmental factors, revealing deep-rooted patterns beyond individual events. While political history may overlook broader structural continuities, the longue duree can underplay sudden political changes and individual agency.
The Impact on Historical Interpretation and Narratives
Political history often emphasizes key events, leaders, and decisions, shaping historical narratives around power dynamics and conflicts. The longue duree approach highlights long-term structural factors such as geography, economy, and social structures, offering deeper analysis of historical continuity and transformation. Integrating both perspectives enhances understanding by balancing episodic political changes with enduring societal trends, thereby enriching historical interpretation.
Integrating Political History with the Longue Durée Framework
Integrating political history with the longue duree framework enriches the analysis of historical events by emphasizing deep structural factors such as social institutions, economic systems, and cultural patterns that persist over centuries. This approach moves beyond episodic political narratives to uncover the long-term processes shaping governance, power relations, and state formation. Combining micro-level political dynamics with macro-historical trends allows historians to contextualize short-term political developments within enduring historical forces.
Political history Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com