A monogram is a distinctive design composed of one or more letters, often your initials, artistically combined to create a unique personal or brand emblem. Used extensively in fashion, stationery, and home decor, monograms signify elegance and individuality by adding a customized touch. Discover how incorporating a monogram can elevate your style and identity in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
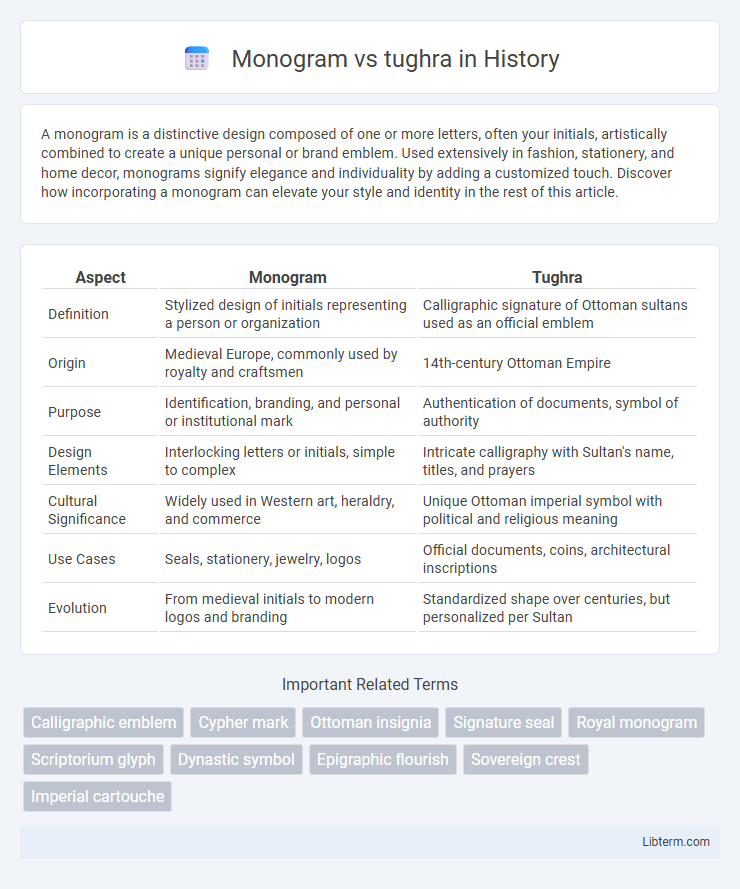
| Aspect | Monogram | Tughra |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Stylized design of initials representing a person or organization | Calligraphic signature of Ottoman sultans used as an official emblem |
| Origin | Medieval Europe, commonly used by royalty and craftsmen | 14th-century Ottoman Empire |
| Purpose | Identification, branding, and personal or institutional mark | Authentication of documents, symbol of authority |
| Design Elements | Interlocking letters or initials, simple to complex | Intricate calligraphy with Sultan's name, titles, and prayers |
| Cultural Significance | Widely used in Western art, heraldry, and commerce | Unique Ottoman imperial symbol with political and religious meaning |
| Use Cases | Seals, stationery, jewelry, logos | Official documents, coins, architectural inscriptions |
| Evolution | From medieval initials to modern logos and branding | Standardized shape over centuries, but personalized per Sultan |
Introduction to Monogram and Tughra
Monograms are stylized motifs composed of two or more interwoven letters, typically representing an individual's initials, widely used in branding and personal identification since the Roman Empire. Tughra is an intricate calligraphic emblem of Ottoman sultans, combining the ruler's name and titles in a distinctive, artistic form symbolizing authority. Both monograms and tughras serve as personalized insignias, but while monograms emphasize simplicity and practicality, tughras exhibit elaborate ornamental design with historical and political significance.
Historical Origins of Monogram and Tughra
Monograms originated in ancient Greece and Rome as combined initials used by artists and rulers to signify authorship or ownership, evolving through medieval Europe as personalized emblems for nobility and merchants. Tughras emerged in the Ottoman Empire during the 14th century as ornate calligraphic signatures of sultans, symbolizing imperial authority and often featuring intricate decorations and flourishes. Both served as unique identifiers, but monograms emphasized individual identity, while tughras functioned as expressions of sovereign power and official decree.
Cultural Significance of Monogram
Monograms hold deep cultural significance as personalized symbols representing identity, heritage, and social status across various cultures, often used in family crests, royal insignias, and historical documents. Unlike the tughra, an elaborate Ottoman royal signature emblem, monograms emphasize individual or familial lineage through intertwined initials, reflecting artistry and tradition in Western and European contexts. Their usage in textiles, seals, and official correspondence highlights their enduring role in personal and cultural expression.
Cultural Significance of Tughra
The tughra holds profound cultural significance as a unique Ottoman emblem symbolizing imperial authority and artistic heritage, intricately designed with stylized calligraphy that conveys the sultan's name and titles. Unlike monograms, which typically represent personal or family initials in Western contexts, the tughra embodies a fusion of political power and aesthetic expression deeply rooted in Islamic art traditions. This emblem served not only as a royal signature on official documents and coins but also as a visual representation of sovereignty and legitimacy within the Ottoman Empire.
Artistic Styles and Design Elements
Monograms typically feature intertwined initials with elegant, symmetrical letterforms emphasizing personal identity, often crafted using classic serif or script fonts for a refined appearance. Tughras showcase intricate flourishes, elaborate curves, and calligraphic strokes characteristic of Ottoman imperial signatures, incorporating symbolic elements like crescents and stars to convey authority and tradition. The monogram's minimalist and structured design contrasts with the tughra's ornate, flowing artistry, reflecting differences in cultural context and purpose.
Symbolic Meanings Compared
Monograms typically combine initials or letters to represent personal identity, often symbolizing ownership, prestige, and individual legacy in Western traditions. Tughras, intricate calligraphic seals of Ottoman sultans, embody imperial authority, sovereignty, and religious power, blending artistic elegance with political symbolism. Both serve as unique emblems of identity, yet monograms emphasize personal legacy, whereas tughras convey state legitimacy and dynastic heritage.
Usage in Historical Contexts
Monograms served as personal or organizational insignias throughout history, prominently used by European royalty and artisans to signify ownership and authenticity. Tughra, an elaborate calligraphic signature of Ottoman sultans, symbolized imperial authority and was prominently featured on official documents, coins, and architectural monuments. Both monograms and tughras functioned as powerful identifiers, reflecting social status and authority in their respective cultures.
Modern Applications and Adaptations
Monograms are widely used in modern branding and personal identification, appearing on logos, fashion, and digital signatures due to their simplicity and versatility. Tughras, traditionally Ottoman imperial monograms, have been adapted in contemporary art and design to evoke cultural heritage and luxury in architectural elements and high-end products. Both forms serve as unique, stylized symbols for identity, blending historical significance with modern aesthetics in various industries.
Key Differences Between Monogram and Tughra
Monograms typically consist of stylized initials of a person's name, often used for personal branding, stationery, or luxury items, emphasizing simplicity and modern design. Tughras are intricate, calligraphic emblems historically used as the official seal or signature of Ottoman sultans, featuring elaborate floral motifs and Arabic script that signify authority and heritage. Key differences lie in their cultural origin, with monograms rooted in Western tradition for personal or corporate identity, while tughras serve as symbolic imperial representations combining artistic calligraphy and historical significance.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Monogram and Tughra
Selecting between a monogram and a tughra depends on the desired cultural resonance and design intent; monograms emphasize modern personalization with interwoven initials, while tughras showcase historical Ottoman artistry with ornate calligraphy representing authority. Brands seeking a contemporary, minimalistic mark benefit from monograms, as tughras convey tradition and heritage through intricate, symbolic motifs. Understanding the context and target audience ensures the emblem aligns perfectly with the brand's identity and message.
Monogram Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com