The Annales School revolutionized historical research by emphasizing long-term social, economic, and cultural factors over traditional political narratives. Its interdisciplinary approach integrates geography, sociology, and economics to uncover deeper patterns in history. Discover how this innovative perspective reshapes your understanding of historical events in the full article.
Table of Comparison
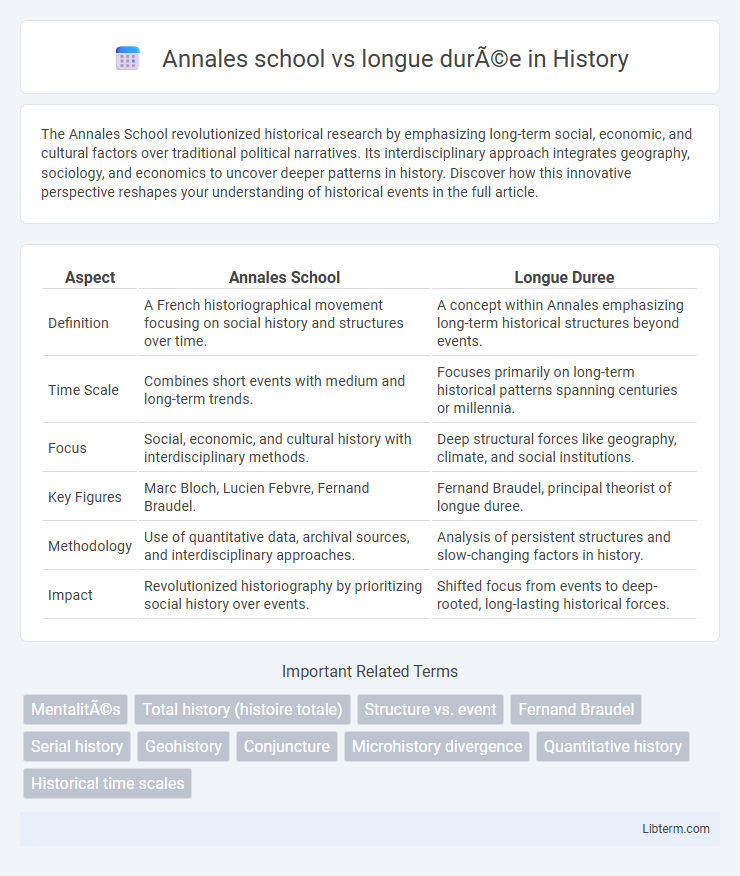
| Aspect | Annales School | Longue Duree |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A French historiographical movement focusing on social history and structures over time. | A concept within Annales emphasizing long-term historical structures beyond events. |
| Time Scale | Combines short events with medium and long-term trends. | Focuses primarily on long-term historical patterns spanning centuries or millennia. |
| Focus | Social, economic, and cultural history with interdisciplinary methods. | Deep structural forces like geography, climate, and social institutions. |
| Key Figures | Marc Bloch, Lucien Febvre, Fernand Braudel. | Fernand Braudel, principal theorist of longue duree. |
| Methodology | Use of quantitative data, archival sources, and interdisciplinary approaches. | Analysis of persistent structures and slow-changing factors in history. |
| Impact | Revolutionized historiography by prioritizing social history over events. | Shifted focus from events to deep-rooted, long-lasting historical forces. |
Introduction to the Annales School
The Annales School revolutionized historical methodology by emphasizing long-term social, economic, and environmental structures over traditional event-focused narratives. This approach prioritizes the longue duree, analyzing deep temporal frameworks to reveal persistent patterns and forces shaping human history. Key figures like Marc Bloch and Fernand Braudel pioneered these techniques, advocating for interdisciplinary methods integrating geography, sociology, and economics.
Origins and Evolution of Longue Durée
The Longue Duree concept, central to the Annales School, originated in the early 20th century with historians like Marc Bloch and Lucien Febvre who emphasized long-term social structures over episodic events. Fernand Braudel further evolved this framework by distinguishing between three temporalities: the short-term events, the medium-term conjunctures, and the enduring structures that shape history over centuries. This analytical shift redirected historical study from political narratives to sustained economic, environmental, and social factors, fundamentally transforming historiography.
Key Figures in the Annales School
The Annales School, founded by historians Marc Bloch and Lucien Febvre in 1929, revolutionized historical methodology by emphasizing the longue duree, or long-term social history, over traditional event-based narratives. Fernand Braudel, a pivotal figure in this school, further developed the longue duree concept, analyzing geographical, social, and economic structures spanning centuries. The Annales School's key figures collectively shifted historical focus from political events to deep social structures, shaping modern historiography.
Defining the Concept of Longue Durée
The Annales School pioneered the concept of longue duree, emphasizing long-term historical structures over fleeting events or individual actions. Longue duree focuses on enduring social, economic, and environmental factors, shaping history across centuries rather than decades. This approach revolutionized historiography by prioritizing deep temporal analysis and structural continuity in the study of historical processes.
Methodological Approaches of the Annales Historians
Annales historians pioneered a methodological approach emphasizing the longue duree, focusing on long-term social, economic, and environmental structures over transient events. Their use of interdisciplinary tools from geography, sociology, and anthropology allowed for a holistic analysis of historical processes spanning centuries. This approach contrasted with traditional history by de-emphasizing political narratives and privileging underlying patterns shaping human societies.
Comparing Structural History and Event-Focused Narratives
The Annales School emphasizes structural history by analyzing long-term social, economic, and environmental factors shaping historical contexts, contrasting sharply with event-focused narratives that prioritize discrete political or military events. Structural history examines enduring patterns and deep-rooted causes over centuries, while event-focused approaches highlight individual actions and short-term consequences. This methodological divergence underlines the Annales priority on the longue duree as a framework to understand historical processes beyond momentary occurrences.
Influence of Geography and Social Structures
The Annales School emphasizes the impact of geographical factors such as climate, terrain, and natural resources in shaping long-term social structures and historical developments. It advocates for the study of the longue duree, analyzing persistent social, economic, and environmental frameworks over centuries rather than isolated events. This approach highlights how enduring geographical conditions influence demographic patterns, settlement forms, and power relations within societies.
Critiques and Debates on Longue Durée
The Annales School pioneered the concept of longue duree, emphasizing long-term structural analysis in history, but critics argue it risks overlooking short-term events and individual agency. Debates center on whether this approach marginalizes pivotal historical moments and socio-political complexities by privileging slow-changing geographical or economic factors. Scholars also question its applicability across diverse historical contexts, calling for a balance between longue duree and event-focused methodologies to capture a fuller historical narrative.
Impact of the Annales School on Modern Historiography
The Annales School revolutionized modern historiography by emphasizing long-term social, economic, and geographic structures over short-term political events, introducing the concept of longue duree as a framework for understanding historical continuity and change. This approach broadened historical analysis to incorporate interdisciplinary methods from geography, sociology, and economics, shifting focus from individual actors to broader societal forces. Its impact endures in contemporary historiography through the prioritization of structural factors and the integration of diverse sources to reconstruct deeper historical processes.
Legacy and Future Directions in Historical Analysis
The Annales School revolutionized historical analysis by emphasizing long-term social, economic, and geographical structures over political events, pioneering the concept of longue duree as a methodological framework. Its legacy endures in interdisciplinary approaches that integrate anthropology, sociology, and geography, fostering a holistic understanding of historical processes. Future directions in historical analysis build on the longue duree by incorporating digital humanities and big data analytics to uncover deep temporal patterns and transform macrohistory studies.
Annales school Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com