Imperium and libertas represent two fundamental concepts in ancient Roman political philosophy, where imperium refers to the authority and power wielded by magistrates or commanders, while libertas embodies the idea of personal freedom and civil liberties of citizens. Balancing the exercise of imperium with the protection of libertas was central to the Roman Republic's governance, ensuring that power did not become tyrannical or suppress individual rights. Explore the rest of the article to understand how these principles shaped political thought and legal systems throughout history.
Table of Comparison
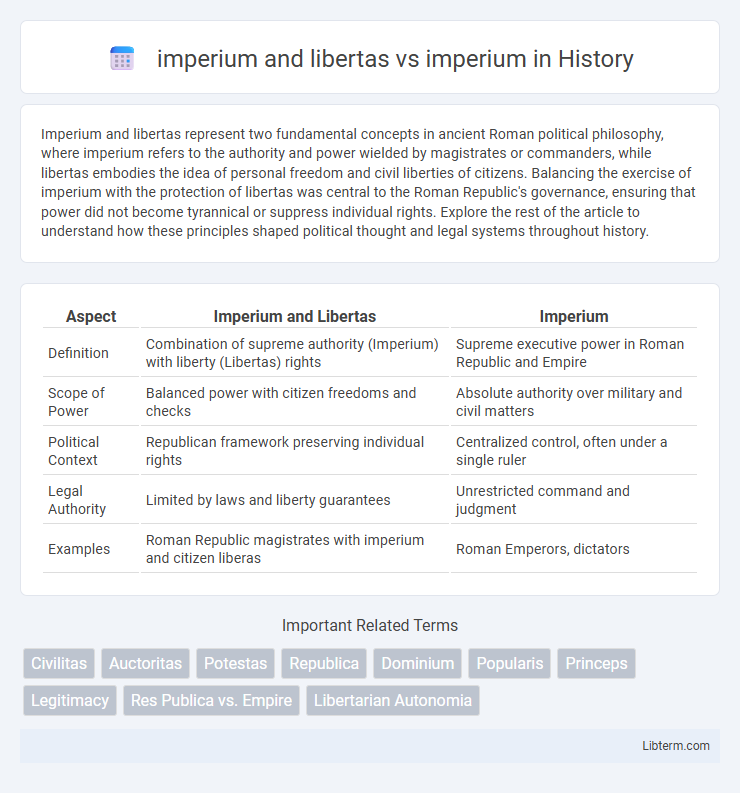
| Aspect | Imperium and Libertas | Imperium |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combination of supreme authority (Imperium) with liberty (Libertas) rights | Supreme executive power in Roman Republic and Empire |
| Scope of Power | Balanced power with citizen freedoms and checks | Absolute authority over military and civil matters |
| Political Context | Republican framework preserving individual rights | Centralized control, often under a single ruler |
| Legal Authority | Limited by laws and liberty guarantees | Unrestricted command and judgment |
| Examples | Roman Republic magistrates with imperium and citizen liberas | Roman Emperors, dictators |
Defining Imperium and Libertas
Imperium in Roman law refers to the supreme executive power held by magistrates or generals, encompassing military command, judicial authority, and governance over territories. Libertas denotes the concept of personal freedom and political rights enjoyed by Roman citizens, opposing arbitrary rule and emphasizing autonomy and civic participation. The tension between imperium and libertas highlights the balance between centralized authority and individual freedoms within the Roman Republic.
Historical Origins of Imperium vs. Libertas
Imperium, rooted in Roman law, signified the authority granted to magistrates to command armies, govern provinces, and administer justice, reflecting a centralized power essential for state control and stability. Libertas, by contrast, embodied the concept of individual freedom and civic rights within the Roman Republic, advocating for personal autonomy and protection against tyranny. The historical tension between imperium and libertas highlights the foundational struggle in Roman political culture between authoritarian governance and the republican ideal of liberty.
Political Philosophy: Authority vs. Freedom
Imperium represents centralized authority and structured governance, emphasizing control and order within political philosophy, while libertas centers on individual freedom and autonomy, advocating minimal interference from power structures. The tension between imperium and libertas highlights the fundamental debate over the extent of state power versus personal liberty, with imperium justifying hierarchical rule and libertas promoting self-determination. Balancing imperium and libertas remains a core challenge in political theory, shaping discussions on sovereignty, rights, and the legitimacy of coercion.
Imperium’s Role in Governance
Imperium serves as the supreme authority in governance, granting rulers the power to enact and enforce laws, command military forces, and administer justice. Unlike the concept of imperium and libertas, where imperium is balanced by individual freedoms, pure imperium emphasizes centralized control and absolute obedience within the state. This concentration of power ensures stability and order but often limits personal liberties and political participation.
Libertas: The Concept of Civic Freedom
Libertas symbolizes the core of Roman civic freedom, embodying individual rights and political participation within the framework of imperium, the supreme executive authority exercised by magistrates and emperors. Unlike the absolute command implied by imperium alone, Libertas represents the balance between governing power and personal liberties essential for sustaining a republic. This dynamic tension between imperium and libertas shaped Roman political thought, emphasizing that true authority must coexist with citizen freedoms to ensure legitimate governance.
Tensions Between Order and Liberty
Imperium and libertas represent the enduring tension between centralized authority and individual freedom in political theory. Imperium emphasizes structured governance and legal order as essential for societal stability, while libertas prioritizes personal autonomy and resistance against oppressive control. This dynamic clash reveals the challenge of balancing effective rule with the protection of civil liberties.
Case Studies: Rome, Britain, and Beyond
Imperium and libertas shaped governance in Rome by balancing autocratic power with citizen freedoms, exemplified in the Republican era where imperium was checked by popular assemblies. In Britain, Roman imperium imposed strict control over conquered territories, contrasting with the relatively autonomous native tribal systems valuing libertas. Beyond these regions, varying degrees of imperium and libertas influenced provincial administration, with case studies revealing how local autonomy coexisted or clashed with imperial authority.
Modern Interpretations of Imperium vs. Libertas
Modern interpretations of imperium emphasize centralized authority and governance, highlighting state power to enforce laws and maintain order, while libertas underscores individual freedoms and civil liberties as foundational democratic values. Contemporary political discourse often frames imperium as necessary for national security and institutional stability, contrasting with libertas, which prioritizes personal autonomy and resistance to authoritarian control. This ongoing tension shapes debates on government intervention, surveillance, and the balance between collective order and personal rights.
The Impact on Civil Society
Imperium and libertas together create a balance where authority coexists with individual freedoms, fostering a civil society that values both governance and personal rights. Imperium alone often leads to centralized control, risking the suppression of dissent and reduced civic participation. The dynamic tension between imperium and libertas shapes the development of democratic institutions and the protection of civil liberties.
Striking a Balance: Lessons for Today
Striking a balance between imperium and libertas highlights the enduring tension between centralized authority and individual freedom essential for stable governance. Modern political systems benefit from integrating checks on imperium to prevent authoritarianism while safeguarding libertas to ensure citizen rights and participation. Lessons from historical struggles illustrate that sustainable governance requires nuanced power distribution embracing both control and personal liberty.
imperium and libertas Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com