Ambilineality refers to a kinship system in which individuals can choose to affiliate with either their mother's or father's lineage, allowing flexible social identity and inheritance patterns. This system influences family ties, property rights, and cultural traditions, often reflecting the unique social dynamics within communities. Explore the rest of the article to understand how ambilineality shapes social structures and affects your perspective on lineage.
Table of Comparison
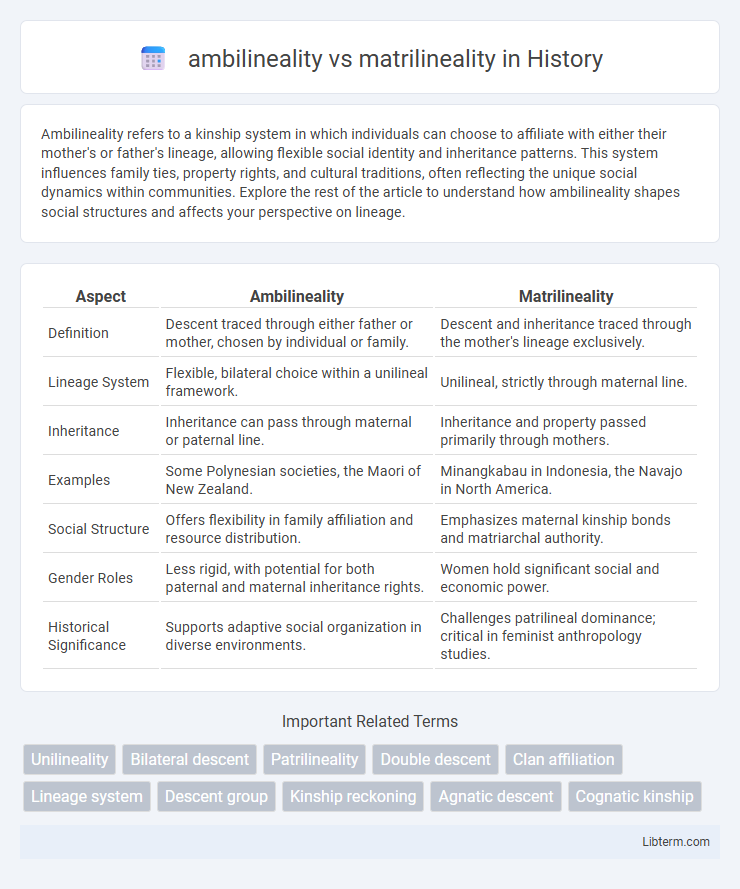
| Aspect | Ambilineality | Matrilineality |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Descent traced through either father or mother, chosen by individual or family. | Descent and inheritance traced through the mother's lineage exclusively. |
| Lineage System | Flexible, bilateral choice within a unilineal framework. | Unilineal, strictly through maternal line. |
| Inheritance | Inheritance can pass through maternal or paternal line. | Inheritance and property passed primarily through mothers. |
| Examples | Some Polynesian societies, the Maori of New Zealand. | Minangkabau in Indonesia, the Navajo in North America. |
| Social Structure | Offers flexibility in family affiliation and resource distribution. | Emphasizes maternal kinship bonds and matriarchal authority. |
| Gender Roles | Less rigid, with potential for both paternal and maternal inheritance rights. | Women hold significant social and economic power. |
| Historical Significance | Supports adaptive social organization in diverse environments. | Challenges patrilineal dominance; critical in feminist anthropology studies. |
Introduction to Lineage Systems
Lineage systems determine how descent and inheritance are traced within a society, significantly influencing social structure and kinship roles. Ambilineality allows individuals to affiliate with either the mother's or father's lineage, providing flexibility in heritage and membership, whereas matrilineality strictly traces descent through the mother's line, emphasizing maternal ancestry in inheritance and social identity. Understanding these systems reveals distinct cultural patterns in property rights, familial responsibilities, and lineage continuity across societies.
Defining Ambilineality
Ambilineality is a kinship system where individuals trace their descent through either the maternal or paternal line, allowing flexibility in lineage affiliation based on personal or social choice. This contrasts with matrilineality, which strictly follows descent through the female line, emphasizing inheritance and social identity from the mother's lineage. Ambilineal descent systems enable members to select the lineage that best suits their social, economic, or cultural circumstances, unlike matrilineal systems which maintain a fixed lineage path.
Understanding Matrilineality
Matrilineality is a system of lineage tracing where descent and inheritance are passed through the mother's line, shaping social structure and family ties. Unlike ambilineality, which allows individuals to choose descent from either maternal or paternal lines, matrilineality strictly emphasizes maternal ancestry for defining kinship and property rights. Understanding matrilineality reveals how cultural values prioritize female lineage in inheritance, residence, and identity formation across various societies.
Key Differences Between Ambilineality and Matrilineality
Ambilineality allows individuals to trace descent through either the paternal or maternal line, providing flexibility in inheritance and kinship recognition based on personal or cultural choice. Matrilineality specifically emphasizes lineage traced exclusively through the mother's side, impacting inheritance, social status, and clan membership within societies that practice this system. The primary difference lies in ambilineality's bilateral descent options versus matrilineality's strict unilineal descent through women.
Cultural Examples of Ambilineal Societies
Ambilineality refers to a kinship system where individuals can trace descent through either the mother's or the father's lineage, allowing flexible inheritance and social affiliation. Cultural examples of ambilineal societies include the Maori of New Zealand, who pass land rights and names through both maternal and paternal lines, and the Nuer of South Sudan, who choose lineage based on social and economic advantages. This contrasts with matrilineality, where descent is strictly traced through the mother's line, as seen in the Minangkabau of Indonesia, emphasizing female lineage for inheritance and clan identity.
Societies Practicing Matrilineality
Societies practicing matrilineality trace descent and inheritance through the female line, emphasizing the importance of maternal relatives in social organization and property rights. Common examples include the Minangkabau of Indonesia and the Khasi of India, where lineage and clan membership are determined by the mother's side. Matrilineal systems often correlate with higher status for women in familial decision-making and cultural roles.
Social Implications of Lineage Descent
Ambilineality allows individuals to choose lineage affiliation, fostering flexibility in inheritance and social identity, which can lead to more fluid family alliances and resource distribution. Matrilineality, by tracing descent through the mother's line, often enhances female clan authority and inheritance rights, strengthening women's social status and group solidarity. These differing systems profoundly shape power dynamics, gender roles, and community cohesion within societies.
Inheritance Patterns in Ambilineal and Matrilineal Systems
Inheritance patterns in ambilineal systems allow individuals to trace descent through either the paternal or maternal line, often providing greater flexibility in property and status transmission. In contrast, matrilineal systems strictly follow the maternal lineage, ensuring inheritance passes primarily through female ancestors, which can affect land, titles, and kinship roles. These differing frameworks influence social organization and resource distribution in evolutionary and ethnographic contexts.
Impact on Gender Roles and Family Structure
Ambilineality allows individuals to choose lineage affiliation, which can create more fluid gender roles and diversify family structures by blending paternal and maternal heritage. Matrilineality emphasizes descent through the female line, often granting women greater authority in inheritance and familial decision-making, reinforcing matriarchal roles within the family. Both systems shape social organization differently, influencing inheritance patterns, residence norms, and gender-based responsibilities.
Modern Perspectives and Future Trends
Ambilineality offers flexible kinship identification, allowing individuals to affiliate with either maternal or paternal descent lines based on social and economic advantages, distinguishing it from the fixed lineage of matrilineality. Modern perspectives emphasize ambilineality's adaptability in increasingly globalized and urbanized societies where diverse family structures challenge traditional matrilineal systems. Future trends suggest a growing preference for ambilineal descent frameworks, accommodating fluid identities and enhancing inclusivity in inheritance, residence patterns, and cultural continuity amid changing societal norms.
ambilineality Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com