Orthodox Christianity emphasizes traditional beliefs and practices rooted in the early Church, preserving ancient liturgies and doctrines. Its rich spiritual heritage includes the veneration of icons, the celebration of the Divine Liturgy, and adherence to the Nicene Creed. Explore the article to deepen your understanding of Orthodox faith and its role in modern spirituality.
Table of Comparison
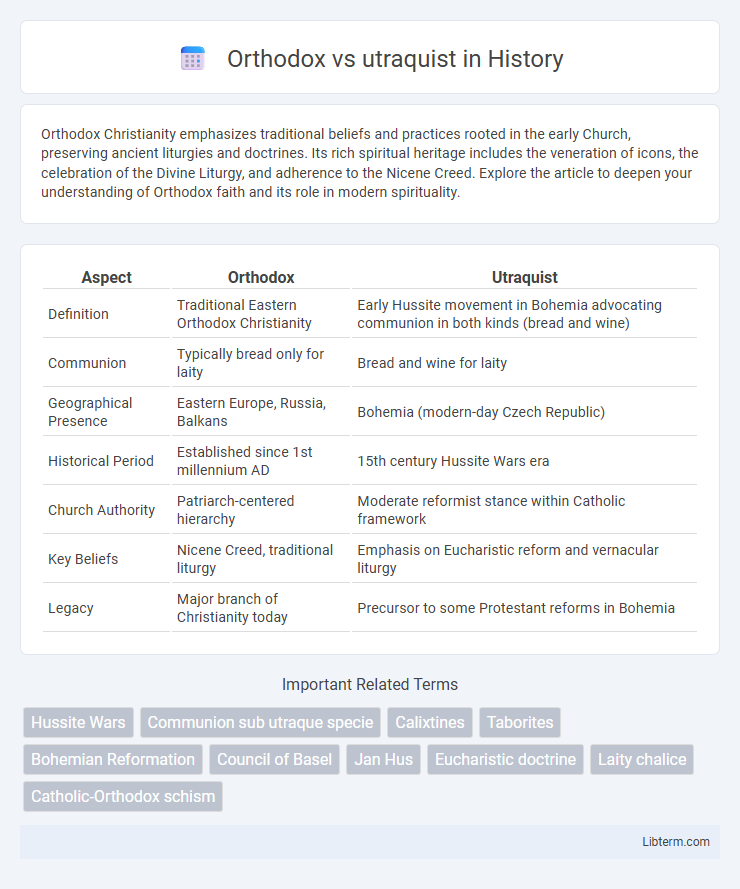
| Aspect | Orthodox | Utraquist |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional Eastern Orthodox Christianity | Early Hussite movement in Bohemia advocating communion in both kinds (bread and wine) |
| Communion | Typically bread only for laity | Bread and wine for laity |
| Geographical Presence | Eastern Europe, Russia, Balkans | Bohemia (modern-day Czech Republic) |
| Historical Period | Established since 1st millennium AD | 15th century Hussite Wars era |
| Church Authority | Patriarch-centered hierarchy | Moderate reformist stance within Catholic framework |
| Key Beliefs | Nicene Creed, traditional liturgy | Emphasis on Eucharistic reform and vernacular liturgy |
| Legacy | Major branch of Christianity today | Precursor to some Protestant reforms in Bohemia |
Introduction to Orthodox and Utraquist Traditions
Orthodox Christianity is characterized by its adherence to the Eastern Orthodox Church, emphasizing the continuity of Holy Tradition, the Nicene Creed, and the Divine Liturgy centered on the Eucharist in Greek or Church Slavonic. The Utraquist tradition emerged during the Hussite movement in Bohemia, advocating for communion under both kinds--bread and wine--for laity, contrasting with the Roman Catholic practice of offering only bread. These distinctive liturgical and theological practices define the core differences between Orthodox and Utraquist Christian expressions.
Historical Background of Orthodox Christianity
Orthodox Christianity, rooted in the early ecumenical councils and Byzantine traditions, emphasizes strict adherence to the Nicene Creed and liturgical continuity. The Utraquist movement emerged during the Hussite Wars in 15th-century Bohemia, advocating for communion under both kinds (bread and wine) for laity, contrasting with Orthodox sacramental practices. Orthodox Christianity's historical development centered around the Eastern Roman Empire, shaping its theological, cultural, and ecclesiastical identity distinct from Western and reformist movements like Utraquism.
Origins and Development of Utraquism
Utraquism originated in the early 15th century during the Hussite Wars in Bohemia as a moderate reform movement advocating for Communion in both kinds--bread and wine--for laity, contrasting with the Roman Catholic practice. Emerging from Hussite religious disputes, utraquism developed into a significant theological stance emphasizing lay participation and was later recognized by the Council of Basel, blending Catholic rituals with reformist ideals. Its development influenced the religious landscape of Central Europe, marking a distinct path between Roman Catholic Orthodoxy and more radical Protestant reforms.
Core Doctrinal Differences
Orthodox Christianity emphasizes the complete authority of Scripture and Tradition, affirming seven sacraments and the veneration of saints, while Utraquists advocate for Communion under both kinds (bread and wine) for laity, rejecting certain Catholic dogmas such as transubstantiation. The Orthodox Church upholds apostolic succession and the infallibility of councils, whereas Utraquists promote a more reformist theological stance rooted in Hussite principles, emphasizing vernacular liturgy and clerical marriage. These core doctrinal differences highlight contrasting views on sacramental theology, ecclesiastical authority, and liturgical practice.
Liturgical Practices Compared
Orthodox liturgical practices emphasize the Divine Liturgy of St. John Chrysostom with extensive use of icons, incense, and chant, reflecting a deep continuity with early Christian traditions. Utraquist liturgy, emerging from Bohemian Reformation, combines elements of Catholic Mass with vernacular Scripture readings and communion administered under both kinds (bread and wine) to laity, highlighting a more accessible and reformist worship experience. The Orthodox Church preserves ancient ritualistic symbolism and sacramental formality, while Utraquism introduces simplified, bilingual services aiming for congregational participation.
Role of the Eucharist in Both Traditions
The Orthodox Church emphasizes the Eucharist as the true and mystical body and blood of Christ, central to divine worship and spiritual life, celebrating it as a holy sacrament that unites believers with God. The Utraquist tradition, emerging from the Hussite movement, uniquely advocates for Communion under both kinds--bread and wine--reflecting a commitment to scriptural practices and lay participation during the Eucharist. Both traditions underscore the Eucharist's role in salvation and communal faith, but differ in liturgical expression and theological emphasis concerning the elements and access.
Impact on Local Societies and Cultures
Orthodox Christianity, with its emphasis on traditional rituals and hierarchical ecclesiastical structures, deeply influenced local societies by reinforcing established social orders and cultural identities, particularly in Eastern Europe. Utraquists, advocating for communion under both kinds and blending Catholic and Protestant elements, fostered religious pluralism and encouraged vernacular worship, which empowered local communities to participate more actively in their spiritual life. This divergence shaped cultural developments by either preserving long-standing customs under Orthodoxy or promoting reformist values and greater individual involvement within Utraquist regions.
Key Figures and Influential Leaders
Key figures in the Orthodox movement included Jan Hus and Jerome of Prague, whose advocacy for reform influenced later Protestant ideals. Utraquist leaders like King Jiri z Podebrad and Bishop Stanislav Thurzo emphasized a moderate approach, supporting communion under both kinds to bridge gaps between Catholics and reformers. Their leadership shaped the religious landscape of Bohemia during the 15th and 16th centuries, balancing doctrinal purity with political pragmatism.
Legacy and Modern Presence
Orthodox Christianity, rooted in Eastern traditions, has left a profound legacy through enduring liturgical practices and theological teachings that continue to shape Eastern European cultures. The Utraquist movement, emerging from Hussite reforms in Bohemia, influenced religious tolerance and the early push toward communion in both kinds, impacting Czech religious identity and historical church reforms. Today, Orthodox communities maintain vibrant congregations primarily in Eastern Europe and the Middle East, while Utraquism's modern presence persists mainly through cultural remembrance and its historic role in Protestant development.
Conclusion: Significance of the Orthodox-Utraquist Debate
The Orthodox-Utraquist debate significantly shaped religious pluralism in Central Europe during the Reformation by highlighting contrasting views on Eucharistic practice and church authority. Orthodox proponents emphasized strict adherence to Catholic dogma, while Utraquists advocated for receiving both bread and wine, influencing the development of religious tolerance and compromise in Bohemia. This theological discourse contributed to the regional balance between Roman Catholicism and emerging Protestant traditions, impacting political and cultural identities.
Orthodox Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com