Compilation is the process of transforming source code written in high-level programming languages into machine code that a computer's processor can execute directly. This conversion enhances program performance and efficiency, enabling your software to run faster and more reliably. Discover how compilation impacts development and optimization in the full article.
Table of Comparison
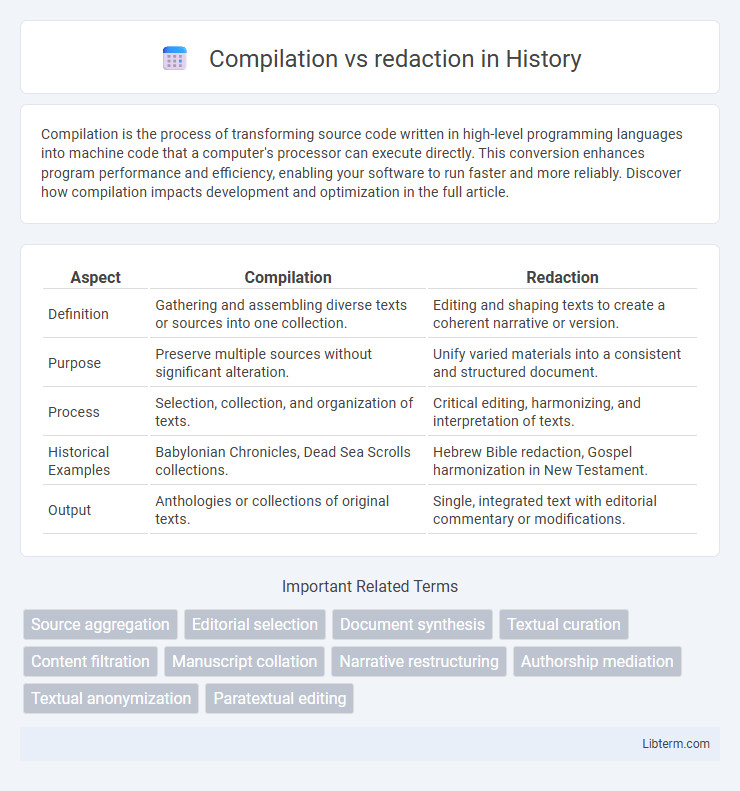
| Aspect | Compilation | Redaction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Gathering and assembling diverse texts or sources into one collection. | Editing and shaping texts to create a coherent narrative or version. |
| Purpose | Preserve multiple sources without significant alteration. | Unify varied materials into a consistent and structured document. |
| Process | Selection, collection, and organization of texts. | Critical editing, harmonizing, and interpretation of texts. |
| Historical Examples | Babylonian Chronicles, Dead Sea Scrolls collections. | Hebrew Bible redaction, Gospel harmonization in New Testament. |
| Output | Anthologies or collections of original texts. | Single, integrated text with editorial commentary or modifications. |
Understanding Compilation and Redaction
Compilation involves gathering and assembling information from various sources into a single document without altering the original content, ensuring the integrity of the collected data. Redaction refers to the process of editing or obscuring sensitive information within a document to protect privacy or confidentiality before distribution. Understanding the distinct purposes of compilation and redaction helps maintain data accuracy while safeguarding sensitive details in legal, governmental, and corporate contexts.
Key Differences Between Compilation and Redaction
Compilation involves gathering and assembling information or data from various sources into a cohesive document without altering the original content, whereas redaction entails selectively obscuring or removing sensitive or confidential information to protect privacy or comply with legal requirements. Key differences include the purpose: compilation aims to organize information for clarity or presentation, while redaction focuses on confidentiality and security. Compiled documents maintain full visibility of all data, whereas redacted documents visibly mask or black out specific details to prevent unauthorized access.
Purposes of Compilation in Content Creation
Compilation in content creation serves to aggregate diverse information, sources, or data into a coherent and accessible format for the audience, enhancing knowledge synthesis and decision-making. It streamlines research efforts by consolidating relevant content, facilitating quicker understanding and comparison of ideas or findings. This process supports content creators in providing comprehensive overviews, making complex subjects more approachable and valuable for readers.
The Role of Redaction in Information Management
Redaction plays a critical role in information management by selectively obscuring sensitive or confidential data to protect privacy and comply with regulatory requirements. Unlike compilation, which involves gathering and organizing information, redaction ensures that only permissible content is accessible, mitigating risks of data breaches or legal violations. Effective redaction techniques enhance data security and support regulatory compliance frameworks such as GDPR and HIPAA.
Compilation Process: Steps and Best Practices
The compilation process involves gathering, organizing, and presenting data or information systematically to create a comprehensive document or report. Key steps include defining objectives, collecting accurate and relevant data, verifying its authenticity, and structuring the content logically to ensure clarity and coherence. Best practices emphasize thorough fact-checking, consistent formatting, and maintaining source transparency to enhance the credibility and usability of the compiled material.
Redaction Techniques and Methods
Redaction techniques primarily involve obscuring or removing sensitive information from documents to prevent unauthorized access while retaining the overall context. Common methods include blacking out text with opaque markers, pixelation of images, and digital redaction using specialized software that securely deletes content from electronic files. Effective redaction requires careful verification to ensure no hidden data remains in metadata or underlying layers, protecting confidentiality during document sharing or publication.
Common Use Cases for Compilation
Compilation involves gathering and organizing data or documents without altering the original content, commonly used in financial reporting, market research, and academic work to present comprehensive information. Redaction, by contrast, focuses on censoring or obscuring sensitive information within documents for privacy or legal compliance. Common use cases for compilation include preparing audit-ready financial statements, assembling research data for analysis, and creating detailed reports by consolidating various sources for stakeholder review.
Legal and Ethical Implications of Redaction
Redaction in legal documents involves the deliberate concealment of sensitive information to comply with privacy laws and protect client confidentiality, distinguishing it from compilation, which merely gathers information without modification. Ethical implications of redaction require attorneys to balance transparency with safeguarding privileged data, ensuring compliance with regulations such as the GDPR and HIPAA. Failure to properly redact can result in legal penalties, compromised evidence integrity, and breaches of attorney-client privilege.
Challenges in Compilation vs Redaction
Compilation faces challenges related to organizing diverse data sources and ensuring consistency across aggregated information, often requiring complex data validation methods. Redaction struggles with accurately identifying sensitive content to prevent data breaches while maintaining the integrity and readability of the document. Both processes demand advanced tools and skilled personnel to balance efficiency, accuracy, and security in handling sensitive information.
Choosing Between Compilation and Redaction for Your Project
Choosing between compilation and redaction depends on the specific goals of your project. Compilation involves gathering and organizing existing information to create a cohesive final document, ideal for reports or research summaries requiring comprehensive data integration. Redaction focuses on selectively editing or obscuring sensitive content in documents, essential for maintaining confidentiality and compliance with privacy regulations.
Compilation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com