Human rights are fundamental freedoms and protections inherent to all individuals, regardless of nationality, ethnicity, or status. These rights encompass civil, political, economic, social, and cultural dimensions that ensure dignity, equality, and justice. Explore the rest of the article to understand how your rights are safeguarded and promoted globally.
Table of Comparison
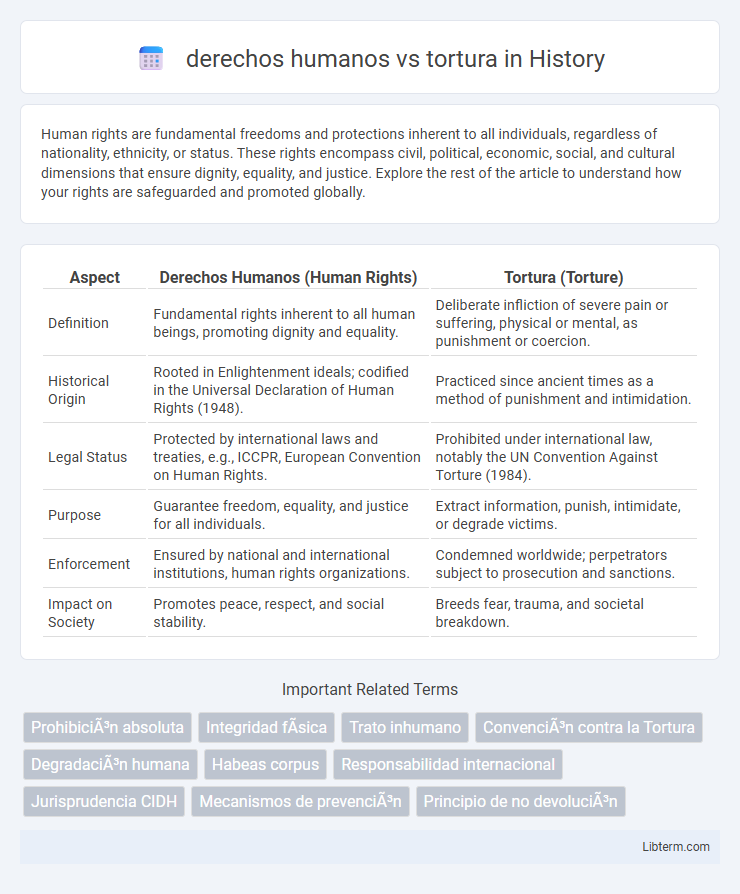
| Aspect | Derechos Humanos (Human Rights) | Tortura (Torture) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fundamental rights inherent to all human beings, promoting dignity and equality. | Deliberate infliction of severe pain or suffering, physical or mental, as punishment or coercion. |
| Historical Origin | Rooted in Enlightenment ideals; codified in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948). | Practiced since ancient times as a method of punishment and intimidation. |
| Legal Status | Protected by international laws and treaties, e.g., ICCPR, European Convention on Human Rights. | Prohibited under international law, notably the UN Convention Against Torture (1984). |
| Purpose | Guarantee freedom, equality, and justice for all individuals. | Extract information, punish, intimidate, or degrade victims. |
| Enforcement | Ensured by national and international institutions, human rights organizations. | Condemned worldwide; perpetrators subject to prosecution and sanctions. |
| Impact on Society | Promotes peace, respect, and social stability. | Breeds fear, trauma, and societal breakdown. |
Introducción a los Derechos Humanos
Human rights establish the fundamental freedoms and protections inherent to every individual, serving as a legal and moral framework that prohibits torture under any circumstances. The Universal Declaration of Human Rights explicitly condemns torture, reinforcing the principle that no person shall be subjected to cruel, inhuman, or degrading treatment. International treaties such as the Convention Against Torture further strengthen the global commitment to safeguard human dignity and ensure accountability for violations.
Definición y Tipos de Tortura
Tortura se define como cualquier acto mediante el cual se inflige intencionadamente dolor o sufrimiento severo, ya sea fisico o psicologico, con el fin de obtener informacion, castigar o intimidar. Los tipos de tortura incluyen metodos fisicos como golpes, asfixia y electrocucion, asi como tortura psicologica como el aislamiento, la humillacion y las amenazas constantes. Los derechos humanos protegen a todas las personas contra estas practicas, reconociendo el derecho a la integridad fisica y mental y prohibiendo la tortura bajo cualquier circunstancia.
Normativas Internacionales contra la Tortura
International human rights frameworks, such as the United Nations Convention Against Torture (UNCAT) and the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR), establish strict prohibitions against torture and other cruel, inhuman, or degrading treatment. These norms obligate states to prevent, investigate, and punish acts of torture, ensuring accountability and the protection of fundamental human dignity. Compliance with these international standards is monitored by entities like the UN Committee Against Torture, which reviews state reports and issues recommendations to uphold global anti-torture commitments.
Historia de la Lucha contra la Tortura
The historia de la lucha contra la tortura is deeply rooted in the evolution of derechos humanos, particularly since the adoption of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights in 1948. Landmark treaties, such as the United Nations Convention Against Torture (1984), have codified the prohibition of torture, reinforcing global legal frameworks. Persistent activism and international monitoring mechanisms, including the work of the Committee Against Torture, have played a crucial role in holding states accountable and promoting human dignity.
Impacto Psicológico y Físico de la Tortura
La tortura genera un impacto psicologico severo, incluyendo trastornos de estres postraumatico, ansiedad cronica y depresion profunda, afectando la salud mental de las victimas a largo plazo. Las consecuencias fisicas pueden ser devastadoras, con danos irreversibles en organos, cicatrices permanentes y discapacidad prolongada. La violacion de los derechos humanos mediante la tortura deteriora la dignidad humana y obstaculiza la rehabilitacion integral de quienes la sufren.
Casos Emblemáticos de Violaciones
Casos emblematicos de violaciones a derechos humanos por tortura incluyen el caso de Abu Ghraib en Irak, donde prisioneros fueron sometidos a abusos fisicos y psicologicos que violan la Convencion contra la Tortura de la ONU. En Argentina, durante la dictadura militar de 1976-1983, miles de personas fueron victimas de desapariciones forzadas y tortura sistematica, evidenciado en juicios como el caso de las Madres de Plaza de Mayo. Otro caso significativo es el de Guantanamo, con denuncias recurrentes de tortura y tratos crueles contra detenidos, desafiando la legislacion internacional sobre derechos humanos.
Rol de ONG y Organismos Internacionales
Non-governmental organizations (ONGs) and international bodies such as the United Nations play a crucial role in combating torture by monitoring, documenting, and reporting violations of human rights. These entities also advocate for stronger legal frameworks and hold governments accountable through mechanisms like the UN Committee Against Torture and the Universal Periodic Review. Their efforts contribute to raising global awareness, supporting victims, and promoting adherence to international conventions like the Convention Against Torture (CAT).
Prevención y Mecanismos de Denuncia
Prevencion de la tortura se basa en la implementacion de normas internacionales como la Convencion contra la Tortura y Protocolos de vigilancia en centros de detencion. Mecanismos de denuncia incluyen organismos nacionales de derechos humanos, comisiones independientes y la participacion de la sociedad civil para garantizar la investigacion y sancion de abusos. La formacion continua y monitoreo transparente son esenciales para fortalecer estos sistemas y proteger los derechos humanos.
Retos Actuales en la Erradicación de la Tortura
The eradication of torture remains a significant challenge in upholding human rights, as systematic abuse persists in many countries despite international treaties like the UN Convention Against Torture. Weak judicial systems, lack of political will, and insufficient accountability mechanisms hinder effective prevention and prosecution of torture cases. Strengthening independent monitoring bodies, enhancing victim support services, and promoting legal reforms are essential strategies to overcome these obstacles and protect fundamental human rights.
Conclusiones y Recomendaciones
Human rights frameworks categorically prohibit torture, recognizing it as a grave violation of human dignity and international law, including treaties like the UN Convention Against Torture. Conclusion: Effective enforcement mechanisms and national legislation must align strictly with international standards to prevent torture and protect victims. Recommendation: States should strengthen oversight bodies, implement comprehensive training for law enforcement, and ensure accessible reporting channels to uphold human rights and eradicate torture practices.
derechos humanos Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com