Gladiators were ancient warriors trained to fight in arenas for public entertainment, often facing life-or-death battles that captivated Roman audiences. Their strength, skill, and bravery symbolized both the extremes of human endurance and the brutal spectacle of ancient Rome's culture. Discover the fascinating history and legacy of gladiators in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
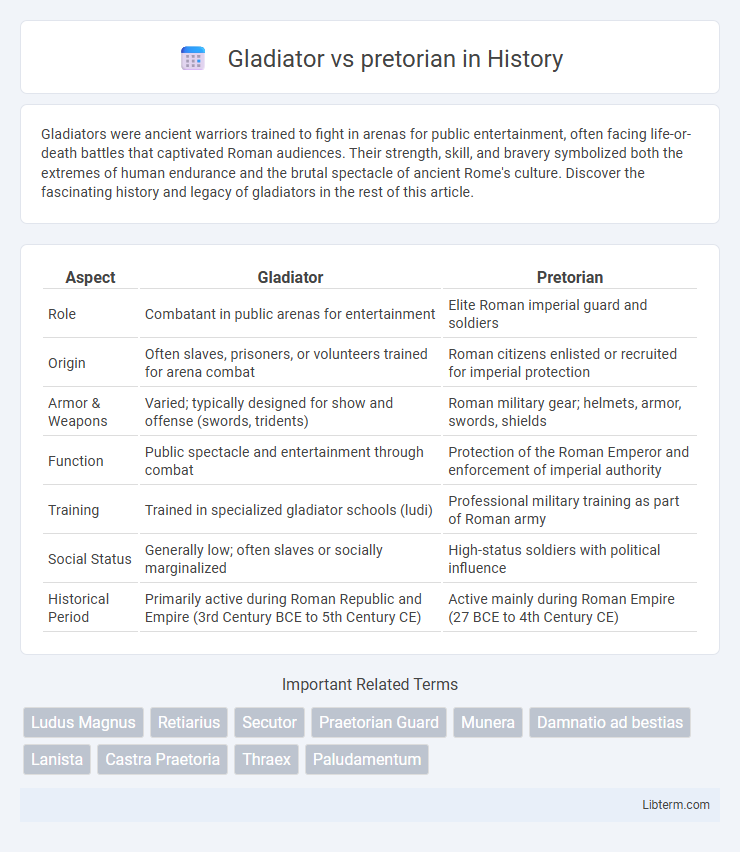
| Aspect | Gladiator | Pretorian |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Combatant in public arenas for entertainment | Elite Roman imperial guard and soldiers |
| Origin | Often slaves, prisoners, or volunteers trained for arena combat | Roman citizens enlisted or recruited for imperial protection |
| Armor & Weapons | Varied; typically designed for show and offense (swords, tridents) | Roman military gear; helmets, armor, swords, shields |
| Function | Public spectacle and entertainment through combat | Protection of the Roman Emperor and enforcement of imperial authority |
| Training | Trained in specialized gladiator schools (ludi) | Professional military training as part of Roman army |
| Social Status | Generally low; often slaves or socially marginalized | High-status soldiers with political influence |
| Historical Period | Primarily active during Roman Republic and Empire (3rd Century BCE to 5th Century CE) | Active mainly during Roman Empire (27 BCE to 4th Century CE) |
Historical Origins: Gladiators and Pretorians
Gladiators originated in ancient Rome as combatants who fought for public entertainment, often slaves or prisoners trained in specialized schools, with roots tracing back to Etruscan funeral rituals. Pretorians were elite Roman imperial guards established by Emperor Augustus around 27 BCE, tasked with protecting the emperor and maintaining order within Rome. Both played crucial roles in Roman society, gladiators symbolizing popular spectacle and Pretorians representing military power and political influence.
Roles in Ancient Roman Society
Gladiators were primarily entertainers who fought in arenas to provide public spectacle and demonstrate martial skill, often slaves or criminals trained for combat. Praetorians served as elite soldiers and personal bodyguards to Roman emperors, wielding significant political influence and enforcing imperial authority. The gladiators' role was centered on public amusement and social control, while Praetorians were crucial for military protection and political power within Ancient Roman society.
Training and Skillsets Compared
Gladiators underwent rigorous training in specialized ludus schools, focusing on weapon mastery, combat techniques, and physical endurance tailored for arena combat. In contrast, Praetorians received extensive military training emphasizing discipline, tactical formations, and skills essential for battlefield strategy and imperial protection. While gladiators specialized in individual fighting styles and showmanship, Praetorians developed versatile skills for collective defense and command execution.
Weapons and Armor Differences
Gladiators primarily used lightweight weapons like tridents, nets, and short swords (gladius) paired with minimal armor such as arm guards and helmets to ensure agility and crowd appeal in the arena. In contrast, Praetorians, elite Roman guards, equipped themselves with heavier weaponry like the pilum (javelin), gladius, and large rectangular scutum shields, complemented by chainmail or lorica segmentata armor for maximum protection. The gladiator's gear emphasized showmanship and varied combat styles, while Praetorian equipment prioritized durability and battlefield effectiveness.
Daily Life: Gladiator vs Pretorian
Gladiators underwent rigorous daily training focused on combat skills, strength, and endurance to prepare for brutal arena battles, living in specialized schools (ludi) with strict discipline and limited freedoms. Praetorians, the elite Roman imperial guards, maintained a structured routine involving military drills, strategic planning, and close proximity to the emperor, enjoying better living conditions, privileges, and higher social status than gladiators. The stark contrast in daily life highlighted gladiators' roles as entertainers and combatants, while Praetorians served as highly trained protectors of imperial power.
Famous Battles and Duels
Famous battles and duels between gladiators and Praetorians often showcased the elite skill and brutal combat techniques of both fighters, with the gladiators representing raw strength and agility while the Praetorians demonstrated disciplined, strategic fighting rooted in Roman military training. Iconic duels, such as those depicted in Roman arenas or dramatized in historical accounts, highlight intense clashes involving weaponry like the gladius and scutum from Praetorians versus the retiarius' net and trident or the murmillo's sword and shield. These encounters not only served as public spectacles in venues like the Colosseum but also reinforced the martial prestige and cultural symbolism surrounding both gladiators and the imperial guard.
Status, Respect, and Privileges
Gladiators held a complex status as both celebrated entertainers and socially marginalized individuals, earning respect through combat prowess but lacking full citizenship rights. Praetorians, elite soldiers guarding the Roman emperor, enjoyed higher social standing with considerable privileges, including political influence and substantial rewards. While gladiators gained popularity among the masses, Praetorians commanded honor and authority within the Roman hierarchy.
Representation in Popular Culture
Gladiators and Praetorians are frequently depicted in popular culture as symbols of strength and political intrigue, with gladiators often portrayed in epic battle scenes showcasing raw combat skills. Praetorians are typically represented as loyal yet ruthless elite guards, highlighting their role in the protection and sometimes betrayal of Roman emperors. Films, video games, and literature emphasize their contrasting roles, with gladiators embodying freedom through combat and Praetorians embodying imperial authority.
Myths vs Reality: Gladiators and Pretorians
Gladiators often appear in myths as brutal fighters battling for survival in deadly arenas, but historically, many were skilled warriors trained for entertainment with strict codes and opportunities for freedom. Pretorians, the elite Roman imperial guards, are commonly perceived as ruthless enforcers who frequently influenced political power through violence, yet they also maintained disciplined loyalty and essential protection for the emperor. The nuanced reality reveals gladiators as both entertainers and athletes, while Pretorians balanced military prowess with political influence, contradicting simplistic stereotypes.
Legacy in Modern History
The gladiator and Praetorian legacies significantly shaped modern concepts of military and entertainment culture. Gladiators symbolize the emergence of public spectacles influencing Western film and sports narratives, while the Praetorian Guard represents early models of elite protective forces and political power brokers. Their historical impacts resonate in modern security protocols and popular culture depictions of Roman martial valor.
Gladiator Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com