Centurion was a professional officer in the Roman army, commanding a company of soldiers called a century, typically consisting of 80 men. Known for their strict discipline, leadership, and battlefield experience, centurions played a crucial role in maintaining order and effectiveness within the legions. Discover how the legacy of the centurion continues to influence modern military leadership by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
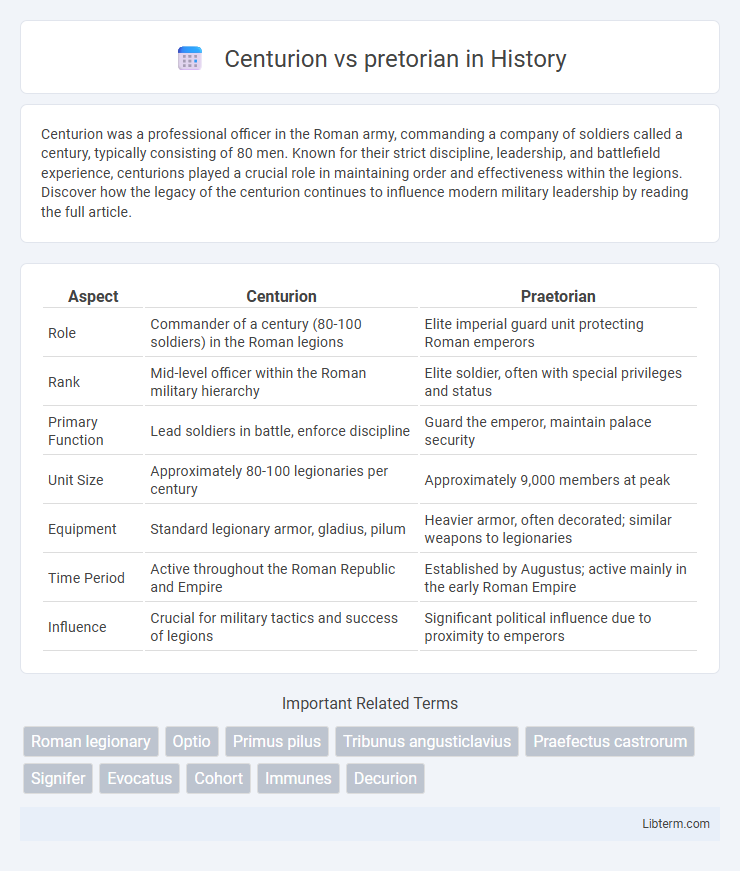
| Aspect | Centurion | Praetorian |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Commander of a century (80-100 soldiers) in the Roman legions | Elite imperial guard unit protecting Roman emperors |
| Rank | Mid-level officer within the Roman military hierarchy | Elite soldier, often with special privileges and status |
| Primary Function | Lead soldiers in battle, enforce discipline | Guard the emperor, maintain palace security |
| Unit Size | Approximately 80-100 legionaries per century | Approximately 9,000 members at peak |
| Equipment | Standard legionary armor, gladius, pilum | Heavier armor, often decorated; similar weapons to legionaries |
| Time Period | Active throughout the Roman Republic and Empire | Established by Augustus; active mainly in the early Roman Empire |
| Influence | Crucial for military tactics and success of legions | Significant political influence due to proximity to emperors |
Introduction to Centurions and Pretorians
Centurions were key officers in the Roman army responsible for commanding centuries of about 80 men, ensuring discipline and tactical effectiveness on the battlefield. Pretorians served as elite guards of the Roman emperor, forming the Praetorian Guard, which held significant political influence and specialized in palace security and swift military response. Both roles were vital in maintaining the structure and power of the Roman military system during the empire's expansion.
Historical Origins: Centurions vs Pretorians
Centurions originated as experienced officers within the Roman legions, commanding units of roughly 80 soldiers and serving as the backbone of military discipline and tactics from the Republic through the Empire. Pretorians, or Praetorian Guards, were elite soldiers established under Augustus to act as personal protectors of the Roman emperor and as a powerful political force within the capital. While Centurions maintained order and effectiveness in the field, Pretorians combined military roles with political influence, shaping imperial power dynamics in ancient Rome.
Roles and Responsibilities in the Roman Army
Centurions served as professional officers commanding a century, typically 80 legionaries, responsible for training, discipline, and battlefield tactics within their units. Praetorians functioned as elite guards of the Roman emperor, tasked with protecting imperial residences and maintaining internal security, while also participating in key military campaigns. The centurion's authority centered on direct troop leadership and operational effectiveness, contrasting with the Praetorian Guard's political influence and specialized protective duties.
Hierarchical Structure and Rank Comparison
The Centurion in the Roman army held a mid-level officer rank commanding a century of approximately 80 soldiers, responsible for discipline and training within the legion. The Praetorian, specifically a member of the Praetorian Guard, served as an elite soldier with roles that included protecting the emperor, often outranking standard centurions due to their special status and proximity to imperial power. Hierarchically, while Centurions were pivotal in legion organization and battlefield tactics, Praetorians operated within a separate command structure, emphasizing their elite guard function rather than conventional legion hierarchy.
Recruitment and Training Methods
Centurions were selected based on demonstrated experience and leadership skills, receiving rigorous training in combat tactics, discipline, and command responsibilities within the Roman legions. Pretorians underwent specialized recruitment from Rome's best soldiers, focusing on elite physical conditioning, advanced weaponry mastery, and strict loyalty to the emperor in their intensive training programs. Both units emphasized discipline and battlefield readiness, but Pretorians combined elite protection duties with political influence, while Centurions focused primarily on tactical leadership and maintaining unit cohesion.
Equipment and Uniform Distinctions
Centurions wore a distinctive transverse crest on their helmets, setting them apart from the standard soldiers and signifying their rank, while praetorians donned more lavishly decorated armor with intricate designs reflecting their elite status. Centurions typically carried the vitis, a vine staff symbolizing authority, whereas praetorians were equipped with specialized weapons such as curved swords and heavier shields for close protection of the emperor. Uniform variations included the centurion's segmented armor (lorica segmentata) designed for mobility, contrasted with the praetorian's ornate scale or chainmail armor that emphasized both prestige and defense.
Battlefield Duties and Tactical Importance
Centurions held critical battlefield duties commanding centuries of 80 legionaries, orchestrating formations, and maintaining discipline that ensured tactical cohesion during Roman military engagements. Pretorians functioned as elite imperial guards with specialized roles protecting the emperor and providing rapid response forces, combining combat readiness with political influence. The tactical importance of centurions lay in their frontline leadership and unit control, while Pretorians served strategic roles in safeguarding imperial command and executing elite missions.
Political Influence and Power
Centurions held significant political influence within the Roman military hierarchy, acting as key enforcers of discipline and advisors to higher-ranking officers, which often translated into localized political power. Praetorians, as elite bodyguards to the emperor, wielded substantial political power by directly influencing imperial succession and participating in key decisions, effectively shaping Roman imperial politics. The Praetorian Guard's proximity to the emperor allowed them to become kingmakers, whereas centurions primarily exercised authority within the legions and local governance.
Notable Centurions and Pretorians in History
Notable Centurions in history include Lucius Vorenus and Titus Pullo, renowned for their leadership and valor in the Roman legions, often depicted in accounts of Julius Caesar's campaigns. Among Pretorians, Sejanus stands out for his role as an influential Praetorian Prefect under Emperor Tiberius, exemplifying the political power wielded by the elite imperial guards. Both Centurions and Pretorians played critical roles in maintaining Roman military discipline and imperial security, shaping the course of Roman history through their strategic and political influence.
Legacy and Impact on Roman Military Tradition
The Centurion and Praetorian Guard each played pivotal roles in shaping Roman military tradition, with the Centurion embodying tactical discipline and leadership across Imperial legions, setting enduring standards for command hierarchy and battlefield strategy. The Praetorian Guard, initially elite protectors of Roman emperors, significantly influenced political power dynamics through their involvement in imperial successions and palace intrigues, impacting civil-military relations within the empire. Together, their legacies contributed to the development of Roman military organization, command structures, and the intricate balance between military authority and imperial governance.
Centurion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com