Buddha, the enlightened teacher, founded Buddhism by sharing profound insights into suffering, mindfulness, and compassion. His teachings emphasize the path to inner peace and liberation through meditation and ethical living. Discover how Buddha's wisdom can transform your life by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
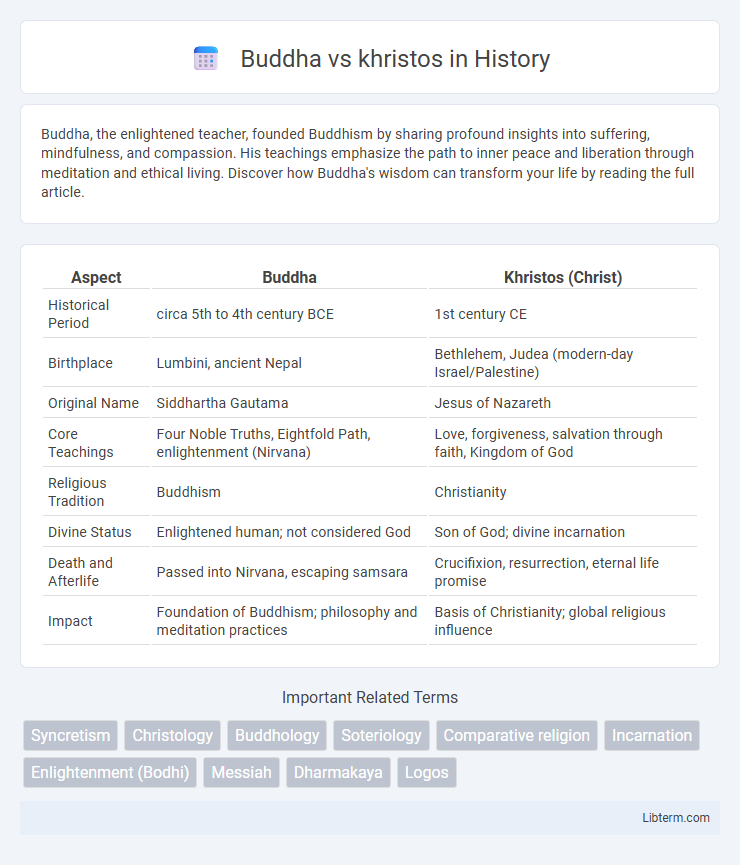
| Aspect | Buddha | Khristos (Christ) |
|---|---|---|
| Historical Period | circa 5th to 4th century BCE | 1st century CE |
| Birthplace | Lumbini, ancient Nepal | Bethlehem, Judea (modern-day Israel/Palestine) |
| Original Name | Siddhartha Gautama | Jesus of Nazareth |
| Core Teachings | Four Noble Truths, Eightfold Path, enlightenment (Nirvana) | Love, forgiveness, salvation through faith, Kingdom of God |
| Religious Tradition | Buddhism | Christianity |
| Divine Status | Enlightened human; not considered God | Son of God; divine incarnation |
| Death and Afterlife | Passed into Nirvana, escaping samsara | Crucifixion, resurrection, eternal life promise |
| Impact | Foundation of Buddhism; philosophy and meditation practices | Basis of Christianity; global religious influence |
Origins and Historical Contexts: Buddha and Khristos
Buddha, originating in 6th-century BCE India, founded Buddhism rooted in the teachings of Siddhartha Gautama, emphasizing enlightenment and the cessation of suffering within a dharmic tradition. Khristos, or Christ, emerged in 1st-century CE Judea as a messianic figure in Christianity, centered on the life and resurrection of Jesus as the savior in a monotheistic Jewish context. Both figures profoundly shaped spiritual philosophies but arose from distinct cultural and religious environments reflective of South Asian and Middle Eastern histories.
Foundational Teachings: Dharma vs Gospel
Buddha's foundational teachings in Dharma emphasize the Four Noble Truths and the Eightfold Path, guiding adherents toward enlightenment through ethical conduct, mental discipline, and wisdom. Khristos' Gospel centers on the message of salvation through faith in Jesus Christ, highlighting grace, redemption, and the Kingdom of God as core principles. Both frameworks offer distinct spiritual paths: Dharma focuses on self-realization and liberation from suffering, while the Gospel emphasizes divine forgiveness and eternal life.
Paths to Enlightenment and Salvation
Buddha's path to enlightenment centers on the Four Noble Truths and the Eightfold Path, emphasizing self-realization, mindfulness, and meditation to overcome suffering (dukkha) and attain Nirvana. Khristos (Christ) teaches salvation through faith in Jesus Christ, grace, and repentance, promising eternal life and redemption from sin through belief in His sacrifice. Both paths offer transformative journeys: Buddhism highlights inner awakening and liberation from the cycle of rebirth (samsara), while Christianity focuses on divine forgiveness and eternal communion with God.
Concepts of Suffering and Compassion
Buddha's teachings emphasize the Four Noble Truths, identifying suffering (dukkha) as an inherent part of existence and advocating the Eightfold Path to overcome it through mindfulness and ethical conduct. In contrast, Khristos (Christ) centers on redemptive suffering and divine compassion, portraying suffering as a pathway to salvation and love through God's grace. Both figures elevate compassion as a transformative response to human suffering, yet Buddha promotes self-realization while Khristos emphasizes faith in divine mercy.
The Nature of Divinity and Humanity
Buddha represents an enlightened human who attained Nirvana through self-realization, embodying the potential for human divinity without being a god himself. Khristos, or Christ, is viewed in Christian theology as both fully divine and fully human, embodying the incarnation of God on Earth. The core distinction lies in Buddha's path as a spiritual teacher and exemplar versus Christ's unique dual nature as God and man central to salvation.
Rituals, Practices, and Devotions
Buddhist rituals emphasize meditation, chanting of sutras, and offerings like incense and candles to cultivate mindfulness and compassion, while Christian practices involve prayer, sacraments such as baptism and communion, and participation in church services to express faith and receive divine grace. Devotions in Buddhism often include prostrations and pilgrimage to sacred sites like Bodh Gaya, contrasting with Christian devotions that center around veneration of the cross, saints, and attending Mass. Both traditions use ritual acts to deepen spiritual connection, with Buddhism focusing on inner enlightenment and Christianity emphasizing salvation through Christ.
Community: Sangha vs Ecclesia
The Buddha's Sangha represents a monastic community dedicated to spiritual practice, emphasizing individual enlightenment and collective support within Buddhism. In contrast, the Christian Ecclesia functions as a congregational body focused on worship, communal faith, and the propagation of Christ's teachings. Both Sangha and Ecclesia establish structured communities that nurture doctrinal adherence, moral guidance, and social cohesion among their followers.
Moral Frameworks and Ethical Living
Buddha's moral framework centers on the Four Noble Truths and the Eightfold Path, promoting ethical living through mindfulness, compassion, and the cessation of suffering. Khristos, or Christ, emphasizes the teachings of love, forgiveness, and grace found in the Sermon on the Mount, advocating for selflessness and adherence to God's commandments. Both spiritual leaders offer ethical living models grounded in compassion and moral discipline, influencing diverse religious and philosophical traditions worldwide.
Legacy and Influence on World Civilizations
Buddha's teachings on compassion, mindfulness, and enlightenment profoundly shaped Asian cultures, inspiring diverse spiritual practices like Buddhism, which influences millions worldwide through meditation, ethical living, and non-violence. Khristos, representing Jesus Christ, established the foundation of Christianity, a major global religion with impact on Western civilization's laws, morality, art, and social institutions for over two millennia. Both figures continue to influence philosophical thought, ethical frameworks, and cultural identities across continents, underscoring their enduring legacy in shaping world civilizations.
Dialogue and Syncretism: Bridging Buddha and Khristos
Dialogue between Buddha and Khristos highlights shared themes of compassion, enlightenment, and moral transformation central to Buddhism and Christianity. Syncretism emerges as followers integrate ethical teachings from both traditions, fostering spiritual bridges that emphasize inner peace and divine love. This fusion encourages cross-cultural understanding by blending Buddhist meditation with Christian faith practices.
Buddha Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com