Pseudepigrapha refers to a collection of ancient texts falsely attributed to biblical figures, often written between 200 BCE and 200 CE. These writings provide valuable insights into the religious beliefs, myths, and traditions of various Jewish and early Christian communities. Explore the article to uncover how your understanding of these influential texts can deepen.
Table of Comparison
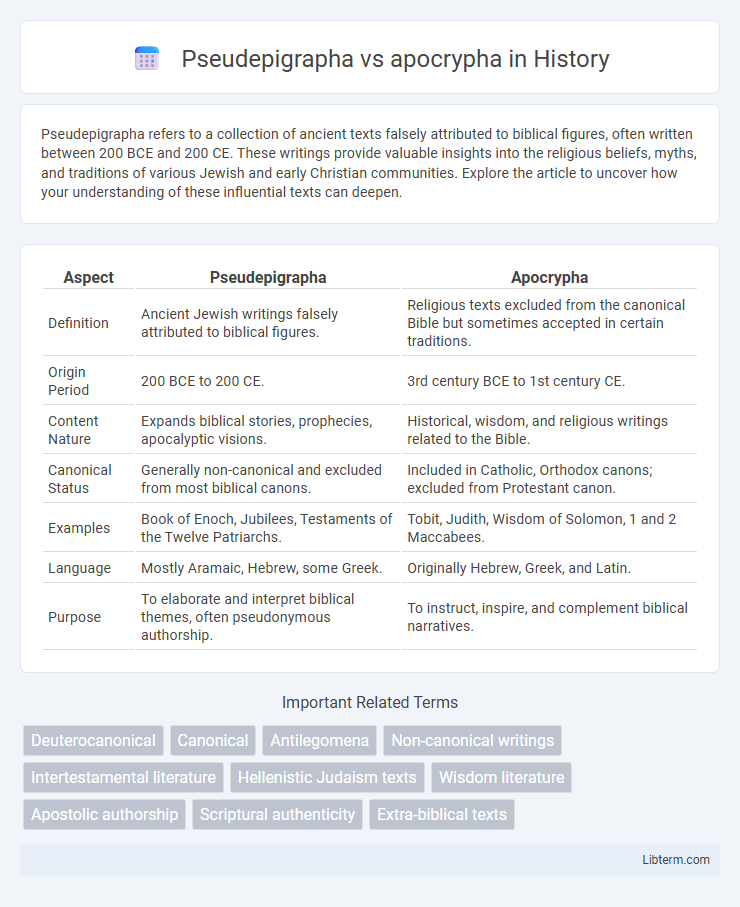
| Aspect | Pseudepigrapha | Apocrypha |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ancient Jewish writings falsely attributed to biblical figures. | Religious texts excluded from the canonical Bible but sometimes accepted in certain traditions. |
| Origin Period | 200 BCE to 200 CE. | 3rd century BCE to 1st century CE. |
| Content Nature | Expands biblical stories, prophecies, apocalyptic visions. | Historical, wisdom, and religious writings related to the Bible. |
| Canonical Status | Generally non-canonical and excluded from most biblical canons. | Included in Catholic, Orthodox canons; excluded from Protestant canon. |
| Examples | Book of Enoch, Jubilees, Testaments of the Twelve Patriarchs. | Tobit, Judith, Wisdom of Solomon, 1 and 2 Maccabees. |
| Language | Mostly Aramaic, Hebrew, some Greek. | Originally Hebrew, Greek, and Latin. |
| Purpose | To elaborate and interpret biblical themes, often pseudonymous authorship. | To instruct, inspire, and complement biblical narratives. |
Introduction to Pseudepigrapha and Apocrypha
The Pseudepigrapha consists of ancient Jewish writings falsely attributed to biblical figures, often expanding on religious themes and offering insights into Second Temple Judaism. The Apocrypha refers to a collection of intertestamental books included in some Christian biblical canons but excluded from the Hebrew Bible, providing historical and theological context. Both represent significant non-canonical literature that shapes understanding of early Jewish and Christian thought.
Definitions: What Are Pseudepigrapha and Apocrypha?
Pseudepigrapha are ancient writings falsely attributed to biblical figures, often composed between 200 BCE and 200 CE, reflecting diverse Jewish and early Christian traditions not included in the canonical Bible. Apocrypha refers to a set of religious texts included in some Christian Old Testament canons, particularly the Catholic and Orthodox traditions, but excluded from the Hebrew Bible and most Protestant Bibles. Both collections contain valuable historical, theological, and literary material but differ primarily in authenticity claims and canonical acceptance across religious communities.
Historical Context and Origins
Pseudepigrapha consists of ancient Jewish and Christian writings falsely attributed to biblical figures, originating primarily between 200 BCE and 200 CE, reflecting diverse theological themes and historical contexts. Apocrypha refers to a collection of early Jewish and Christian texts written roughly from the 3rd century BCE to the 1st century CE, often excluded from canonical scriptures but valued for their historical and religious insights. Both sets of writings provide critical perspectives on the religious beliefs, cultural influences, and scriptural developments during the Second Temple period and early Christianity.
Key Differences Between Pseudepigrapha and Apocrypha
Pseudepigrapha refers to ancient writings falsely attributed to biblical figures, often composed between 200 BCE and 200 CE, while Apocrypha consists of religious texts included in some Christian Bibles but excluded from the Hebrew Bible. The key difference lies in their canonical status: Apocrypha is recognized as scripture by certain traditions like Catholicism and Eastern Orthodoxy, whereas Pseudepigrapha is generally regarded as non-canonical and apocryphal by most denominations. Moreover, Apocryphal books typically provide historical or theological expansion on biblical themes, whereas Pseudepigraphal texts often contain legendary, mystical, or pseudonymous elements not found in canonical scriptures.
Examples of Pseudepigraphal Texts
Pseudepigraphal texts include notable works such as the Book of Enoch, the Testament of Solomon, and the Apocalypse of Abraham, which were falsely attributed to biblical figures. These texts often contain elaborate expansions on biblical themes and apocalyptic visions but are excluded from the canonical Bible. In contrast, apocryphal books like Tobit and Judith have historically been recognized in some Christian traditions, such as Catholicism and Eastern Orthodoxy, though not in the Protestant canon.
Notable Books Classified as Apocrypha
Notable books classified as Apocrypha include the Gospel of Thomas, Tobit, Judith, and the Wisdom of Solomon, which are often included in Catholic and Eastern Orthodox biblical canons but excluded from the Protestant Old Testament. These texts provide valuable historical and theological insights, reflecting Jewish traditions and Christian beliefs from the intertestamental period. In contrast, the Pseudepigrapha comprises works like 1 Enoch and the Testament of Abraham, which are generally not accepted into any biblical canon and often contain more elaborate mythological content.
Canonical Status: Inclusion and Exclusion from the Bible
Pseudepigrapha refers to ancient writings falsely attributed to biblical figures, often excluded from both Jewish and Christian biblical canons due to questionable authorship and theological inconsistencies. Apocrypha comprises texts like Tobit and Judith that hold canonical status in some Christian traditions, such as the Catholic and Orthodox Churches, while being excluded from the Protestant Bible. The canonical status hinges on historical acceptance by religious communities, with Pseudepigrapha largely regarded as non-canonical and Apocrypha variably included depending on denominational beliefs.
Theological and Doctrinal Implications
The Pseudepigrapha and Apocrypha differ significantly in their theological and doctrinal implications; Pseudepigrapha texts, often attributed falsely to biblical figures, frequently introduce teachings that diverge from canonical orthodoxy, challenging established doctrines on prophecy and messianism. In contrast, the Apocrypha, while not universally accepted in all Christian traditions, generally aligns more closely with canonical theology, offering valuable historical and ethical insights that complement scriptural teachings. The distinction influences doctrinal authority and textual interpretation, shaping varying denominational views on inspiration, revelation, and the boundaries of sacred scripture.
Influence on Judaism and Christianity
Pseudepigrapha and Apocrypha both significantly shaped early Judaism and Christianity by expanding theological ideas and scriptural boundaries. Pseudepigrapha, often attributed to ancient biblical figures, influenced Jewish mysticism and eschatology, while the Apocrypha, included in certain Christian biblical canons, contributed to doctrinal development and liturgical practices. The distinction between these texts affected canon formation, with Apocryphal books accepted in Catholic and Orthodox traditions, whereas Pseudepigraphal works remained outside most canonical scriptures but informed religious thought and interpretation.
Contemporary Relevance and Scholarly Debates
Pseudepigrapha and Apocrypha continue to shape contemporary biblical scholarship by challenging traditional views on scriptural canonicity and historical authenticity. The Pseudepigrapha, often attributed to false authorship, prompt debates about theological intentions and literary contexts, while the Apocrypha's inclusion or exclusion from religious canons affects modern religious practices and interfaith dialogues. Current scholarly discussions emphasize their impact on understanding Second Temple Judaism, early Christian communities, and evolving notions of sacred texts.
Pseudepigrapha Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com