Koinonia represents deep fellowship and communal sharing that fosters strong bonds within a group. Rooted in ancient Greek culture, it emphasizes unity, mutual support, and spiritual connection. Explore this article to discover how koinonia can enrich your relationships and community life.
Table of Comparison
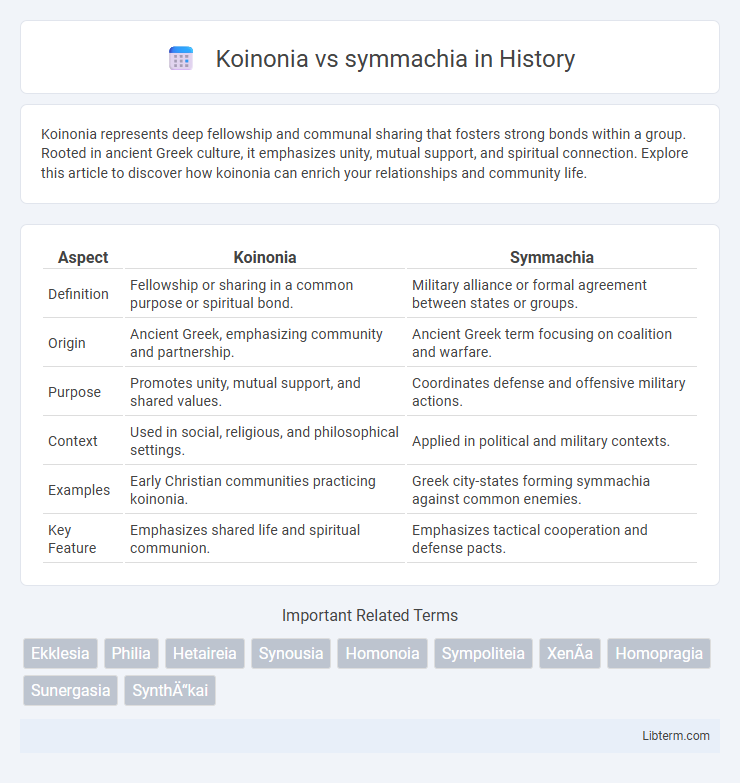
| Aspect | Koinonia | Symmachia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fellowship or sharing in a common purpose or spiritual bond. | Military alliance or formal agreement between states or groups. |
| Origin | Ancient Greek, emphasizing community and partnership. | Ancient Greek term focusing on coalition and warfare. |
| Purpose | Promotes unity, mutual support, and shared values. | Coordinates defense and offensive military actions. |
| Context | Used in social, religious, and philosophical settings. | Applied in political and military contexts. |
| Examples | Early Christian communities practicing koinonia. | Greek city-states forming symmachia against common enemies. |
| Key Feature | Emphasizes shared life and spiritual communion. | Emphasizes tactical cooperation and defense pacts. |
Introduction to Koinonia and Symmachia
Koinonia denotes deep fellowship and communal participation rooted in shared values and mutual support, often emphasizing spiritual unity within groups or communities. Symmachia refers to a strategic alliance or military coalition formed for common defense or mutual benefit, prioritizing practical cooperation over emotional or spiritual bonds. Understanding the distinction between koinonia's intimate relational aspect and symmachia's tactical partnership clarifies their roles in social and historical contexts.
Defining Koinonia: Meaning and Origins
Koinonia, a Greek term meaning fellowship or communion, originates from the New Testament, emphasizing deep relational unity and shared participation among members of a community. It reflects mutual support, spiritual partnership, and collective involvement in spiritual and social activities. Unlike symmachia, which denotes a strategic alliance or military coalition, koinonia centers on intimate, cooperative bonds fostering inclusivity and common purpose.
Understanding Symmachia: Concept and Context
Symmachia, originating from ancient Greek political thought, refers to a military alliance or coalition formed between city-states or nations for mutual defense and strategic cooperation. Unlike Koinonia, which emphasizes communal fellowship and shared spiritual or social bonds, Symmachia is primarily structured around pragmatic, external objectives such as defense pacts or wartime collaboration. Understanding Symmachia requires contextualizing it within the framework of geopolitical alliances where trust and obligation are formalized through treaties to ensure collective security.
Historical Background of Koinonia
Koinonia, rooted in ancient Greek culture, signifies fellowship and communal participation, reflecting shared spiritual and social bonds within early Christian communities. Its historical background highlights its role in fostering unity, mutual support, and collective worship among believers, contrasting with symmachia, which denotes military alliances or strategic coalitions. The development of koinonia emphasized relational depth and inclusive partnership, foundational for communal identity and cohesion in religious and social contexts.
Historical Development of Symmachia
Symmachia, a term rooted in ancient Greek political and military contexts, historically refers to formal alliances or coalitions between independent city-states for mutual defense and strategic cooperation, differing from Koinonia, which emphasizes shared participation and communal fellowship. The historical development of Symmachia began prominently during the Classical period of Greece, where city-states like Athens and Sparta forged such alliances to counter external threats such as Persian invasions. Over time, Symmachia evolved into complex federations influencing political dynamics and military strategies in the Hellenistic and Roman eras, shaping the nature of interstate relations through legally binding treaties and collective defense obligations.
Key Differences Between Koinonia and Symmachia
Koinonia refers to a deep fellowship or partnership characterized by shared values, spiritual unity, and mutual support, often seen in religious or communal contexts. Symmachia denotes a formal alliance or military coalition focused on mutual defense and strategic cooperation between distinct political or military entities. The key differences lie in koinonia's focus on relational and spiritual bonding, whereas symmachia centers on pragmatic, tactical collaboration for external protection.
Roles in Ancient Greek Society
Koinonia in Ancient Greek society referred to a communal partnership emphasizing shared resources and mutual responsibilities among citizens, fostering social cohesion and collective well-being. Symmachia represented a military alliance where city-states pooled armed forces for common defense or warfare, highlighting cooperation in strategic and protective roles. The distinction shaped societal roles, with koinonia promoting civic collaboration and symmachia concentrating on martial cooperation.
Examples of Koinonia and Symmachia in Practice
Koinonia exemplifies shared fellowship and mutual participation, as seen in early Christian communities where members contributed resources and supported each other's spiritual growth. Symmachia represents formal military alliances, such as the Delian League in ancient Greece, where city-states united for collective defense against common enemies. While Koinonia fosters deep communal bonds and collaboration, Symmachia emphasizes strategic cooperation for political or military objectives.
Lasting Influence on Modern Alliances
Koinonia emphasizes deep fellowship and shared purpose, fostering enduring trust and cooperation that shapes the foundation of lasting alliances worldwide. Symmachia, based on strategic military or political coalitions, influences modern alliances through formal agreements and collective defense mechanisms such as NATO. The interplay of koinonia's relational depth and symmachia's tactical cooperation defines the resilience and adaptability of contemporary international partnerships.
Conclusion: Relevance Today
Koinonia and symmachia represent distinct types of relationships in social and political contexts, with koinonia emphasizing deep fellowship and shared purpose, while symmachia centers on strategic alliances for mutual defense or advantage. In today's interconnected world, koinonia remains crucial for fostering community resilience and collaborative growth, promoting trust and long-term solidarity. Symmachia is relevant in international relations and organizational partnerships, where temporary coalitions address specific challenges without the need for profound unity.
Koinonia Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com