The Agoge was the rigorous education and training system in ancient Sparta designed to mold boys into disciplined warriors and responsible citizens. Unlike Roman education, which emphasized rhetoric, literature, and civic responsibility, the Agoge focused primarily on physical endurance, obedience, and combat skills. Discover how these contrasting approaches shaped the unique societies of Sparta and Rome by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
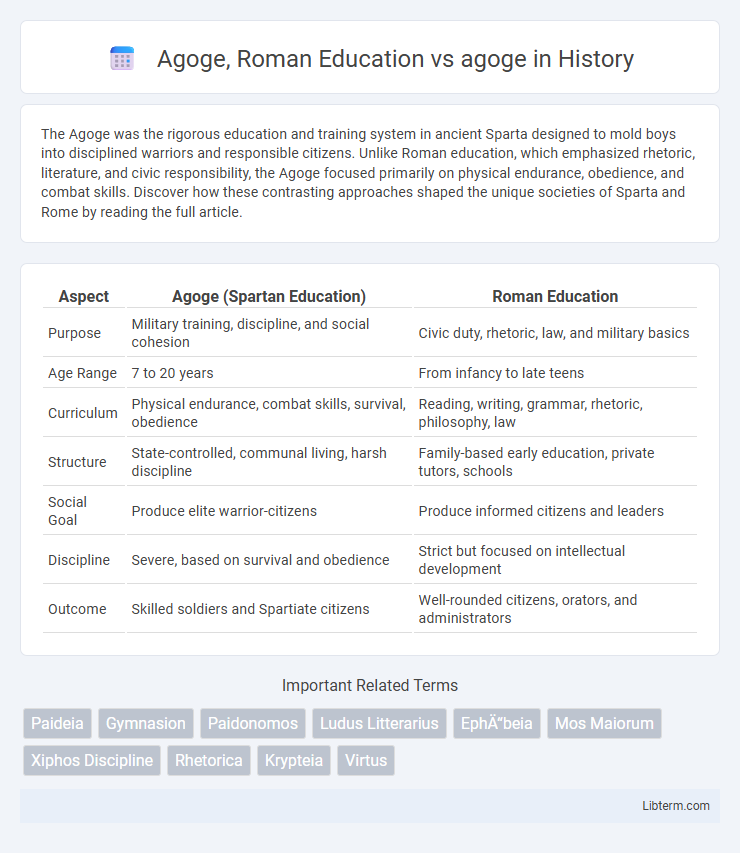
| Aspect | Agoge (Spartan Education) | Roman Education |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Military training, discipline, and social cohesion | Civic duty, rhetoric, law, and military basics |
| Age Range | 7 to 20 years | From infancy to late teens |
| Curriculum | Physical endurance, combat skills, survival, obedience | Reading, writing, grammar, rhetoric, philosophy, law |
| Structure | State-controlled, communal living, harsh discipline | Family-based early education, private tutors, schools |
| Social Goal | Produce elite warrior-citizens | Produce informed citizens and leaders |
| Discipline | Severe, based on survival and obedience | Strict but focused on intellectual development |
| Outcome | Skilled soldiers and Spartiate citizens | Well-rounded citizens, orators, and administrators |
Introduction to Agoge and Roman Education
The Agoge was the rigorous education and training regime mandatory for Spartan boys, emphasizing discipline, endurance, and military skills critical for maintaining Sparta's warrior society. Roman education focused on rhetoric, philosophy, and law to prepare young citizens for public life, emphasizing intellectual development over physical training. While the Agoge cultivated obedience and combat readiness, Roman education aimed to produce skilled orators and statesmen.
Historical Background of the Agoge
The Agoge was the rigorous education and training system of ancient Sparta designed to produce disciplined warriors and loyal citizens, instilling military skills, endurance, and social cohesion from a young age. In contrast, Roman education emphasized rhetoric, literature, and civic responsibilities to prepare individuals for public life and leadership within the Republic and later the Empire. The Agoge's historical background reflects Sparta's militaristic society centered on maintaining a dominant army, while Roman education evolved to support governance and administrative efficiency.
Structure and Curriculum of the Agoge
The Agoge was a rigorous Spartan education system emphasizing physical endurance, military training, and discipline, structured around age-specific stages starting from childhood to adulthood. Its curriculum integrated athletic exercises, survival skills, communal living, and loyalty to Sparta, creating disciplined warriors through practical, experiential learning rather than academic knowledge. In contrast, Roman education combined rhetoric, literature, and moral philosophy with military training, focusing on producing well-rounded citizens and leaders skilled in law and governance.
Core Values and Objectives of Spartan Training
The Agoge emphasized discipline, endurance, loyalty, and military excellence as core values, aiming to cultivate resilient warriors committed to Sparta's collective strength and obedience to the state. Roman education prioritized rhetoric, legal knowledge, and civic responsibility, focusing on preparing citizens for public life and governance rather than solely military prowess. Spartan training sought to create a unified, highly disciplined fighting force, while Roman education balanced physical training with intellectual development to produce versatile leaders.
Overview of Roman Education System
The Roman education system emphasized rhetoric, grammar, and law to prepare citizens for public life, contrasting with the Spartan agoge's focus on military training, discipline, and physical endurance. Roman education was structured in stages, beginning with primary schooling (ludus) and advancing to grammar schools and rhetorical studies for elite males. This system fostered intellectual development and civic responsibility, vital for participation in Roman political and legal institutions.
Key Stages in Roman Educational Development
The Agoge, the rigorous Spartan education system, emphasized physical endurance, military training, and discipline beginning at age seven. Roman education featured distinct key stages: ludus (early schooling), grammaticus (literary and rhetorical training), and rhetor (advanced oratory skills), shaping citizens for public life. Unlike the uniform Agoge, Roman education progressed from basic literacy and numeracy to sophisticated rhetoric, reflecting a broader civic and cultural focus.
Comparative Analysis: Discipline and Socialization
The agoge system in Sparta emphasized rigorous discipline through physical training and mentorship, aiming to produce loyal warriors embedded in communal values from a young age. Roman education combined formal rhetoric, literature, and philosophy with discipline rooted in obedience and respect for authority, shaping well-rounded citizens prepared for public life. Unlike the agoge's collective socialization fostering unity and military readiness, Roman education prioritized individual achievement and civic responsibility within a structured, hierarchical society.
Military Training: Spartan vs Roman Approaches
The Agoge system in Sparta emphasized rigorous physical endurance, combat skills, and communal discipline from a young age, aiming to create elite warriors through intense military training and socialization. Roman military education, while also focused on discipline and combat readiness, integrated broader civic education, including rhetoric and leadership, preparing soldiers not only for battlefield tactics but also for command roles within the Roman legions. Spartan training prioritized collective strength and loyalty to the state, whereas Roman education balanced military prowess with strategic thinking and administrative skills.
Lasting Legacies of Agoge and Roman Education
The Agoge system instilled rigorous discipline, physical endurance, and communal loyalty, shaping Sparta's military dominance and influencing modern concepts of structured youth training and state-controlled education. Roman education emphasized rhetoric, law, and civic responsibility, laying foundational principles for Western legal systems, literacy, and public administration. Both Agoge and Roman education left lasting legacies by fostering societal values--Sparta through militaristic resilience and Rome via intellectual development and governance frameworks.
Conclusion: Cultural Impact and Modern Relevance
Agoge shaped Spartan society by cultivating discipline, endurance, and loyalty, creating a militaristic culture distinct from Roman education's emphasis on rhetoric, law, and civic duty that influenced Roman governance and societal order. The enduring cultural impact of Agoge underscores the value of rigorous physical and moral training in fostering resilience and communal identity, while Roman education's legacy persists in modern legal and political institutions. Contemporary education systems draw from both models, integrating physical resilience and civic responsibility to prepare individuals for complex social roles.
Agoge, Roman Education Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com