Parliament serves as the supreme legislative body responsible for making laws, representing citizens, and overseeing the government's actions. It plays a critical role in shaping national policies and ensuring accountability through debates and committee work. Discover how Parliament functions and why it matters to your daily life by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
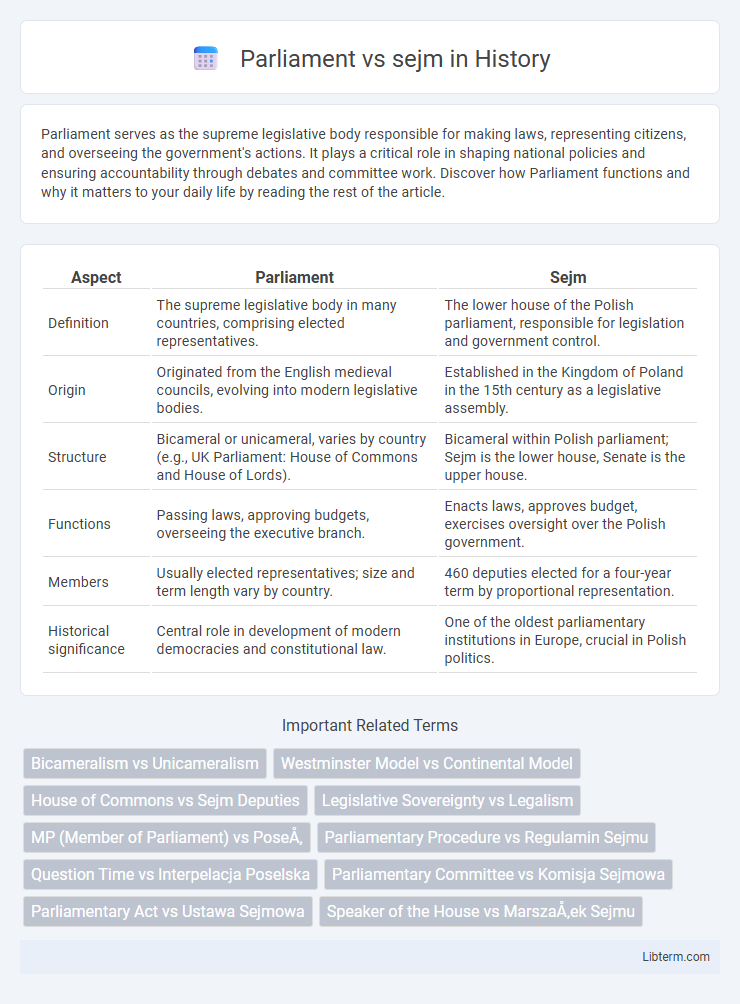
| Aspect | Parliament | Sejm |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The supreme legislative body in many countries, comprising elected representatives. | The lower house of the Polish parliament, responsible for legislation and government control. |
| Origin | Originated from the English medieval councils, evolving into modern legislative bodies. | Established in the Kingdom of Poland in the 15th century as a legislative assembly. |
| Structure | Bicameral or unicameral, varies by country (e.g., UK Parliament: House of Commons and House of Lords). | Bicameral within Polish parliament; Sejm is the lower house, Senate is the upper house. |
| Functions | Passing laws, approving budgets, overseeing the executive branch. | Enacts laws, approves budget, exercises oversight over the Polish government. |
| Members | Usually elected representatives; size and term length vary by country. | 460 deputies elected for a four-year term by proportional representation. |
| Historical significance | Central role in development of modern democracies and constitutional law. | One of the oldest parliamentary institutions in Europe, crucial in Polish politics. |
Introduction to Legislative Bodies: Parliament and Sejm
Parliament is a general term for a legislative body that creates laws and oversees government actions, often consisting of two chambers: an upper house and a lower house. The Sejm is the lower house of Poland's bicameral Parliament, known for its significant role in legislative processes, including passing laws, approving the budget, and supervising the executive branch. Understanding the distinction between Parliament as the overall legislative institution and the Sejm as a key component within the Polish system highlights their respective functions and powers.
Definition and Origins of Parliament
Parliament is a legislative body originating from medieval England, designed to represent the electorate and enact laws, typically comprising two houses: the House of Commons and the House of Lords. The Sejm, Poland's primary legislative chamber, traces its origins to the 15th century as a regional assembly evolving into a national parliamentary institution. While Parliament embodies a bicameral system rooted in constitutional monarchy, the Sejm serves as the lower house within Poland's bicameral legislature, emphasizing democratic representation.
Definition and Historical Roots of the Sejm
The Sejm is the lower house of the Polish Parliament, historically rooted in the Kingdom of Poland's parliamentary tradition dating back to the 15th century as a royal advisory assembly. Unlike the broader concept of Parliament, which refers to the entire legislative body of a country, the Sejm specifically denotes Poland's legislative chamber responsible for shaping national laws. Its evolution from a noble assembly reflects the development of Poland's political system and legislative authority within the bicameral Parliament, which also includes the Senate as the upper house.
Structural Differences: Parliament vs Sejm
The Parliament of Poland consists of two chambers: the Sejm and the Senate, with the Sejm being the lower house composed of 460 deputies elected through proportional representation. Structural differences include the Sejm's significant legislative authority, such as initiating bills and controlling the budget, contrasted by the Senate's role mainly as a revising chamber with limited veto power. The Sejm operates under a strict party discipline system, which influences its decision-making process, while the Senate provides a more deliberative review function, contributing to the system of checks and balances within the parliamentary framework.
Legislative Functions Compared
The Parliament of the United Kingdom consists of the House of Commons and the House of Lords, with primary legislative functions including passing laws, scrutinizing government policies, and authorizing budgets. In contrast, the Polish Sejm, as the lower house of the National Assembly, holds exclusive rights to initiate legislation, approve the budget, and exercise control over the Council of Ministers through votes of confidence and interpellations. Both bodies engage in law-making, but the Sejm exercises more direct oversight over government actions, while the UK Parliament emphasizes bicameral collaboration in legislative review.
Sejm’s Role in the Polish Political System
The Sejm serves as the lower house of the Polish Parliament, playing a crucial role in the legislative process, including the creation and approval of laws. It is composed of 460 deputies elected through proportional representation, reflecting the diverse political landscape of Poland. The Sejm holds significant powers such as controlling the government, approving the budget, and ratifying international agreements, making it central to the Polish political system.
Parliaments in Global Context
Parliament, as a legislative body, varies significantly worldwide, but it generally functions as the supreme law-making institution in democratic systems, encompassing two chambers or houses in many countries. The Sejm, specifically the lower house of Poland's Parliament, holds vital powers including initiating legislation, controlling the budget, and overseeing the executive branch, reflecting a common parliamentary structure seen in other nations. Global parliaments share core functions of lawmaking, budget approval, and government oversight, though their composition and powers differ according to constitutional frameworks and political traditions.
Election Processes and Membership
The Sejm, Poland's lower house, consists of 460 deputies elected through proportional representation using the D'Hondt method in multi-member constituencies, promoting party-list voting and reflecting diverse political views. Parliament, comprising the Sejm and the Senate, incorporates different election systems; while the Sejm uses party lists, the Senate's 100 members are elected via single-member districts employing a first-past-the-post system. Membership duration in the Sejm lasts four years, allowing for regular electoral cycles that enhance democratic accountability within Poland's bicameral legislative framework.
Key Responsibilities and Powers
The Parliament serves as the supreme legislative body in a country, responsible for enacting laws, approving the budget, and overseeing the executive branch. The Sejm, as the lower house of Poland's bicameral Parliament, holds crucial powers including initiating legislation, controlling government activities, and ratifying international agreements. Both institutions share duties like legislative scrutiny, but the Sejm has unique authority to vote on confidence motions impacting the government's stability.
Comparative Influence on Governance
The Parliament of the United Kingdom wields significant legislative power, including the ability to pass laws, scrutinize the government, and control public spending, with the House of Commons holding primary influence over governance. In contrast, the Polish Sejm is the lower house of Poland's bicameral legislature and plays a crucial role in shaping laws, overseeing government activities, and approving the budget, but shares legislative responsibilities with the Senate. While both bodies influence governance profoundly, the UK Parliament's fusion of executive and legislative powers grants it broader authority compared to the Sejm's more balanced system of checks and collaboration with the Senate.
Parliament Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com