A legate was an official envoy or ambassador in ancient Rome, often appointed by the emperor to represent imperial authority in military or diplomatic matters. This role combined political influence with military command, making the legate a key figure in expanding and maintaining Roman power. Explore the full article to understand how legates shaped Roman history and their lasting impact on governance.
Table of Comparison
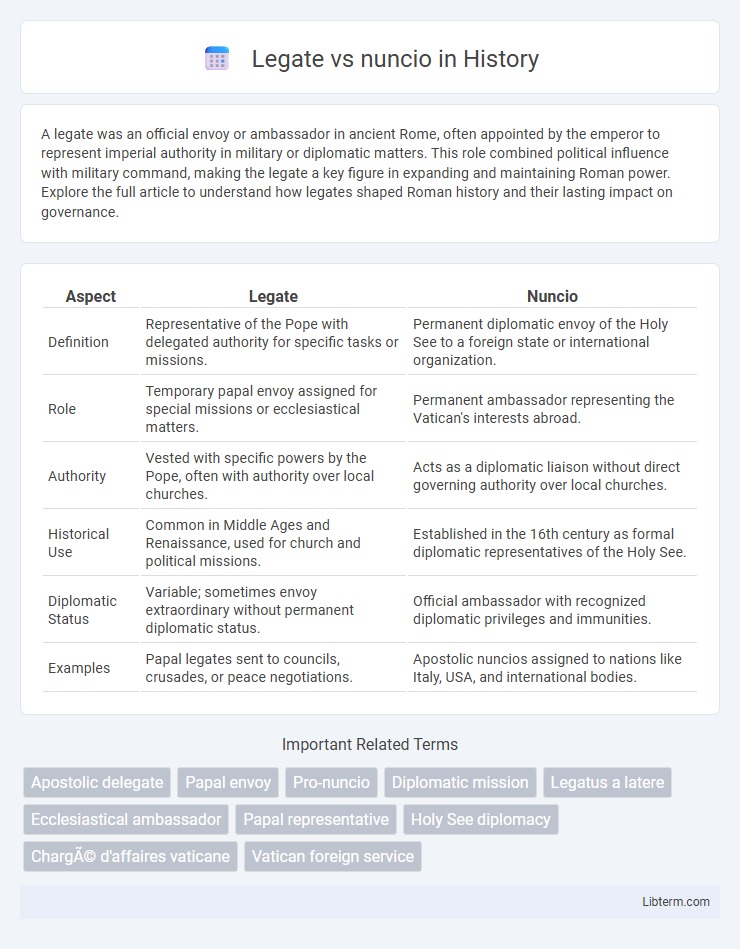
| Aspect | Legate | Nuncio |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Representative of the Pope with delegated authority for specific tasks or missions. | Permanent diplomatic envoy of the Holy See to a foreign state or international organization. |
| Role | Temporary papal envoy assigned for special missions or ecclesiastical matters. | Permanent ambassador representing the Vatican's interests abroad. |
| Authority | Vested with specific powers by the Pope, often with authority over local churches. | Acts as a diplomatic liaison without direct governing authority over local churches. |
| Historical Use | Common in Middle Ages and Renaissance, used for church and political missions. | Established in the 16th century as formal diplomatic representatives of the Holy See. |
| Diplomatic Status | Variable; sometimes envoy extraordinary without permanent diplomatic status. | Official ambassador with recognized diplomatic privileges and immunities. |
| Examples | Papal legates sent to councils, crusades, or peace negotiations. | Apostolic nuncios assigned to nations like Italy, USA, and international bodies. |
Introduction to Legate and Nuncio
A Legate is a high-ranking representative appointed by the Pope to act on his behalf in specific diplomatic or ecclesiastical missions, often carrying broad authority in church governance. A Nuncio serves as the Vatican's diplomatic envoy to a foreign state or international organization, functioning as both ambassador and liaison between the Holy See and local churches. Both roles are crucial in maintaining the Catholic Church's diplomatic relations and overseeing ecclesiastical affairs globally.
Historical Origins of Legates and Nuncios
Legates originated in the Roman Catholic Church as papal envoys representing the pope's authority in political and ecclesiastical matters, established during the early centuries of Christianity to maintain communication and control over distant dioceses. Nuncios developed later in the 16th century as permanent diplomatic representatives of the Holy See to sovereign states, evolving from the legatine tradition to function within the modern system of international diplomacy. The historical origins of legates lie in their role as temporary papal delegates, while nuncios emerged as institutionalized ambassadors reflecting the growing complexity of church-state relations.
Defining the Role of a Papal Legate
A papal legate serves as the pope's personal representative, entrusted with diplomatic and ecclesiastical authority to convey papal directives and oversee church matters in appointed regions. Unlike a nuncio, who primarily functions as a diplomatic envoy to states, a legate holds broader ecclesiastical jurisdiction and can command synods, resolve disputes, and implement church reforms directly. The legate's role is pivotal in maintaining papal influence across distant dioceses and ensuring alignment with Vatican policies.
Understanding the Position of a Nuncio
A nuncio serves as a diplomatic representative of the Holy See, acting as both an ambassador to the state and a liaison to the local Catholic Church, embodying a unique dual role in ecclesiastical and diplomatic affairs. Unlike a legate, whose mission may be temporary or specific to certain church matters, a nuncio holds a permanent position with responsibilities including the promotion of communion between the Vatican and the national church hierarchy. This office requires a deep understanding of canon law, diplomacy, and ecclesiastical governance to effectively represent papal interests and facilitate communication between the Holy See and civil governments.
Key Differences Between Legates and Nuncios
Legates serve as personal representatives of the Pope with broad authority, often dispatched for specific missions or diplomatic tasks, while nuncios act as permanent ambassadors to foreign states and the Catholic Church, managing ongoing diplomatic relations. Legates typically hold temporary or special mandates with ecclesiastical or diplomatic functions, whereas nuncios have established roles as papal diplomats and often participate in the selection of bishops within their assigned territories. The key distinction lies in legates' mission-based, flexible authority compared to nuncios' enduring diplomatic presence and administrative responsibilities in the Holy See's international relations.
Diplomatic Functions and Responsibilities
A legate serves as a personal representative of the Pope, often tasked with delivering important messages or overseeing specific missions within the Church, blending both diplomatic and ecclesiastical authority. A nuncio acts as an official diplomatic envoy, accredited to foreign states to represent the Holy See, managing diplomatic relations, and liaising with local Catholic communities and governments. Both roles involve significant diplomatic functions, but the nuncio primarily focuses on state-to-state interactions, while the legate's responsibilities may include broader ecclesiastical governance.
Selection and Appointment Processes
Legates are appointed directly by the Pope and often selected from among cardinals or archbishops based on their diplomatic experience and service to the Church. Nuncios are also papal representatives but usually enter the Vatican diplomatic service early in their careers, undergoing specialized training at the Pontifical Ecclesiastical Academy before selection. Both roles require a formal appointment by the Holy See, emphasizing theological expertise, diplomatic skills, and ecclesiastical rank.
Impact on International Relations
Legates often serve as direct envoys of the pope with broad diplomatic powers, facilitating high-level negotiations that can significantly influence political alliances and religious diplomacy. Nuncios act as permanent diplomatic representatives of the Holy See to states, playing a crucial role in maintaining ongoing diplomatic relations and influencing local church-state interactions. Both roles impact international relations by shaping Vatican diplomacy, with legates typically addressing urgent or exceptional matters, while nuncios sustain continuous dialogue and foster long-term diplomatic stability.
Famous Legates and Nuncios in History
Famous legates such as Cardinal Wolsey, who served as papal legate in the early 16th century, played pivotal roles in diplomatic and ecclesiastical affairs during the Renaissance period. Notable nuncios include Archbishop Agostino Casaroli, whose diplomatic skill contributed significantly to the Vatican's Ostpolitik in the 20th century, and Archbishop Giovanni Battista Montini, later Pope Paul VI, known for his influential nuncio tenure in several countries. Both legates and nuncios historically acted as key papal representatives, with legates often possessing broader mandates and nuncios serving as permanent diplomatic envoys to states.
Modern Relevance of Legates and Nuncios
Legates and nuncios serve as papal representatives, with nuncios often acting as diplomatic envoys to states, while legates hold a broader ecclesiastical mandate. In modern times, nuncios play a critical role in maintaining Vatican diplomatic relations, influencing both religious and political spheres across over 180 countries. Legates, though less common today, are appointed for specific missions or events, reinforcing the Pope's authority in regional or global Church matters.
Legate Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com