The Annales School revolutionized historical research by emphasizing long-term social, economic, and cultural structures over traditional political narratives. Its interdisciplinary approach integrates geography, sociology, and economics to uncover deeper historical patterns. Discover how this methodology can transform your understanding of history in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
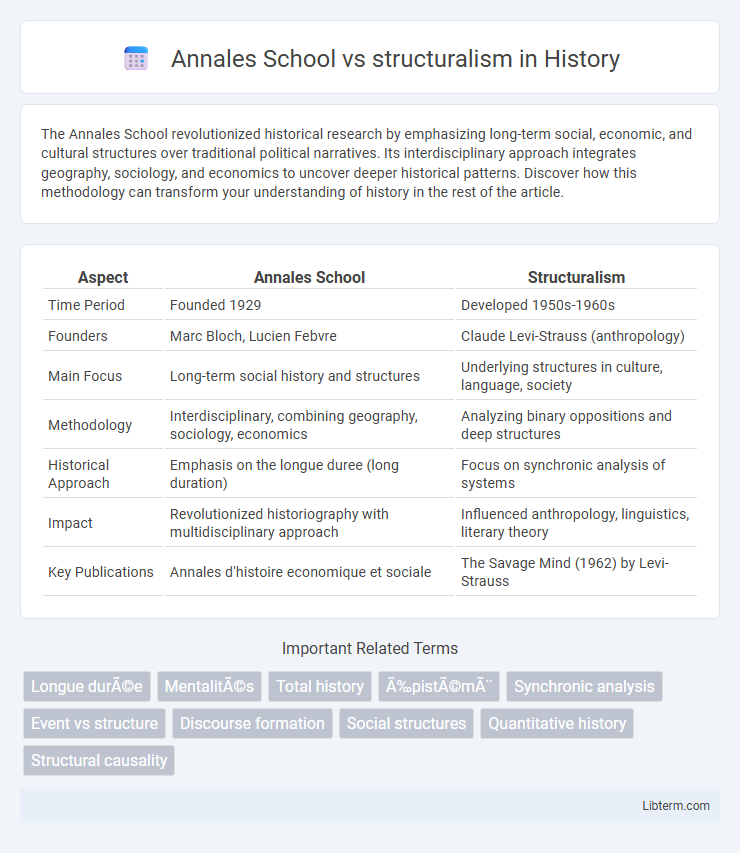
| Aspect | Annales School | Structuralism |
|---|---|---|
| Time Period | Founded 1929 | Developed 1950s-1960s |
| Founders | Marc Bloch, Lucien Febvre | Claude Levi-Strauss (anthropology) |
| Main Focus | Long-term social history and structures | Underlying structures in culture, language, society |
| Methodology | Interdisciplinary, combining geography, sociology, economics | Analyzing binary oppositions and deep structures |
| Historical Approach | Emphasis on the longue duree (long duration) | Focus on synchronic analysis of systems |
| Impact | Revolutionized historiography with multidisciplinary approach | Influenced anthropology, linguistics, literary theory |
| Key Publications | Annales d'histoire economique et sociale | The Savage Mind (1962) by Levi-Strauss |
Introduction to the Annales School and Structuralism
The Annales School, founded in 1929 by historians Marc Bloch and Lucien Febvre, revolutionized historiography by emphasizing long-term social history and interdisciplinary approaches that integrated geography, economics, and sociology. Structuralism, emerging primarily in the mid-20th century through thinkers like Claude Levi-Strauss, focuses on understanding underlying structures in culture, language, and society, positing that human experience is shaped by universal cognitive patterns. While the Annales School highlights temporal continuity and material conditions in history, structuralism prioritizes the analysis of deep, often unconscious systems shaping human behavior and thought.
Historical Contexts of Annales School and Structuralism
The Annales School emerged in the early 20th century, emphasizing long-term social history through interdisciplinary methods that integrate geography, economics, and sociology, responding to the limitations of traditional political history. Structuralism, developing in the mid-20th century largely through the work of Claude Levi-Strauss, focused on uncovering underlying cognitive structures shaping human culture and history, influenced by linguistic theory and anthropology. Both movements arose as critiques of conventional historiography, with Annales prioritizing social conditions and collective mentalities over events, and Structuralism analyzing deep-seated patterns in myths, language, and customs within historical contexts.
Key Figures of the Annales School
Marc Bloch and Fernand Braudel are seminal figures of the Annales School, pioneering a multidisciplinary approach that emphasizes long-term social history over events or individuals. Braudel's concept of the longue duree reshaped historiography by analyzing the slow, structural changes in geography, economy, and society. Emmanuel Le Roy Ladurie expanded this framework by integrating quantitative methods and microhistory, cementing the Annales School's influence on understanding historical processes beyond structuralism's focus on underlying system structures and language.
Foundational Thinkers in Structuralism
Foundational thinkers in structuralism include Ferdinand de Saussure, whose theories on linguistic structures laid the groundwork for analyzing cultural phenomena through underlying systems. Claude Levi-Strauss further developed structuralism by applying these concepts to anthropology, emphasizing the deep structures of myths and social relations. Unlike the Annales School, which focuses on long-term historical processes and socio-economic factors, structuralism prioritizes the hidden patterns and structures that shape human experience.
Core Methodologies Compared
The Annales School emphasizes long-term historical structures, integrating social, economic, and geographical data to analyze the broad context shaping events over centuries, often using quantitative methods and interdisciplinary approaches. Structuralism focuses on uncovering underlying structures in culture, language, and society, analyzing binary oppositions and deep patterns through linguistics and anthropology to explain human behavior and meaning. Both methodologies prioritize systemic frameworks but differ in scope: Annales approaches historical time and material conditions, while structuralism deciphers mental frameworks and symbolic systems.
Interpretations of History and Society
The Annales School emphasizes a long-term historical perspective, analyzing social structures, geography, and collective mentalities to interpret history beyond individual events. Structuralism, rooted in linguistic and anthropological theory, focuses on uncovering universal patterns and binary oppositions within cultural systems to explain societal organization. While the Annales School prioritizes temporal depth and social context, structuralism centers on underlying cognitive frameworks shaping human experience and historical phenomena.
The Concept of Structure in Both Approaches
The Annales School emphasizes long-term social structures and collective mentalities shaping historical processes, analyzing economic, geographic, and social factors over centuries. Structuralism focuses on underlying cognitive and linguistic structures that govern human culture, seeking universal patterns in myths, language, and kinship systems. Both approaches prioritize "structure" but differ as Annales examines material and temporal frameworks while Structuralism investigates abstract, symbolic systems shaping human perception and behavior.
Influence on Modern Historiography and Social Sciences
The Annales School revolutionized modern historiography by emphasizing long-term social, economic, and environmental factors over traditional political narratives, influencing fields like social history and anthropology. Structuralism, rooted in linguistics and anthropology, introduced the concept of underlying structures shaping culture, language, and society, significantly impacting sociology, literary theory, and psychology. Both methodologies transformed social sciences by promoting interdisciplinary approaches and prioritizing deep, systemic analyses over surface-level events.
Criticisms and Limitations of Each School
The Annales School faces criticism for its broad focus on long-term social structures that often downplays individual agency and cultural nuances, leading to a sometimes overly deterministic view of history. Structuralism is limited by its rigid emphasis on underlying systems and binary oppositions, which can overlook historical context and the fluidity of human experience. Both schools struggle to fully integrate subjective interpretations and the complexities of lived human realities, creating challenges in addressing the dynamic interplay between structure and individual action.
Legacy and Continued Relevance in Contemporary Studies
The Annales School revolutionized historiography by emphasizing long-term social structures and interdisciplinary approaches, profoundly influencing contemporary historical and social science research. Structuralism contributed to understanding underlying systems in culture, language, and society, shaping modern analysis in anthropology, linguistics, and literary theory. Both frameworks remain relevant, with Annales promoting holistic historical context and structuralism providing tools to decode complex social patterns in today's academic studies.
Annales School Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com