Leather offers unmatched durability and timeless style, making it an essential material for fashion, furniture, and accessories. Its natural texture and breathability ensure comfort while aging gracefully over time. Discover how leather can elevate your everyday items by exploring the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
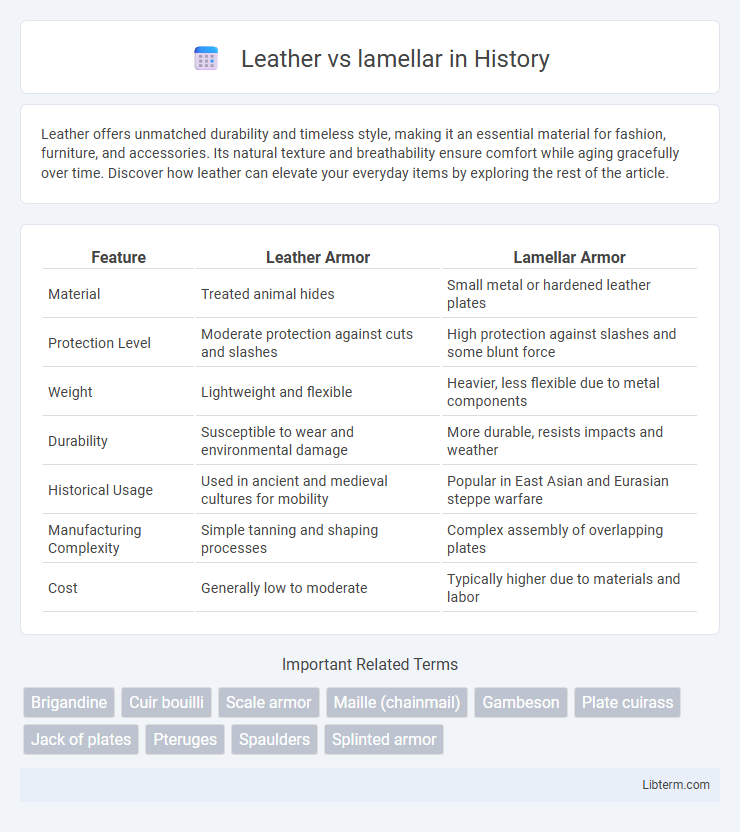
| Feature | Leather Armor | Lamellar Armor |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Treated animal hides | Small metal or hardened leather plates |
| Protection Level | Moderate protection against cuts and slashes | High protection against slashes and some blunt force |
| Weight | Lightweight and flexible | Heavier, less flexible due to metal components |
| Durability | Susceptible to wear and environmental damage | More durable, resists impacts and weather |
| Historical Usage | Used in ancient and medieval cultures for mobility | Popular in East Asian and Eurasian steppe warfare |
| Manufacturing Complexity | Simple tanning and shaping processes | Complex assembly of overlapping plates |
| Cost | Generally low to moderate | Typically higher due to materials and labor |
Introduction to Leather and Lamellar Armor
Leather armor, crafted from treated animal hides, offers flexibility and moderate protection, commonly used by ancient warriors for its lightweight and affordable properties. Lamellar armor consists of small, overlapping plates laced together, providing superior defense against slashing and piercing attacks while maintaining mobility. Both armor types played crucial roles in historical warfare, with leather favored for comfort and lamellar for enhanced durability.
Historical Background of Leather Armor
Leather armor dates back to ancient civilizations such as Mesopotamia and Egypt, where it was crafted from hardened animal hides to provide lightweight protection. It was widely used across various cultures, including Roman soldiers who employed cuir bouilli techniques, hardening leather through boiling to enhance durability. Leather armor's historical significance lies in its accessibility and flexibility before the widespread adoption of metal lamellar armor in East Asia and the Byzantine Empire.
The Evolution of Lamellar Armor
Lamellar armor evolved from early leather designs, consisting of small, rectangular plates laced together to provide superior flexibility and protection compared to traditionally crafted leather armor. Originating in East Asia and widely adopted by nomadic tribes, lamellar armor allowed for enhanced mobility on the battlefield while maintaining durability against arrows and sword strikes. This construction method influenced medieval armor development, bridging the gap between rawhide protection and fully metal plate armor.
Materials and Craftsmanship
Leather armor, crafted from tanned animal hides, offers flexibility and durability through meticulous curing and stitching techniques. Lamellar armor consists of small, overlapping metal or hardened leather plates laced together, requiring precise alignment and binding for enhanced protection. The craftsmanship of leather emphasizes pliability and comfort, while lamellar demands intricate assembly to balance mobility with comprehensive defense.
Protection and Effectiveness Comparison
Leather armor offers moderate protection, primarily absorbing blunt force and providing flexibility, making it suitable for light combat scenarios. Lamellar armor, constructed from small, overlapping plates tied together, delivers superior defense against slashing and piercing attacks due to its rigid structure and distributed impact resistance. In terms of effectiveness, lamellar armor outperforms leather by combining durability and coverage, although it is heavier and less maneuverable than leather counterparts.
Comfort and Mobility Factors
Leather offers superior comfort due to its natural breathability and flexibility, allowing for extended wear without excessive heat or chafing. Lamellar armor, made from small overlapping plates, provides structured protection but often restricts mobility due to its rigidity and weight. The choice between leather and lamellar depends on prioritizing either enhanced flexibility for agile movements or higher defense at the cost of some comfort.
Weight and Wearability
Leather armor typically weighs between 10 to 20 pounds, offering considerable flexibility and comfort for prolonged wear in various climates. Lamellar armor, constructed from small overlapping plates bound together, tends to be heavier, often ranging from 20 to 30 pounds, but provides enhanced protection with moderate mobility. Wearability depends on the application: leather excels in lighter, more agile roles, whereas lamellar suits better for scenarios demanding higher defense despite added weight.
Cost and Accessibility
Leather armor generally offers higher accessibility and lower upfront costs due to its widespread availability and simpler crafting process using animal hides. Lamellar armor is often more expensive and less accessible, requiring numerous small plates made from metal or hardened leather, which increases material and labor costs. The complexity of lamellar construction and specialized skills needed for assembly make it less economical and more challenging to obtain compared to traditional leather armor.
Popularity in Different Cultures
Leather armor has maintained widespread popularity across various cultures such as Native American tribes, medieval Europeans, and ancient Asians due to its flexibility, affordability, and ease of crafting. Lamellar armor, however, found prominence primarily in East Asia, Mongolia, and Eastern Europe, valued for its segmented design offering superior protection and mobility in battle. The cultural preference for leather versus lamellar often depended on available materials, technological advancements, and the specific combat needs of each society.
Modern Applications and Legacy
Leather armor, historically prized for its flexibility and lightweight protection, finds modern applications in high-end fashion and specialized protective gear, such as motorcycle jackets and historical reenactment costumes. Lamellar armor, composed of small, overlapping plates, remains influential in the design of contemporary body armor and tactical vests due to its superior deflection capabilities and modular construction. The legacy of leather and lamellar armor continues to shape material innovation, balancing durability, mobility, and historical authenticity in both protective and aesthetic uses.
Leather Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com