Chronology organizes events in their sequential order, providing a clear timeline that helps you understand the progression and context of historical or personal occurrences. Accurate chronological records are essential for studying cause and effect, identifying patterns, and preserving important milestones. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your knowledge of how chronology can enhance your comprehension and planning.
Table of Comparison
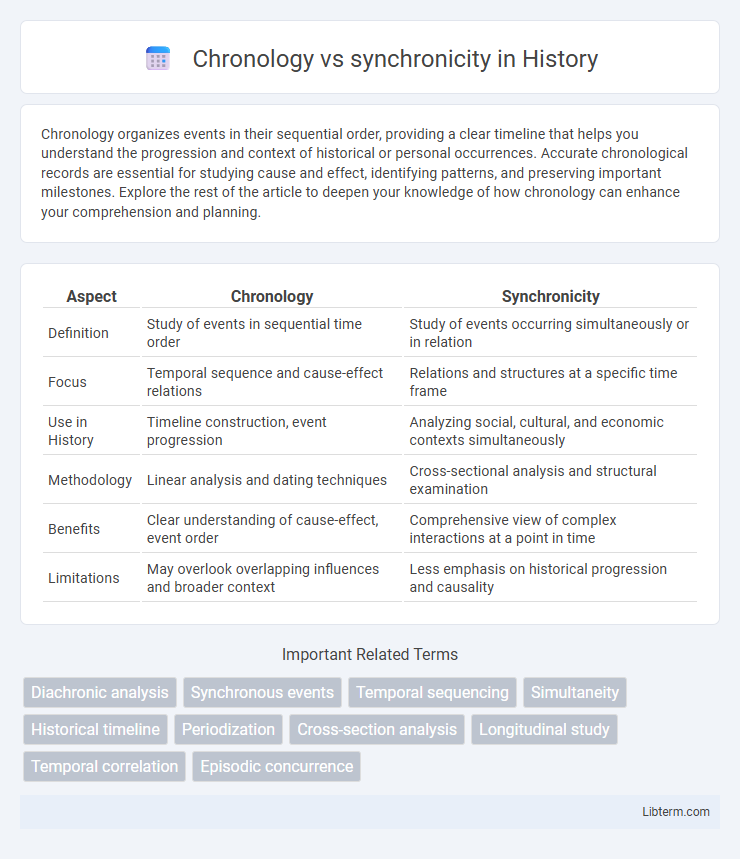
| Aspect | Chronology | Synchronicity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of events in sequential time order | Study of events occurring simultaneously or in relation |
| Focus | Temporal sequence and cause-effect relations | Relations and structures at a specific time frame |
| Use in History | Timeline construction, event progression | Analyzing social, cultural, and economic contexts simultaneously |
| Methodology | Linear analysis and dating techniques | Cross-sectional analysis and structural examination |
| Benefits | Clear understanding of cause-effect, event order | Comprehensive view of complex interactions at a point in time |
| Limitations | May overlook overlapping influences and broader context | Less emphasis on historical progression and causality |
Understanding Chronology: Definition and Importance
Chronology refers to the systematic arrangement of events in the order of their occurrence, serving as a fundamental framework in historical and scientific studies. Understanding chronology is crucial because it allows researchers to establish cause-and-effect relationships and trace the development of phenomena over time. Accurate chronological sequencing enhances the interpretation of past events, enabling clearer insights and more reliable conclusions.
Exploring Synchronicity: Beyond Linear Time
Synchronicity transcends linear time by emphasizing meaningful coincidences that occur simultaneously without causal connection, challenging traditional chronological frameworks. This concept, rooted in Jungian psychology, reveals how events can be interconnected through symbolic relationships rather than sequential progression. Exploring synchronicity involves recognizing patterns that align across different dimensions of experience, suggesting a holistic understanding of time beyond mere chronological order.
Key Differences Between Chronology and Synchronicity
Chronology organizes events in sequential order based on time, emphasizing temporal progression and cause-effect relationships. Synchronicity explores meaningful coincidences that occur simultaneously without a direct causal link, highlighting interpretative connections. Understanding their key differences involves distinguishing linear temporal sequences from non-linear, symbolic alignments in time.
Historical Perspectives on Chronology and Synchronicity
Historical perspectives on chronology emphasize linear progression and cause-effect relationships to understand events in a sequential timeline, essential for constructing accurate historical narratives. In contrast, synchronicity, rooted in Jungian psychology, highlights meaningful coincidences occurring simultaneously without causal connection, challenging traditional temporal frameworks by emphasizing interconnectedness across time. These differing approaches influence the interpretation of historical events, where chronology seeks order and causality, while synchronicity invites deeper exploration of symbolic and relational meanings beyond mere temporal sequence.
The Role of Chronology in Storytelling and Narratives
Chronology establishes a clear temporal framework that guides audience understanding and enhances narrative coherence by presenting events in sequential order. This linear progression aids in character development and plot evolution, enabling readers to perceive cause-and-effect relationships effectively. Deviations from strict chronology, when used strategically, can create suspense or highlight thematic elements without sacrificing overall narrative clarity.
Synchronicity in Psychology and Human Experience
Synchronicity in psychology refers to meaningful coincidences that occur with no causal relationship yet hold significant personal relevance, a concept introduced by Carl Jung. This phenomenon highlights the interconnectedness of the unconscious mind and external events, influencing human experience by providing insights, guidance, or a sense of order. Studies in depth psychology and transpersonal psychology explore synchronicity as a lens to understand the collective unconscious and the symbolic meanings shaping perception and behavior.
Advantages of Chronological Approaches
Chronological approaches provide a clear, sequential framework that enhances understanding of cause-and-effect relationships over time. This method allows for accurate tracking of historical developments, making it easier to identify trends, changes, and patterns within specific periods. Researchers utilizing chronological analysis benefit from structured timelines that support precise data organization and facilitate longitudinal studies.
Benefits of Embracing Synchronicity
Embracing synchronicity enhances intuitive decision-making by aligning actions with meaningful coincidences, fostering a deeper sense of purpose and connection. It cultivates mindfulness and openness, encouraging adaptive responses to unexpected opportunities that chronological frameworks might overlook. This approach promotes creative problem-solving and holistic understanding beyond linear time constraints, benefiting personal growth and innovation.
When to Use Chronology vs Synchronicity
Use chronology when detailing historical events, developments, or sequences that require clear temporal order and cause-effect relationships, enhancing understanding of progressions over time. Employ synchronicity to analyze phenomena within a specific time frame, emphasizing simultaneous occurrences or contextual interrelations without prioritizing temporal sequence. Opting between chronology and synchronicity depends on whether the focus is on temporal progression or holistic, cross-sectional analysis of events and interactions.
Blending Chronology and Synchronicity: A Holistic Approach
Blending chronology and synchronicity offers a holistic approach to understanding events by integrating temporal sequences with meaningful connections across time. This method enhances analysis by considering not only the linear progression of occurrences but also their simultaneous relationships and symbolic significance. Applying this dual perspective leads to richer insights in historical research, narrative construction, and complex system analysis.
Chronology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com