A vicarage serves as the residence provided for a vicar, often located near or attached to a church. It holds historical and architectural significance, reflecting the religious and community life of the parish. Discover more about the history, purpose, and design of vicarages in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
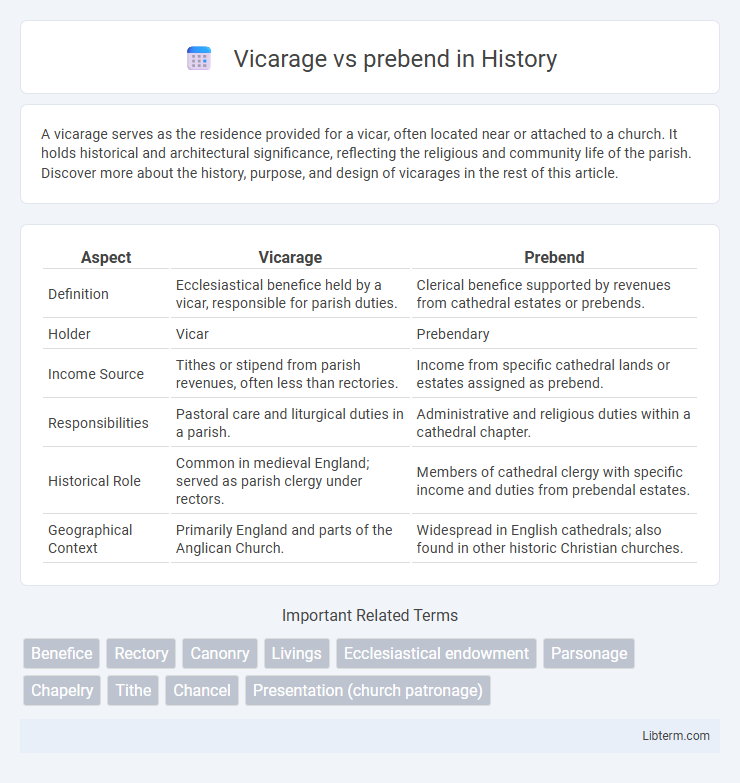
| Aspect | Vicarage | Prebend |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ecclesiastical benefice held by a vicar, responsible for parish duties. | Clerical benefice supported by revenues from cathedral estates or prebends. |
| Holder | Vicar | Prebendary |
| Income Source | Tithes or stipend from parish revenues, often less than rectories. | Income from specific cathedral lands or estates assigned as prebend. |
| Responsibilities | Pastoral care and liturgical duties in a parish. | Administrative and religious duties within a cathedral chapter. |
| Historical Role | Common in medieval England; served as parish clergy under rectors. | Members of cathedral clergy with specific income and duties from prebendal estates. |
| Geographical Context | Primarily England and parts of the Anglican Church. | Widespread in English cathedrals; also found in other historic Christian churches. |
Introduction to Church Benefices
Church benefices are ecclesiastical offices providing income to clergy through endowments or property holdings. A vicarage typically refers to the office held by a vicar, who receives a stipend in place of tithes, often acting as the parish priest without full ownership of the benefice's revenues. A prebend, on the other hand, is a type of benefice attached to a cathedral or collegiate church, providing a prebendary with income derived from specific church estates or revenues in exchange for duties in the cathedral chapter.
Defining Vicarage: Meaning and Role
A vicarage refers to the benefice held by a vicar, who is a cleric appointed to serve a parish where the tithes are appropriated to a religious institution, with the vicar receiving a stipend instead of the full income. The vicar's role primarily includes pastoral care, conducting religious services, and overseeing the spiritual well-being of the congregation. Unlike a prebend, which involves a canon's stipend derived from cathedral revenues, a vicarage represents a localized parish responsibility within the Church hierarchy.
Understanding Prebend: Definition and Significance
A prebend is a stipend derived from the revenues of a cathedral or collegiate church, historically granted to a canon or member of the clergy for their religious duties. This ecclesiastical benefice provided financial support tied to specific church lands or endowments, reflecting a prestigious position within the church hierarchy. Understanding the prebend highlights its role in sustaining clerical responsibilities and maintaining the administrative structure of medieval and early modern churches.
Historical Origins of Vicarage and Prebend
The historical origins of vicarage trace back to the medieval Church when vicars were appointed to serve parishes where the tithes were appropriated by religious institutions, acting as clerical substitutes. Prebends originated from cathedral or collegiate church estates designated to support canons, established during the early Middle Ages to ensure clergy received income from specific land revenues. Both vicarages and prebends emerged as institutional responses to managing clerical income and responsibilities within the feudal and ecclesiastical frameworks of medieval Europe.
Structural Differences Between Vicarage and Prebend
A vicarage is a benefice held by a vicar who serves as a parish priest responsible for spiritual care without ownership of the parish's revenues, whereas a prebend is a stipend attached to a cathedral or collegiate church, granted to a canon as part of their duties. Structurally, the vicarage is centered on pastoral responsibilities within a defined parish, supported financially through tithes or glebe, while the prebend is an ecclesiastical office tied to specific revenues from cathedral estates or lands, often with broader administrative or liturgical roles. This distinction highlights the vicar's direct community engagement contrasted with the prebendary's role embedded in cathedral chapter governance and income allocation.
Clerical Duties: Vicar vs. Prebendary
Vicars are responsible for the pastoral care and daily spiritual needs of their parish, including conducting services, administering sacraments, and providing guidance to parishioners. Prebendaries typically hold honorary positions within a cathedral or collegiate church and perform specific liturgical duties, often attending chapter meetings and assisting in ceremonial functions. While vicars engage directly in parish ministry and community leadership, prebendaries focus more on administrative roles tied to their prebendal stall and less on direct pastoral care.
Financial Aspects: Stipends and Endowments
Vicars typically received a stipend funded by an endowment or the parish's tithes, which often provided a modest but steady income. Prebendaries benefitted from prebendal endowments attached to specific cathedral or collegiate church revenues, frequently ensuring a larger and more secure financial support compared to vicars. The financial distinction lies in vicars managing parish revenues mainly for pastoral duties, whereas prebendaries hold a fixed income tied to their prebend within the ecclesiastical institution.
Appointment Processes and Eligibility
The appointment process for a vicarage typically involves presentation by a patron followed by institution by the bishop, whereas a prebendary is appointed through a cathedral chapter, often requiring a cleric already holding a benefice. Eligibility for a vicarage generally requires ordination and adherence to diocesan criteria, while prebendaries must usually be ordained clergy with specific qualifications tied to cathedral statutes. Both roles demand canonical compliance, but prebendaries often undergo a more rigorous selection reflecting their collegiate responsibilities.
Influence on Parish and Cathedral Life
A vicarage typically involves direct pastoral care and spiritual oversight within a parish, fostering close relationships with congregants and influencing local worship practices. A prebend, linked to a cathedral or collegiate church, provides clergy with income derived from cathedral estates, often emphasizing cathedral chapter duties and broader ecclesiastical governance rather than parish engagement. The prebendary's role enhances cathedral liturgy and administration, while the vicar focuses on community-centered parish ministry and local spiritual life.
Modern Relevance and Evolution of Vicarage and Prebend
The vicarage, originally a benefice providing income to clergy serving parishes, has evolved into a role emphasizing pastoral care and community leadership within modern ecclesiastical structures. Prebends, historically financial endowments allocated to cathedral canons, now often function as honorary titles reflecting a blend of tradition and contemporary administrative duties. The modern relevance of both lies in their adaptation to changing church governance and the shifting focus from purely economic support to active ministry and heritage preservation.
Vicarage Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com