Reform reshapes existing systems and structures to improve efficiency, fairness, and functionality. It often addresses social, political, or economic issues by implementing changes that reflect evolving values and needs. Explore the rest of the article to understand how reform can impact Your community and drive meaningful progress.
Table of Comparison
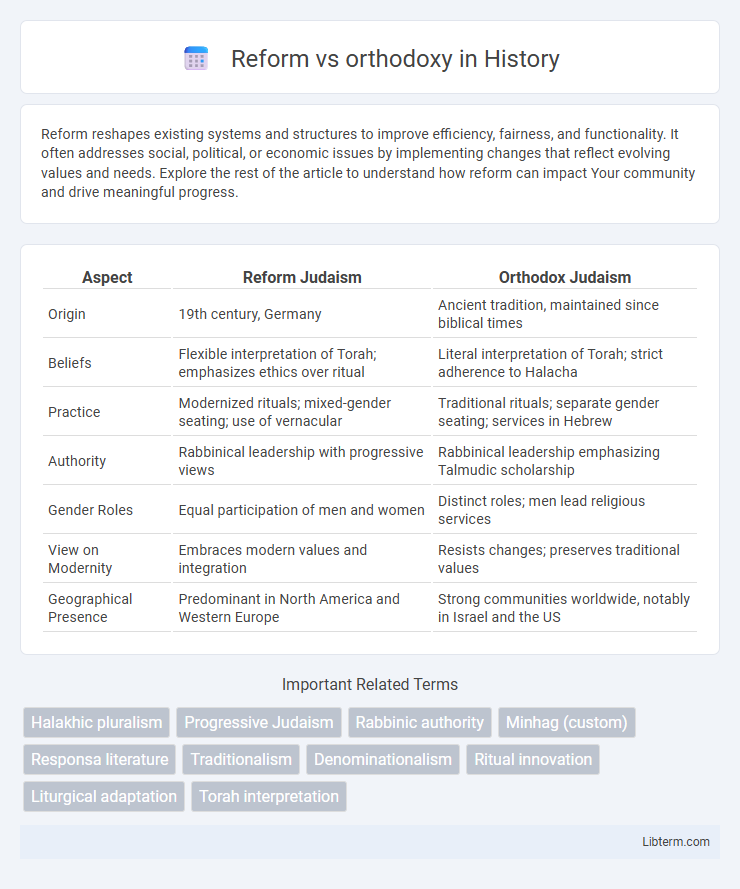
| Aspect | Reform Judaism | Orthodox Judaism |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | 19th century, Germany | Ancient tradition, maintained since biblical times |
| Beliefs | Flexible interpretation of Torah; emphasizes ethics over ritual | Literal interpretation of Torah; strict adherence to Halacha |
| Practice | Modernized rituals; mixed-gender seating; use of vernacular | Traditional rituals; separate gender seating; services in Hebrew |
| Authority | Rabbinical leadership with progressive views | Rabbinical leadership emphasizing Talmudic scholarship |
| Gender Roles | Equal participation of men and women | Distinct roles; men lead religious services |
| View on Modernity | Embraces modern values and integration | Resists changes; preserves traditional values |
| Geographical Presence | Predominant in North America and Western Europe | Strong communities worldwide, notably in Israel and the US |
Understanding Reform and Orthodoxy: Key Definitions
Reform Judaism emphasizes individual autonomy in interpreting Jewish law, advocating for modern values and adapting religious practices to contemporary life. Orthodoxy insists on strict adherence to traditional Jewish laws and customs as codified in the Torah and Talmud, maintaining continuity with historic religious authority. Understanding these core definitions highlights the distinct approaches to faith, law, and community within the Jewish spectrum.
Historical Origins of Reform and Orthodox Movements
The historical origins of Reform Judaism trace back to early 19th-century Germany, where figures like Rabbi Abraham Geiger sought to modernize Jewish practice by emphasizing ethical monotheism and integrating Enlightenment ideals. Orthodox Judaism emerged as a response, led by rabbis such as Rabbi Samson Raphael Hirsch, who emphasized strict adherence to Halacha (Jewish law) and resisted theological innovations to preserve traditional Jewish identity. These movements represent divergent paths in adapting Judaism to modernity, rooted in contrasting interpretations of religious authority and cultural assimilation.
Core Beliefs: Reform vs Orthodoxy
Reform Judaism emphasizes individual autonomy, embracing modern values and adapting traditions to contemporary life, often allowing mixed-gender worship and flexible interpretations of Jewish law. Orthodox Judaism adheres strictly to traditional Jewish law (Halacha), maintaining established rituals, gender roles, and belief in the divine origin of the Torah. Core beliefs in Orthodoxy include the immutability of Halacha and commitment to lifelong Torah study, whereas Reform Judaism prioritizes ethical principles and personal spirituality over strict legal observance.
Ritual Practices: Differences and Similarities
Reform Judaism adapts ritual practices to contemporary values, often employing vernacular language and abbreviated services to enhance accessibility, while Orthodox Judaism strictly adheres to traditional Hebrew prayers and established liturgical structures, emphasizing continuity and halachic observance. Both movements prioritize core rituals such as Shabbat and kosher dietary laws but differ in interpretation and application, with Reform allowing flexibility in gender roles and observance levels versus Orthodox maintaining gender separation and stringent ritual standards. Shared practices like Passover Seders and daily prayers underscore a common heritage, even as each embodies distinct theological and cultural expressions within Judaism.
Authority and Interpretation of Sacred Texts
Reform Judaism emphasizes individual autonomy in interpreting sacred texts, often employing modern critical methods and contextual understanding to adapt religious laws to contemporary life. Orthodox Judaism upholds the divine origin and unaltered authority of the Torah and Talmud, maintaining traditional interpretations and strict adherence to Halacha as immutable. This fundamental difference in the source and application of religious authority shapes divergent practices and beliefs within each movement.
Social and Cultural Adaptation
Reform Judaism embraces social and cultural adaptation by actively integrating contemporary values and modern lifestyles into religious practices, promoting gender equality, LGBTQ+ inclusion, and the use of vernacular languages in services. Orthodox Judaism maintains strict adherence to traditional interpretations of Jewish law (Halacha), emphasizing the preservation of established customs and rituals that resist adaptation to modern secular culture. The tension between Reform and Orthodoxy centers on balancing evolving social norms with the commitment to religious authenticity and continuity.
Gender Roles and Leadership in Reform and Orthodoxy
Reform Judaism advocates for egalitarian gender roles, promoting equal participation of men and women in religious leadership, including rabbis and cantors. Orthodox Judaism maintains traditional gender roles, restricting leadership positions to men and emphasizing distinct, complementary roles for women, often centered around family and community support. These differing perspectives reflect broader theological approaches to scriptural interpretation and religious authority within each movement.
Community Life and Religious Observance
Reform Judaism emphasizes individual autonomy and adaptability in religious observance, often allowing mixed-gender worship, use of vernacular languages, and flexible adherence to dietary laws, fostering inclusive community life. Orthodox Judaism maintains strict adherence to Halacha (Jewish law), with gender-segregated services, traditional Hebrew liturgy, and rigorous kashrut observance, reinforcing a cohesive, tradition-centered community. These divergent approaches significantly shape communal practices, social structures, and religious experiences within their respective Jewish populations.
Contemporary Challenges and Debates
Contemporary challenges in the Reform vs. Orthodoxy debate center on balancing tradition with modern societal values, including gender equality, LGBTQ+ inclusion, and religious authority. Reform Judaism emphasizes adaptability and progressive interpretations of Jewish law, while Orthodoxy maintains strict adherence to Halacha and traditional practices. These differing approaches create ongoing debates over community cohesion, religious authenticity, and responses to secularization in the modern world.
Future Perspectives on Reform and Orthodoxy
Future perspectives on Reform and Orthodoxy reveal evolving dialogues centered on adaptability and tradition preservation within Judaism. Reform Judaism emphasizes progressive values and inclusivity, appealing to younger generations seeking cultural relevance, while Orthodoxy maintains strict adherence to Halakha, ensuring continuity of ancient religious laws. Technological advancements and changing societal norms challenge both movements to balance innovation with faithfulness to their core principles.
Reform Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com