Muscovites, the residents of Russia's bustling capital, experience a unique blend of rich history and modern urban life. The city's diverse culture, architectural marvels, and vibrant arts scene offer endless opportunities for exploration and engagement. Discover more about Muscovites and what makes their lifestyle exceptional in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
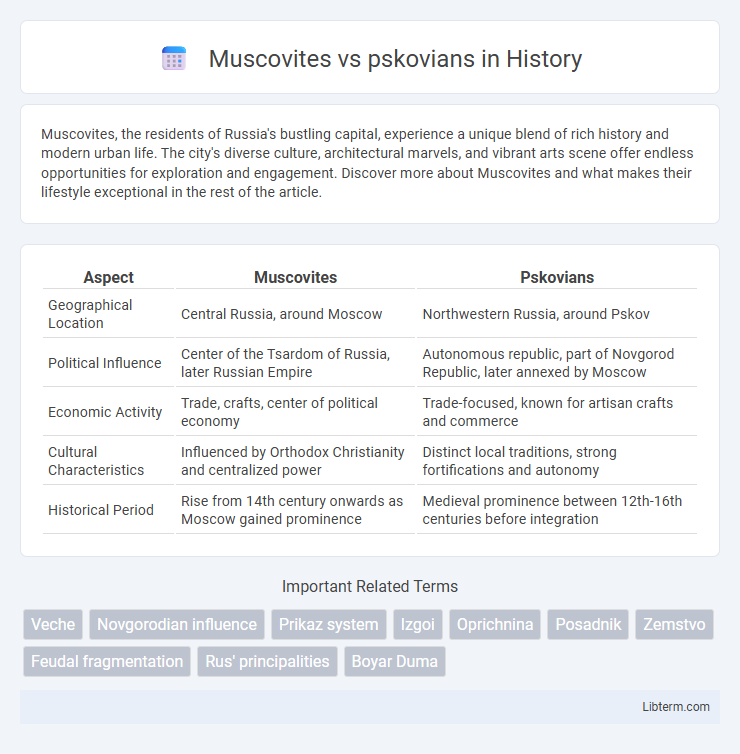
| Aspect | Muscovites | Pskovians |
|---|---|---|
| Geographical Location | Central Russia, around Moscow | Northwestern Russia, around Pskov |
| Political Influence | Center of the Tsardom of Russia, later Russian Empire | Autonomous republic, part of Novgorod Republic, later annexed by Moscow |
| Economic Activity | Trade, crafts, center of political economy | Trade-focused, known for artisan crafts and commerce |
| Cultural Characteristics | Influenced by Orthodox Christianity and centralized power | Distinct local traditions, strong fortifications and autonomy |
| Historical Period | Rise from 14th century onwards as Moscow gained prominence | Medieval prominence between 12th-16th centuries before integration |
Historical Background of Muscovites and Pskovians
Muscovites, originating from the Grand Duchy of Moscow, rose to prominence in the 14th century, consolidating power through strategic marriages and military conquests, ultimately forming the nucleus of the Russian state. Pskovians, inhabitants of the Pskov Republic, maintained a semi-independent medieval city-state known for its strong merchant guilds and autonomous veche assembly until its annexation by Moscow in the early 16th century. The contrasting political structures and alliances of Muscovites and Pskovians highlight the complex regional dynamics of medieval Rus'.
Geographic Distinctions and Urban Development
Muscovites inhabit Moscow, the capital city of Russia, characterized by its sprawling urban landscape, extensive metro system, and status as the country's political and economic hub. Pskovians reside in Pskov, a historic city near the Estonian border, known for its preserved medieval architecture and smaller population density compared to Moscow. The geographic distinction between the two highlights Moscow's role as a modern metropolitan center versus Pskov's emphasis on heritage and limited urban expansion.
Cultural Traditions and Regional Identity
Muscovites exhibit cultural traditions deeply rooted in metropolitan influences, reflecting a blend of historic Russian Orthodox practices and modern urban lifestyles that emphasize arts, theater, and contemporary festivals. Pskovians preserve a regional identity shaped by ancient Slavic customs and strong ties to medieval heritage, showcasing traditional folk music, craftmanship, and local religious ceremonies unique to the Pskov region. These distinctive cultural expressions highlight the contrast between Muscovite cosmopolitanism and Pskovian dedication to historical preservation and rural community values.
Linguistic Differences and Dialects
Muscovites primarily speak the Moscow dialect, characterized by clear vowel pronunciation and the use of "okan'e," where unstressed "o" is pronounced as [o], while Pskovians speak a dialect influenced by both Northern Russian and Belarusian linguistic features, exhibiting "akan'e," where unstressed "o" is pronounced as [a]. The Pskov dialect also retains archaic vocabulary and phonetic elements, such as softened consonants and distinct intonation patterns, distinguishing it from the more standardized Moscow speech. These differences reflect historical regional development and contribute to the rich diversity within the Russian language.
Political Influence and Governance Styles
Muscovites historically centralized political power, establishing autocratic governance with strong institutional control, shaping Russia's imperial and modern state structures. Pskovians exhibited a more decentralized and participatory governance style, emphasizing local assemblies (veche) and collective decision-making rooted in traditional self-governance. The contrast between Muscovite autocracy and Pskov's republicanism underscores divergent regional political cultures influencing Russian state evolution.
Economic Foundations and Trade Activities
Muscovites established a robust economic foundation centered on centralized trade routes and the collection of tribute, leveraging their position along the Volga River to control commerce between Northern Europe and Asia. In contrast, Pskovians thrived on maritime trade through their access to the Baltic Sea, fostering vibrant market towns and engaging in extensive trade networks with Hanseatic League cities. While Muscovites emphasized internal economic consolidation and political centralization, Pskovians excelled in international commerce and operated semi-autonomously as a mercantile republic.
Religious Practices and Spiritual Heritage
Muscovites traditionally follow Russian Orthodox Christianity, with rich liturgical traditions centered around the Moscow Patriarchate, featuring iconic churches like the Cathedral of Christ the Savior. Pskovians maintain similarly Orthodox beliefs but emphasize ancient rites and local saints linked to Pskov's medieval spiritual history, preserving unique liturgical chants and iconography. Both communities contribute to Russia's spiritual heritage, but Muscovy's liturgical grandeur contrasts with Pskov's intimate monastic traditions.
Architectural Styles: Moscow vs. Pskov
Muscovite architecture is characterized by grandiose, richly decorated structures featuring onion domes, intricate brickwork, and colorful facades, exemplified by St. Basil's Cathedral and the Kremlin's towers. In contrast, Pskovian architecture emphasizes fortress-like, austere designs with thick stone walls, simple geometric forms, and functional fortifications such as the Pskov Kremlin and ancient churches with minimal ornamentation. The stylistic divergence reflects Moscow's role as a political and religious center fostering elaborate artistic expression, while Pskov's architecture prioritizes defense and practicality shaped by its borderland history.
Folklore, Myths, and Local Legends
Muscovite folklore often centers around grand princely lore and the mythical origins of Moscow, featuring tales of heroes like Ilya Muromets and legendary events such as the founding of the Kremlin by Yuri Dolgoruky. Pskovian legends emphasize resilience and spiritual mysticism, highlighting the ancient Pskov Fortress and stories of saints like Saint Olga, blending historical battles with supernatural elements. Both regions' myths reflect their distinct cultural identities through epic narratives, sacred symbols, and local heroes tied to their unique historical landscapes.
Legacy and Modern Perceptions
Muscovites are often associated with the legacy of centralized political power and cultural dominance in Russia, reflecting their historical role as the capital's inhabitants and key players in state formation. Pskovians are recognized for their rich medieval heritage, emphasizing defensive architecture and early republican governance, which shapes modern perceptions of regional pride and resilience. Contemporary views distinguish Muscovites as symbols of modern Russian ambition and innovation, while Pskovians are respected for preserving traditional values and historical identity.
Muscovites Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com