The Lombards were a Germanic people who ruled large parts of Italy from the 6th to 8th centuries, significantly shaping the region's cultural and political landscape. Their legacy includes influencing Italian law, architecture, and the foundation of early medieval European kingdoms. Discover more about the Lombards' impact on history and their enduring contributions in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
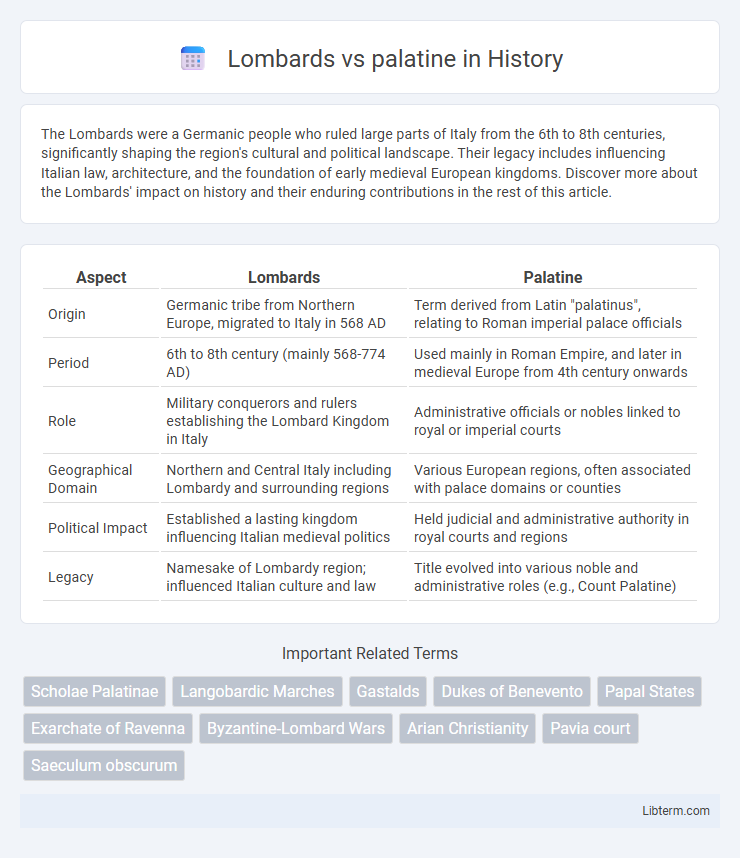
| Aspect | Lombards | Palatine |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Germanic tribe from Northern Europe, migrated to Italy in 568 AD | Term derived from Latin "palatinus", relating to Roman imperial palace officials |
| Period | 6th to 8th century (mainly 568-774 AD) | Used mainly in Roman Empire, and later in medieval Europe from 4th century onwards |
| Role | Military conquerors and rulers establishing the Lombard Kingdom in Italy | Administrative officials or nobles linked to royal or imperial courts |
| Geographical Domain | Northern and Central Italy including Lombardy and surrounding regions | Various European regions, often associated with palace domains or counties |
| Political Impact | Established a lasting kingdom influencing Italian medieval politics | Held judicial and administrative authority in royal courts and regions |
| Legacy | Namesake of Lombardy region; influenced Italian culture and law | Title evolved into various noble and administrative roles (e.g., Count Palatine) |
Introduction to the Lombards and Palatine
The Lombards, a Germanic tribe originating in Scandinavia, migrated to Italy in the 6th century, establishing a powerful kingdom that significantly influenced medieval European politics and culture. The Palatine refers to the Palatine Hill in Rome, a central area historically significant as the birthplace of Rome and the residence of emperors and aristocrats, symbolizing imperial authority and prestige. Understanding the Lombards alongside the Palatine context highlights the contrast between a migrating warrior kingdom and the established center of Roman imperial power.
Historical Origins of the Lombards
The Lombards originated as a Germanic tribe that migrated from Scandinavia into the Roman Empire during the early Middle Ages, establishing a kingdom in Northern Italy by the 6th century. Their name, derived from "Longobardi," indicates "long beards," highlighting their distinct cultural identity. In contrast, the Palatine refers to a title or region linked to administrative authority in the medieval Holy Roman Empire, unrelated to the ethnic and migratory origins of the Lombards.
The Rise of the Palatine Group
The rise of the Palatine Group marked a significant shift in Lombard power dynamics during the early medieval period, characterized by their strategic consolidation of territories and influence within the Frankish Kingdom. Leveraging royal favor and military prowess, the Palatine Group expanded their control over key regions in northern Italy, eclipsing traditional Lombard nobility. Their ascendancy facilitated the integration of Lombard legal and administrative structures into the evolving Carolingian Empire, reshaping political authority in early medieval Europe.
Geographic and Cultural Differences
The Lombards, originating from Northern Italy, established a kingdom primarily across the Po Valley and parts of modern-day Lombardy, exhibiting strong Germanic cultural influences merged with Latin traditions. In contrast, the Palatines, originating from the Rhineland region, were known for their migration to various parts of Central Europe and America, carrying a distinct Germanic culture influenced by their proximity to French and Dutch populations. Geographic settlement shaped their cultural identities, with Lombards integrating Roman customs in Italy, while Palatines maintained a diversified culture influenced by multiple European regions during their migrations.
Political Structures and Influence
The Lombards established a hierarchical political structure centered around autonomous duchies governed by dukes who owed allegiance to a king, enabling decentralized control while maintaining overall unity. In contrast, the Palatine system was characterized by a more centralized authority, where Palatines held imperial or royal powers, often acting as the emperor's or king's representatives with judicial and administrative functions. The Lombard model influenced the development of early medieval European governance through its feudal decentralization, whereas the Palatine institutions shaped imperial administration and regional governance within the Holy Roman Empire.
Key Figures Among Lombards and Palatine
Key figures among the Lombards include King Alboin, who led the invasion of Italy in 568 AD and established the Lombard Kingdom, and Queen Theodelinda, instrumental in promoting Christianity and political stability. The Palatine group was marked by influential figures such as Emperor Otto I, who strengthened the Holy Roman Empire's control over the Palatinate region, and Count Palatine Siegfried, often credited with founding the County Palatine of the Rhine. These leaders shaped the political and cultural landscapes of their respective realms during the early medieval period.
Military Strategies and Conflicts
The Lombards employed swift cavalry maneuvers and fortified hilltop positions to counter the Palatine forces, who favored heavy infantry formations and strategic use of natural terrain for defense. Significant conflicts such as the 7th-century battles around Pavia showcased the Lombards' adaptability in guerrilla tactics against the Palatine's disciplined phalanx-like units. These military strategies reflect the broader warfare evolution during the early medieval period in Italy, highlighting contrasting approaches to mobility and fortification.
Economic Systems and Trade Practices
The Lombards established a robust economic system centered on agriculture, craftsmanship, and control of key trade routes across Northern Italy, facilitating the growth of market towns and fostering a currency-based economy. In contrast, the Palatine economy, tied closely to royal estates and imperial administration, emphasized centralized resource management and redistribution through feudal obligations, limiting widespread commercial activity. Trade practices under the Lombards featured expanded merchant networks and increased use of coinage, while the Palatine system relied more on localized exchanges and barter within aristocratic estates.
Legacy and Impact on European History
The Lombards established a foundation for medieval Italy's political landscape, influencing the region's cultural and legal development through their codification of laws and the establishment of duchies that later integrated into the Holy Roman Empire. The Palatines, particularly those in the Holy Roman Empire, served as key administrative and judicial authorities, shaping the governance structure and contributing to the centralization of power in medieval Europe. Both groups left enduring legacies in the form of territorial organization, feudal practices, and the evolution of European medieval statehood.
Conclusion: Lombards vs Palatine in Retrospect
The Lombards and Palatine represent distinct historical entities with unique cultural, social, and political impacts in medieval Europe. The Lombards, a Germanic people, significantly influenced the Italian Peninsula's formation through their kingdom's establishment and interactions with the Papacy, while the Palatine refers mainly to territorial jurisdictions or noble titles with administrative importance in the Holy Roman Empire. Evaluating their legacies reveals the Lombards' direct role in shaping regional power dynamics, whereas the Palatine embodied decentralized governance and noble authority within imperial structures.
Lombards Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com