Epigraphy is the study of inscriptions or epigraphs engraved on durable materials like stone, metal, or pottery, providing valuable historical and linguistic insights. This field helps decode ancient languages, understand cultural practices, and preserve records of past civilizations. Explore the rest of the article to uncover how epigraphy reveals secrets etched in time and enriches your understanding of human history.
Table of Comparison
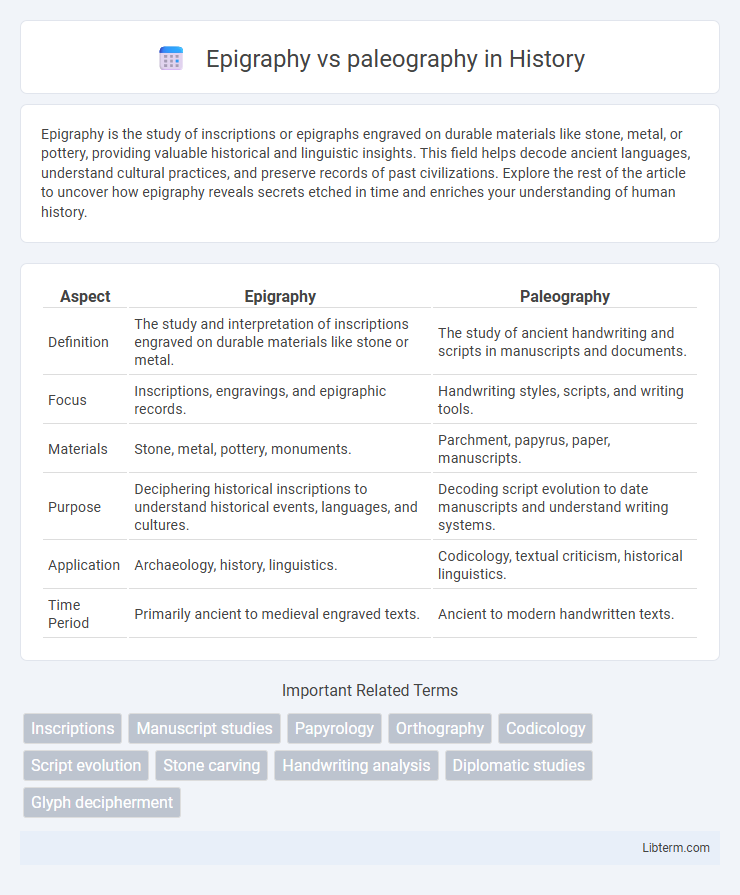
| Aspect | Epigraphy | Paleography |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The study and interpretation of inscriptions engraved on durable materials like stone or metal. | The study of ancient handwriting and scripts in manuscripts and documents. |
| Focus | Inscriptions, engravings, and epigraphic records. | Handwriting styles, scripts, and writing tools. |
| Materials | Stone, metal, pottery, monuments. | Parchment, papyrus, paper, manuscripts. |
| Purpose | Deciphering historical inscriptions to understand historical events, languages, and cultures. | Decoding script evolution to date manuscripts and understand writing systems. |
| Application | Archaeology, history, linguistics. | Codicology, textual criticism, historical linguistics. |
| Time Period | Primarily ancient to medieval engraved texts. | Ancient to modern handwritten texts. |
Introduction to Epigraphy and Paleography
Epigraphy studies ancient inscriptions engraved on durable materials like stone or metal, providing direct evidence of historical languages, cultures, and events. Paleography analyzes handwritten manuscripts and documents to understand the evolution of scripts, handwriting styles, and the context of textual transmission over time. Both disciplines are essential for reconstructing historical knowledge but differ in their sources and methods.
Defining Epigraphy: Scope and Significance
Epigraphy is the study of inscriptions or epigraphs engraved on durable materials such as stone, metal, or pottery, essential for understanding ancient languages, cultures, and historical events. It encompasses the analysis of the content, context, and form of inscriptions, revealing insights into social, political, and religious practices of past civilizations. Unlike paleography, which focuses primarily on the handwriting and script evolution in manuscripts, epigraphy emphasizes the physical and material aspects of inscriptions, making it critical for archaeological and historical research.
What Is Paleography? Overview and Importance
Paleography is the study of ancient handwriting and scripts to decipher, date, and contextualize historical documents. It plays a crucial role in understanding cultural, linguistic, and historical developments by analyzing the evolution of writing styles across different periods and regions. Mastery of paleography enables accurate interpretation of manuscripts, inscriptions, and archival records, contributing significantly to historical research and preservation.
Key Differences Between Epigraphy and Paleography
Epigraphy studies ancient inscriptions engraved on durable materials like stone, metal, or pottery, focusing on deciphering, dating, and interpreting texts to understand historical contexts. Paleography analyzes ancient handwriting on manuscripts and documents, emphasizing the evolution of script styles and writing techniques across different time periods. Key differences include their sources--inscriptions versus manuscripts--and their primary methods, with epigraphy dealing primarily with fixed texts and paleography concentrating on script analysis and manuscript dating.
Methodologies in Epigraphic Studies
Methodologies in epigraphic studies emphasize the systematic analysis of inscriptions, including detailed examination of letterforms, material context, and inscription techniques to establish authenticity and historical significance. Digital imaging technologies, such as 3D scanning and Reflectance Transformation Imaging (RTI), enhance epigraphers' ability to capture surface details and reveal eroded texts. Comparative analysis with paleographic data helps refine dating and stylistic attribution, distinguishing epigraphy's focus on inscriptions from paleography's broader study of ancient handwriting and manuscripts.
Techniques Used in Paleographic Analysis
Paleographic analysis employs techniques such as examining handwriting styles, letter forms, and ink composition to date manuscripts and understand historical writing practices. It involves detailed scrutiny of script types like uncial, minuscule, or cursive, alongside the material of writing surfaces, including parchment or papyrus. These methods provide crucial insights into cultural and chronological contexts that differentiate paleography from epigraphy, which primarily focuses on inscriptions on durable materials.
Major Applications of Epigraphy
Epigraphy primarily involves the study and interpretation of inscriptions on durable materials such as stone, metal, or pottery, serving as a critical tool for deciphering ancient languages, legal codes, and historical events. It plays a major role in archaeology, providing primary data for dating monuments and understanding socio-political structures of past civilizations. Epigraphy also supports linguistics and cultural studies by offering direct evidence of writing systems, official decrees, and religious practices etched in antiquity.
Practical Uses of Paleography Today
Paleography plays a crucial role in authenticating and dating historical manuscripts, enabling accurate interpretation of ancient texts and documents. It assists archivists and historians in deciphering handwriting styles, scripts, and abbreviations used across different periods and regions. Practical applications of paleography extend to preserving cultural heritage, facilitating genealogical research, and supporting legal investigations involving historical records.
Challenges in Epigraphy and Paleography
Epigraphy faces challenges such as weathering and erosion of inscriptions, inconsistent ancient scripts, and difficulties in dating texts accurately without contextual clues. Paleography struggles with deciphering handwriting variations, identifying regional script styles, and dealing with incomplete or damaged manuscripts that hinder precise interpretation. Both fields require advanced analytical techniques and interdisciplinary collaboration to overcome problems related to preservation, legibility, and historical context.
Future Trends in Epigraphy and Paleography Research
Emerging technologies such as multispectral imaging and artificial intelligence are transforming epigraphy and paleography by enhancing the accuracy of text restoration and decipherment. Digital databases and machine learning algorithms enable large-scale analysis of inscriptions and manuscripts, facilitating new discoveries and comparative studies. Collaborative platforms and 3D modeling are increasingly used to preserve and share epigraphic and paleographic artifacts, ensuring broader accessibility and interdisciplinary research advancements.
Epigraphy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com