The Renaissance was a transformative period marked by a surge in art, science, and culture, redefining European society from the 14th to the 17th century. Innovations in literature, exploration, and humanism reshaped how people understood the world and themselves. Discover how this rich era continues to influence your worldview as you explore the full article.
Table of Comparison
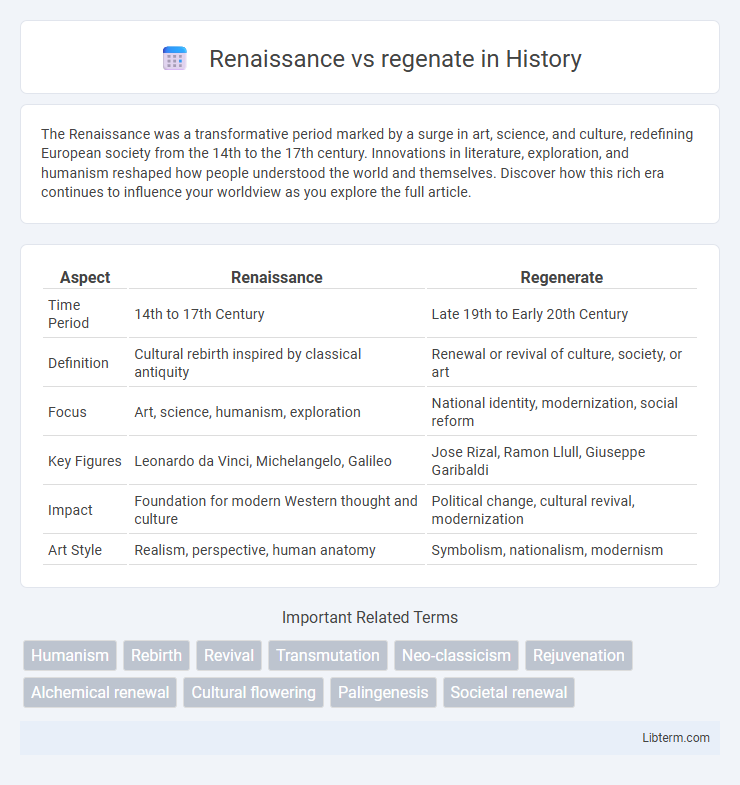
| Aspect | Renaissance | Regenerate |
|---|---|---|
| Time Period | 14th to 17th Century | Late 19th to Early 20th Century |
| Definition | Cultural rebirth inspired by classical antiquity | Renewal or revival of culture, society, or art |
| Focus | Art, science, humanism, exploration | National identity, modernization, social reform |
| Key Figures | Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, Galileo | Jose Rizal, Ramon Llull, Giuseppe Garibaldi |
| Impact | Foundation for modern Western thought and culture | Political change, cultural revival, modernization |
| Art Style | Realism, perspective, human anatomy | Symbolism, nationalism, modernism |
Introduction to the Renaissance and Regeneration
The Renaissance, spanning the 14th to 17th centuries, marked a profound cultural rebirth in Europe with a resurgence of art, science, and humanism rooted in classical antiquity. Regeneration refers to a biological or ecological process of renewal and restoration, emphasizing growth and the replacement of lost or damaged tissues or environments. Understanding the Renaissance as a historical transformation contrasts with regeneration's focus on natural and biological restoration processes.
Historical Context: Roots of Renaissance and Regeneration
The Renaissance originated in 14th-century Italy as a cultural rebirth sparked by a renewed interest in classical antiquity, humanism, and artistic innovation, marking a shift from medieval to early modern European society. The Regeneration, notably referenced in 19th-century Portuguese history, signifies a political and social reform movement aimed at modernizing institutions and infrastructure following a period of stagnation and decline. Both movements reflect responses to historical crises, with the Renaissance revitalizing intellectual and artistic pursuits, while the Regeneration focused on governmental and economic renewal.
Defining Renaissance: Revival and Transformation
The Renaissance marked a profound cultural revival and transformation in Europe, characterized by renewed interest in classical art, literature, and humanism from the 14th to 17th centuries. It ignited advancements in science, exploration, and philosophy, bridging medieval thought with modern perspectives. This period fostered a dynamic shift in societal values, emphasizing individualism and intellectual inquiry.
Understanding Regeneration: Renewal and Innovation
Regeneration emphasizes continuous renewal and innovation by restoring ecosystems, urban areas, or biological systems to a healthier, more adaptive state. Unlike the Renaissance, which highlights a historical period of cultural rebirth and artistic revival, regeneration applies modern principles of sustainability and resilience to promote long-term growth and environmental balance. This approach integrates cutting-edge technologies and holistic practices to create systems that evolve dynamically and sustainably.
Key Philosophies: Renaissance Humanism vs. Regenerative Thinking
Renaissance Humanism prioritized the revival of classical knowledge, emphasizing individual potential, reason, and secularism grounded in Greco-Roman texts. Regenerative Thinking centers on systemic interconnectedness, focusing on restoring and enhancing natural and social ecosystems through sustainability and resilience. The key philosophical contrast lies in Humanism's anthropocentric ideals versus Regenerative Thinking's holistic integration of human and environmental well-being.
Impact on Art, Science, and Society
The Renaissance sparked a profound transformation in art, science, and society by emphasizing humanism, realism, and empirical observation, leading to masterpieces by artists like Leonardo da Vinci and breakthroughs in anatomy and astronomy. In contrast, the Regenate movement, rooted in revitalizing and restoring traditional values, influenced art by reintroducing classical styles and reinforced societal structures based on cultural and spiritual renewal. Both eras contributed significantly to the evolution of European thought, but the Renaissance catalyzed a broader intellectual and scientific revolution while the Regenate focused on consolidating cultural identity and continuity.
Methods of Change: Restoration vs. Sustainable Growth
The Renaissance emphasized restoration through the revival of classical art, literature, and humanist values, aiming to restore cultural achievements of antiquity. In contrast, Regenerate focuses on sustainable growth by promoting innovative environmental practices, holistic urban planning, and long-term ecological balance. While the Renaissance sought to recover past glory, Regenerate prioritizes continuous renewal and resilience within natural and social systems.
Influential Figures in Each Movement
Leonardo da Vinci and Michelangelo exemplify the Renaissance's emphasis on humanism and artistic mastery, influencing art, science, and culture from the 14th to 17th centuries. In the Regenerate movement, figures like Mahatma Gandhi and Mustafa Kemal Ataturk played pivotal roles in political and social renewal during the early 20th century, spearheading national independence and modernization efforts. These influential leaders shaped their respective eras through transformative contributions to culture, governance, and societal values.
Lasting Legacy: Renaissance and Regenerative Futures
The Renaissance established a lasting legacy through profound advancements in art, science, and humanism that shaped Western culture for centuries. Regenerative futures emphasize sustainability and ecological restoration, aiming to create resilient systems that replenish natural resources while fostering economic and social well-being. Together, Renaissance innovation inspires regenerative approaches that integrate cultural heritage with forward-thinking environmental stewardship.
Conclusion: Comparing Their Relevance Today
The Renaissance remains a cornerstone of Western cultural and intellectual history, characterized by a revival of classical art, literature, and scientific inquiry. In contrast, the Regenerate movement, often tied to social and political reform, emphasizes renewal through modern innovation and ethical progress. Today, the Renaissance influences contemporary education and artistic standards, while regeneration fuels ongoing societal transformation and sustainable development initiatives.
Renaissance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com