Textual criticism examines ancient manuscripts to identify and correct errors introduced over time, ensuring the accuracy of historical texts. Scholars compare multiple versions to reconstruct the original wording as closely as possible. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your understanding of how textual criticism preserves literary heritage.
Table of Comparison
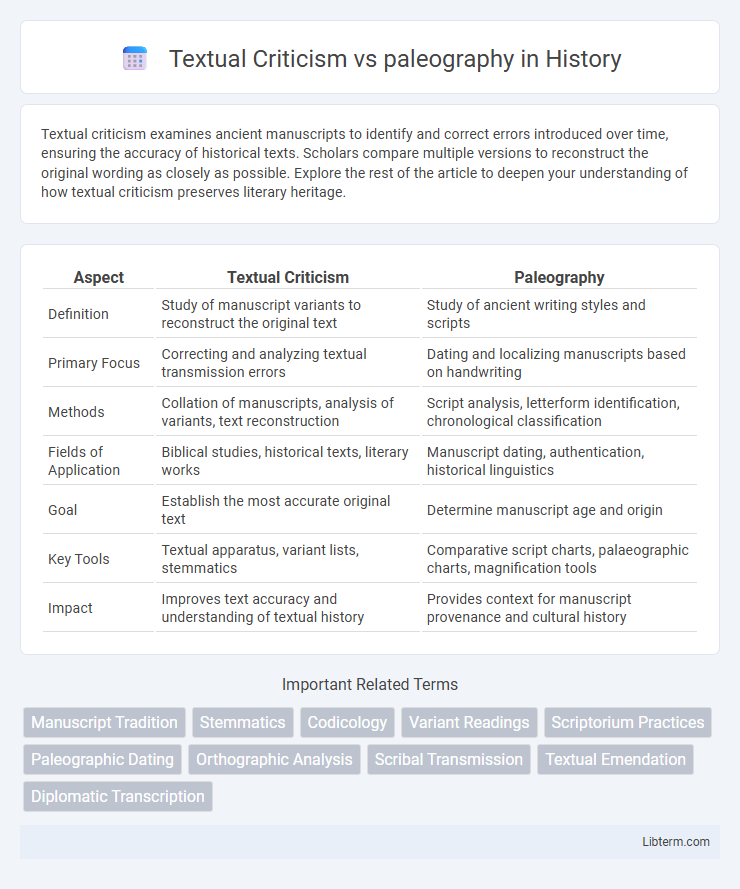
| Aspect | Textual Criticism | Paleography |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of manuscript variants to reconstruct the original text | Study of ancient writing styles and scripts |
| Primary Focus | Correcting and analyzing textual transmission errors | Dating and localizing manuscripts based on handwriting |
| Methods | Collation of manuscripts, analysis of variants, text reconstruction | Script analysis, letterform identification, chronological classification |
| Fields of Application | Biblical studies, historical texts, literary works | Manuscript dating, authentication, historical linguistics |
| Goal | Establish the most accurate original text | Determine manuscript age and origin |
| Key Tools | Textual apparatus, variant lists, stemmatics | Comparative script charts, palaeographic charts, magnification tools |
| Impact | Improves text accuracy and understanding of textual history | Provides context for manuscript provenance and cultural history |
Introduction to Textual Criticism and Paleography
Textual criticism involves analyzing and comparing manuscript variants to reconstruct original texts, focusing on identifying scribal errors and transmission history. Paleography studies ancient handwriting styles, scripts, and the dating of manuscripts based on letter formation and writing materials. Both disciplines are essential for understanding historical documents, with textual criticism focusing on content accuracy and paleography emphasizing the physical characteristics and chronological context of manuscripts.
Defining Textual Criticism: Goals and Methods
Textual criticism involves analyzing and comparing manuscript variants to reconstruct the most accurate version of a text, aiming to identify errors introduced through copying processes. It employs methods such as collation, stemmatics, and conjectural emendation to evaluate textual evidence from different sources. Paleography complements this by studying ancient handwriting styles and scripts to date and authenticate manuscripts, providing critical context for textual critics.
Understanding Paleography: History and Techniques
Paleography studies ancient handwriting styles to date and authenticate manuscripts, tracing the evolution of scripts from antiquity to the modern era. It employs techniques such as analyzing letter forms, ink composition, and writing materials to reconstruct historical contexts and scribal practices. Understanding paleography enhances textual criticism by providing critical insights into the physical origins and transmission of texts.
Key Differences Between Textual Criticism and Paleography
Textual criticism analyzes manuscript variants to reconstruct original texts, emphasizing the evaluation of scribal errors and transmission history. Paleography studies ancient handwriting styles, dating and localizing manuscripts based on script characteristics and material evidence. The key difference lies in textual criticism's focus on textual content and transmission fidelity, while paleography centers on the physical script and historical context of the manuscript production.
Overlapping Areas: How Both Fields Complement Each Other
Textual criticism and paleography intersect significantly in the analysis of ancient manuscripts, where understanding handwriting styles enhances the dating and authentication of texts crucial for textual variants assessment. Both fields contribute to reconstructing original texts by combining paleographic dating methods with textual variant comparisons, ensuring a more accurate historical context. Their complementary expertise allows scholars to verify manuscript provenance and establish reliable text transmission histories, critical for biblical, classical, and medieval studies.
Tools and Technologies Used in Textual Criticism
Textual criticism employs advanced tools such as digital collation software, multispectral imaging, and computational algorithms to analyze manuscript variants and reconstruct original texts. These technologies enable precise comparison of text fragments, identification of scribal errors, and restoration of corrupted passages. Unlike paleography, which primarily uses visual analysis of handwriting styles to date and localize manuscripts, textual criticism leverages digital databases and machine learning to systematically evaluate textual transmission history.
Paleographic Methods for Manuscript Dating and Analysis
Paleographic methods for manuscript dating and analysis involve examining handwriting styles, ink composition, and parchment or paper characteristics to establish the historical context of a document. By comparing script forms with well-dated samples, paleographers can estimate the manuscript's creation period, often narrowing it down to specific centuries or decades. These techniques provide critical evidence for reconstructing the authenticity and provenance of ancient texts, complementing textual criticism which focuses primarily on content variations and transmission history.
Case Studies: Applying Textual Criticism vs. Paleographic Approaches
Case studies in textual criticism reveal how scholars meticulously analyze manuscript variants to reconstruct original texts, emphasizing linguistic patterns and scribal errors. Paleographic approaches focus on dating and authenticating manuscripts by examining handwriting styles, material composition, and ink characteristics, providing essential historical context. Comparing these methods highlights that textual criticism prioritizes textual accuracy while paleography offers critical insights into the manuscript's provenance and chronology.
Challenges and Limitations in Both Disciplines
Textual criticism and paleography face inherent challenges, such as the limited availability of original manuscripts and the variability in handwriting styles over centuries, complicating accurate textual reconstruction and dating. Both disciplines encounter limitations due to the subjective interpretation of scribal errors, marginalia, and deteriorated materials, which can affect the reliability of historical analysis. Furthermore, technological constraints and the incomplete provenance of documents hinder definitive conclusions in establishing authoritative texts or precise chronological frameworks.
The Future of Textual Criticism and Paleography in Digital Humanities
The future of textual criticism and paleography in digital humanities centers on advanced computational tools that enhance manuscript analysis and textual reconstruction. Machine learning algorithms and digital imaging techniques enable more precise identification of scribal hands, textual variants, and historical annotations, which revolutionize manuscript studies. Integration of these technologies fosters collaborative platforms that facilitate global access, preservation, and interactive scholarly research.
Textual Criticism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com