A conscript is an individual who is compulsorily enlisted into military service, typically through a government-mandated draft system. This process ensures that armed forces maintain necessary troop levels during times of conflict or national emergency. Discover how conscription affects your country's military readiness and personal freedoms by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
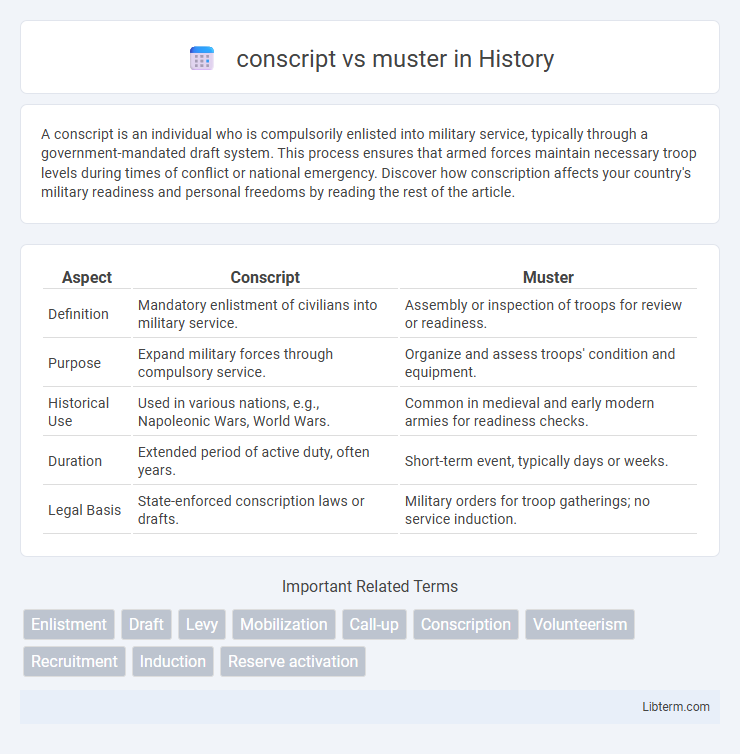
| Aspect | Conscript | Muster |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Mandatory enlistment of civilians into military service. | Assembly or inspection of troops for review or readiness. |
| Purpose | Expand military forces through compulsory service. | Organize and assess troops' condition and equipment. |
| Historical Use | Used in various nations, e.g., Napoleonic Wars, World Wars. | Common in medieval and early modern armies for readiness checks. |
| Duration | Extended period of active duty, often years. | Short-term event, typically days or weeks. |
| Legal Basis | State-enforced conscription laws or drafts. | Military orders for troop gatherings; no service induction. |
Introduction to Conscript and Muster
Conscript refers to a person who is compulsorily enrolled for military service, often during wartime or national emergencies. Muster involves the assembly of troops for inspection, roll call, or preparation before deployment or training. Understanding the distinction is essential for grasping military organization and personnel management.
Definition of Conscript
A conscript is an individual who is compulsorily enrolled in the armed forces by law, often during wartime or national emergencies. Unlike a muster, which refers to the assembly or inspection of troops, conscription mandates military service through governmental authority. This legal requirement aims to ensure adequate military personnel to meet defense needs.
Definition of Muster
Muster refers to the formal assembly of troops for inspection, roll call, or preparation for duty, ensuring organization and readiness within a military unit. Unlike conscription, which involves the compulsory enlistment of individuals into service, muster emphasizes gathering and accountability of already enlisted personnel. This process is critical for maintaining discipline, verifying presence, and coordinating military operations effectively.
Historical Background of Conscription
Conscription, historically known as the draft, originated in ancient societies such as Sparta and Rome where citizens were obligated to serve in the military to defend their city-states. Unlike muster, which typically refers to the assembly or inspection of troops, conscription involves the compulsory enlistment of individuals into national service, often during periods of war or national emergency. The evolution of conscription reflects changing military needs and social structures, becoming institutionalized in many modern states by the 19th and 20th centuries to maintain standing armies.
Historical Background of Mustering
Mustering historically refers to the assembly and inspection of troops, a practice dating back to medieval Europe where knights and soldiers were gathered to ensure readiness for battle. This medieval tradition evolved through feudal systems for organizing levies and later for colonial militias, emphasizing periodic reviews rather than compulsory enlistment. Unlike conscription, which mandates individuals to serve, mustering focused on verifying the preparedness and equipment of already enlisted or volunteer forces.
Legal Differences Between Conscript and Muster
Conscription is a legal mandate requiring eligible individuals to serve in the military, enacted through formal government laws and enforceable by penalties for non-compliance, whereas a muster is an administrative procedure involving the assembly and inspection of troops without compulsory enlistment authority. Conscript status obligates individuals under national defense laws, often accompanied by defined terms of service and rights, while muster serves as a readiness or accountability check within existing military or militia units. Legal frameworks for conscription include specific statutes and regulations that outline eligibility, exemptions, and enforcement, whereas muster operates under military regulations focused on organization and troop management rather than mandatory service.
Process and Procedures: Conscript vs Muster
The conscription process involves mandatory enrollment of individuals into military service through official government orders, requiring thorough documentation, medical examinations, and training schedules to ensure readiness. In contrast, a muster is a systematic procedure of assembling and accounting for personnel, typically for inspection, roll call, or readiness assessment, emphasizing verification of presence rather than formal enrollment. While conscription initiates service commitments, musters monitor active personnel status and operational preparedness.
Impact on Military Organization
Conscription enforces mandatory enlistment, significantly expanding military personnel and ensuring a steady supply of troops, which enhances overall military readiness and organizational strength. Muster involves assembling existing forces for inspection or duty, serving as a tool for organizational control and rapid deployment rather than increasing manpower. The impact of conscription on military organization is profound through long-term force expansion, while muster primarily influences short-term operational efficiency and unit cohesion.
Societal Perceptions of Conscription and Mustering
Conscription often carries negative societal perceptions, with many viewing it as an infringement on personal freedom and a source of social tension. Mustering is generally perceived as a voluntary or community-driven mobilization effort, fostering a sense of collective responsibility and civic duty. Public opinion favors mustering for its emphasis on choice and local engagement, while conscription faces criticism for compulsory service and potential impacts on individual rights.
Conclusion: Conscript vs Muster Compared
Conscript and muster both involve military personnel recruitment but differ fundamentally in approach and scope. Conscription is a compulsory enlistment mandated by the government, often targeting all eligible citizens for service during a specific period, ensuring a steady supply of troops. Muster refers to the assembly or inspection of troops, focusing on organizing and verifying manpower rather than the recruitment process itself.
conscript Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com