Affirmationism focuses on the power of positive affirmations to reshape your mindset and enhance overall well-being. By consistently reinforcing affirming beliefs, it encourages motivation, confidence, and personal growth. Explore the rest of the article to discover how incorporating affirmationism can transform your daily life.
Table of Comparison
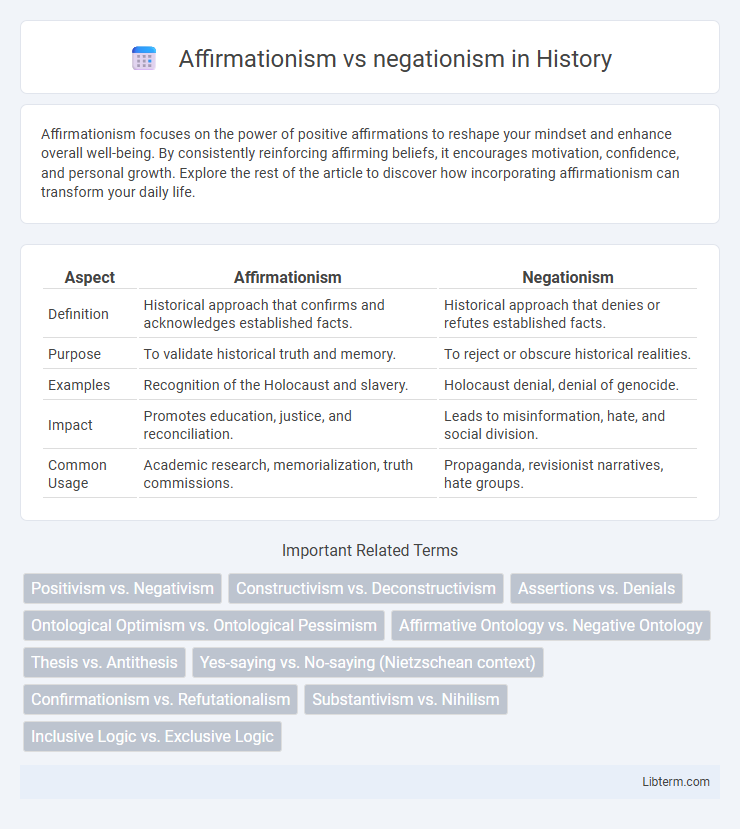
| Aspect | Affirmationism | Negationism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Historical approach that confirms and acknowledges established facts. | Historical approach that denies or refutes established facts. |
| Purpose | To validate historical truth and memory. | To reject or obscure historical realities. |
| Examples | Recognition of the Holocaust and slavery. | Holocaust denial, denial of genocide. |
| Impact | Promotes education, justice, and reconciliation. | Leads to misinformation, hate, and social division. |
| Common Usage | Academic research, memorialization, truth commissions. | Propaganda, revisionist narratives, hate groups. |
Understanding Affirmationism: Definition and Core Concepts
Affirmationism centers on the psychological and philosophical practice of reinforcing positive beliefs and realities through affirmations, aiming to foster mental well-being, self-confidence, and goal achievement. Core concepts include the consistent repetition of positive statements to reshape cognition, the alignment of subconscious beliefs with conscious objectives, and the acknowledgment that affirmations influence motivation and behavior through neuroplasticity. This approach is rooted in cognitive-behavioral principles and emphasizes the proactive cultivation of constructive thought patterns as a pathway to personal growth and resilience.
Exploring Negationism: Meaning and Philosophical Roots
Negationism refers to the denial or distortion of historical facts, often relating to atrocities or politically sensitive events, aiming to erase or rewrite collective memory. It contrasts with affirmationism, which acknowledges and validates historical truths, thereby fostering understanding and accountability. Philosophically, negationism stems from epistemological skepticism and ideological bias, challenging the acceptance of objective reality in favor of constructed narratives.
Historical Background of Affirmationism and Negationism
Affirmationism and Negationism emerged in the 20th century as contrasting approaches to interpreting historical events, particularly in the context of political and ideological conflicts. Affirmationism emphasizes the constructive validation of national or cultural identity by affirming historical narratives that support unity and pride, often linked to post-World War II efforts in rebuilding and reconciliation. Negationism, by contrast, seeks to deny or minimize certain historical facts, such as genocides or war crimes, often as part of revisionist agendas aimed at distorting collective memory or absolving responsibility.
Key Differences Between Affirmationism and Negationism
Affirmationism emphasizes the recognition and validation of positive experiences and beliefs, fostering constructive attitudes and self-confidence. Negationism denies or dismisses certain facts or realities, often leading to distortion or rejection of historical or social truths. Key differences include their approach to truth acceptance, where affirmationism promotes acknowledgment and integration, while negationism involves denial and avoidance of uncomfortable realities.
Real-World Applications of Affirmationism
Affirmationism serves as a practical framework in psychology, promoting positive reinforcement techniques that enhance motivation and self-efficacy across educational and therapeutic settings. In organizational behavior, affirmationism underpins employee engagement strategies by fostering a constructive work environment emphasizing strengths and achievable goals. This approach also influences cognitive-behavioral therapies, where affirmational practices support mental health improvements through structured positive affirmations and resilience training.
The Impact of Negationism on Society and Culture
Negationism, by denying or distorting historical facts, particularly regarding atrocities and genocides, undermines collective memory and impedes justice for victims. This manipulation fosters social polarization, erodes trust in institutions, and hampers efforts toward reconciliation and education. Societies impacted by negationism often experience heightened conflict and a weakened cultural identity, as truth is replaced with revisionism that benefits oppressive agendas.
Affirmationism in Modern Psychology
Affirmationism in modern psychology emphasizes reinforcing positive beliefs and self-affirming thoughts to improve mental well-being and resilience. This approach leverages cognitive-behavioral techniques to foster adaptive self-schemas, enhance motivation, and reduce cognitive dissonance. Research shows that affirmation interventions can effectively decrease stress, promote self-regulation, and support psychological growth.
The Dangers and Consequences of Negationist Thinking
Negationist thinking undermines historical truth by denying or distorting well-documented events such as genocides and human rights violations, leading to widespread misinformation and societal division. This denial erodes collective memory and impedes justice for victims, fostering environments where prejudice and hatred can flourish unchecked. Persistent negationism threatens democratic values and obstructs reconciliation efforts, ultimately destabilizing social cohesion and delaying progress toward equality and recognition.
Balancing Affirmationist and Negationist Perspectives
Balancing Affirmationist and Negationist perspectives requires integrating positive recognition of achievements with critical analysis of mistakes to foster comprehensive understanding and growth. Affirmationism emphasizes highlighting successes and strengths, which boosts motivation and resilience, while Negationism addresses shortcomings to promote accountability and improvement. Striking an equilibrium between these approaches enhances decision-making, encourages constructive feedback, and supports sustainable development across social, educational, and organizational contexts.
Future Trends: The Evolving Debate Between Affirmationism and Negationism
Future trends in the debate between Affirmationism and Negationism reveal a growing emphasis on integrative epistemologies that challenge binary paradigms in knowledge validation. Advances in cognitive science and artificial intelligence are expected to influence this discourse by providing empirical data that may blur the rigid distinctions between affirmation and negation processes. As interdisciplinary research progresses, the evolving debate will likely reflect a synthesis of nuanced perspectives that accommodate complexity in belief systems and truth assertions.
Affirmationism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com