Girondins were a prominent political faction during the French Revolution, advocating for republican ideals and opposing royalist forces. Their influence shaped key revolutionary events and debates, emphasizing liberty and democratic principles. Explore the rest of the article to understand how the Girondins impacted France's transformation and what legacy they left behind.
Table of Comparison
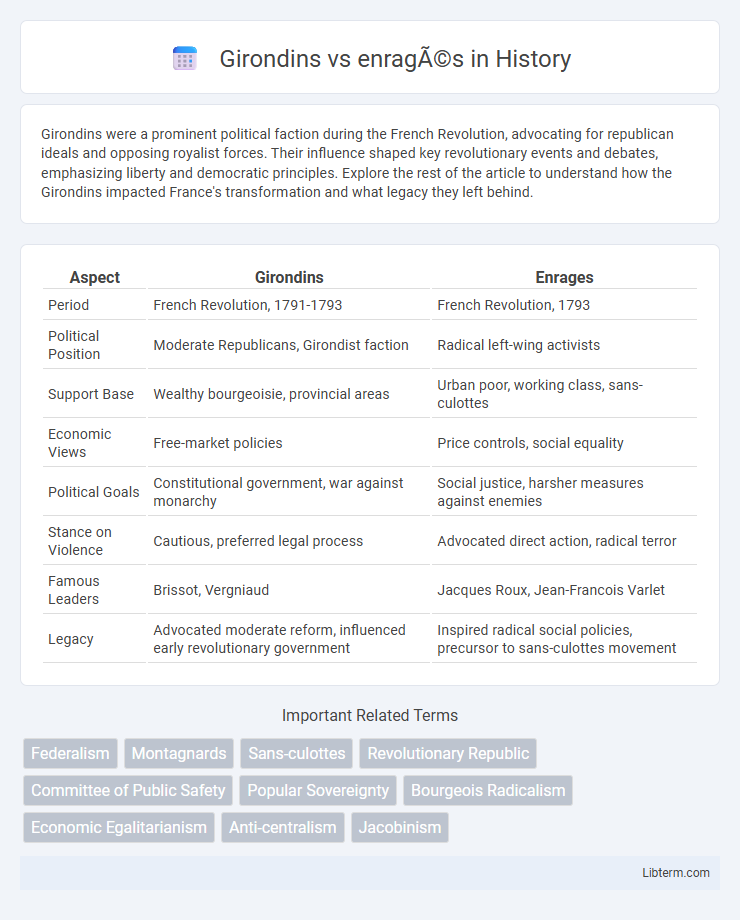
| Aspect | Girondins | Enrages |
|---|---|---|
| Period | French Revolution, 1791-1793 | French Revolution, 1793 |
| Political Position | Moderate Republicans, Girondist faction | Radical left-wing activists |
| Support Base | Wealthy bourgeoisie, provincial areas | Urban poor, working class, sans-culottes |
| Economic Views | Free-market policies | Price controls, social equality |
| Political Goals | Constitutional government, war against monarchy | Social justice, harsher measures against enemies |
| Stance on Violence | Cautious, preferred legal process | Advocated direct action, radical terror |
| Famous Leaders | Brissot, Vergniaud | Jacques Roux, Jean-Francois Varlet |
| Legacy | Advocated moderate reform, influenced early revolutionary government | Inspired radical social policies, precursor to sans-culottes movement |
Origins of the Girondins and Enragés
The Girondins originated as a moderate political faction during the French Revolution, primarily composed of wealthy provincial lawyers and merchants advocating for a constitutional government and opposed to the radicalism of Parisian mobs. The Enrages emerged as an ultra-radical group representing the interests of the working-class sans-culottes, demanding direct democracy, price controls, and harsh measures against counter-revolutionaries. Both factions played crucial roles in the ideological conflicts of 1793-1794, with the Girondins seeking to balance revolutionary ideals and order, while the Enrages pushed for immediate social and economic reforms to support the popular masses.
Ideological Foundations and Key Differences
The Girondins championed a moderate republicanism grounded in federalism and economic liberalism, advocating for a decentralized government structure that protected property rights and individual freedoms. In contrast, the Enrages promoted radical egalitarianism and direct democracy, emphasizing social justice and the redistribution of wealth to address widespread poverty and inequality. These ideological foundations created key differences, with the Girondins favoring gradual reform through constitutional means, while the Enrages supported immediate and revolutionary actions to dismantle existing power hierarchies.
Political Goals and Strategies
The Girondins aimed to establish a decentralized republic with moderate economic reforms and maintained support for a constitutional monarchy, prioritizing political stability and property rights. The Enrages sought radical social and economic changes, advocating for direct democracy, price controls, and wealth redistribution to empower the working class. While the Girondins relied on legislative means and diplomatic solutions, the Enrages employed popular mobilization and mass protests to enforce revolutionary policies.
Influential Leaders and Main Figures
The Girondins were led by influential figures like Jacques Pierre Brissot and Jean-Marie Roland, who advocated for a moderate republican government and supported war against Austria. The Enrages, representing the radical populist faction, were spearheaded by Jean-Francois Varlet and Jacques Roux, known for their fiery rhetoric demanding social equality and direct action against counter-revolutionaries. These leaders shaped the political divide during the French Revolution, with the Girondins favoring federalism and the Enrages pushing for radical economic reforms to assist the urban poor.
Social Base and Popular Support
The Girondins drew their support primarily from the provincial middle class, wealthy merchants, and moderate urban professionals, representing a more conservative bourgeoisie seeking to preserve economic stability and property rights. In contrast, the Enrages garnered intense backing from the urban working class and impoverished sans-culottes, advocating for radical social equality, price controls, and direct action against perceived enemies of the Revolution. This stark division in social base underscored the growing class tensions and competing visions for revolutionary change in late 18th-century France.
Role in the French Revolution
The Girondins played a key role in advocating for a constitutional government and promoting the war against Austria to unify France during the French Revolution. The Enrages, radical militants led by figures like Jacques Roux, pushed for extreme economic reforms and direct action to support the lower classes, especially during the upheaval of 1793. Both factions influenced revolutionary policies, with the Girondins often clashing with the more radical Jacobins and Enrages over the direction and intensity of revolutionary change.
Major Conflicts and Confrontations
The Girondins and the Enrages clashed intensely during the French Revolution, representing moderate republicans and radical left-wing activists, respectively. Major conflicts centered on issues like war policy, the fate of King Louis XVI, and economic reforms, with Enrages demanding harsher measures against counter-revolutionaries and economic equality. These confrontations fueled political instability, contributing to the downfall of the Girondins during the Reign of Terror and the rise of radical Jacobin influence.
Impact on Revolutionary Policies
The conflict between the Girondins and the Enrages significantly shaped revolutionary policies by intensifying debates over the direction of the French Revolution. The Girondins advocated for a more moderate and federalist approach, while the Enrages pushed for radical social and economic reforms, including price controls and direct action against aristocratic privileges. This ideological clash accelerated the shift towards more radical measures, influencing the adoption of policies like the Reign of Terror and the establishment of the Committee of Public Safety.
Decline and Suppression of the Factions
The Girondins faced a rapid decline following their loss of influence in 1793, as the more radical Enrages gained prominence during the French Revolution. The Enrages, advocating extreme measures against perceived enemies of the revolution, were instrumental in intensifying the Reign of Terror, which ultimately led to the suppression of moderate factions like the Girondins. The fall of the Girondins was marked by arrests and executions, cementing the dominance of radical revolutionary groups and signaling the violent suppression of political dissent within the revolutionary government.
Legacy of the Girondins and Enragés
The Girondins left a lasting legacy as advocates for a moderate republican government and supporters of free-market principles during the French Revolution, influencing the development of liberal political thought. The Enrages, known for their radical social demands and vocal opposition to both the monarchy and moderate revolutionaries, shaped early revolutionary policies by pushing for greater economic equality and harsh measures against aristocrats. Together, these factions embodied the tension between moderation and radicalism, critically impacting the evolution of revolutionary France's political landscape and social reforms.
Girondins Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com