Uvulectomy is a medical procedure involving the removal of the uvula, often performed to treat obstructive sleep apnea or chronic snoring. This surgery can improve airway function and reduce related symptoms, enhancing overall sleep quality. Explore the article to understand the benefits, risks, and recovery process associated with uvulectomy.
Table of Comparison
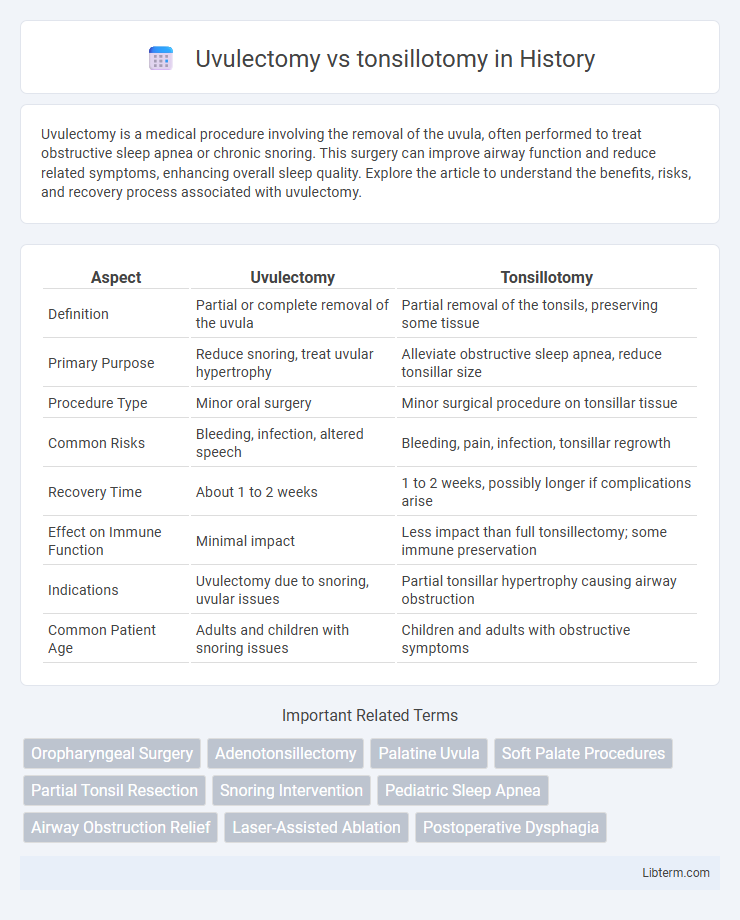
| Aspect | Uvulectomy | Tonsillotomy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Partial or complete removal of the uvula | Partial removal of the tonsils, preserving some tissue |
| Primary Purpose | Reduce snoring, treat uvular hypertrophy | Alleviate obstructive sleep apnea, reduce tonsillar size |
| Procedure Type | Minor oral surgery | Minor surgical procedure on tonsillar tissue |
| Common Risks | Bleeding, infection, altered speech | Bleeding, pain, infection, tonsillar regrowth |
| Recovery Time | About 1 to 2 weeks | 1 to 2 weeks, possibly longer if complications arise |
| Effect on Immune Function | Minimal impact | Less impact than full tonsillectomy; some immune preservation |
| Indications | Uvulectomy due to snoring, uvular issues | Partial tonsillar hypertrophy causing airway obstruction |
| Common Patient Age | Adults and children with snoring issues | Children and adults with obstructive symptoms |
Uvulectomy vs Tonsillotomy: Overview
Uvulectomy and tonsillotomy are surgical procedures targeting different anatomical structures within the oropharynx; uvulectomy involves partial or complete removal of the uvula, while tonsillotomy refers to the partial removal of the tonsils. Indications for uvulectomy often include treatment of uvular hypertrophy or snoring, whereas tonsillotomy is commonly performed to alleviate obstructive sleep apnea or recurrent tonsillitis with less postoperative pain and faster recovery compared to tonsillectomy. Both procedures carry risks such as postoperative bleeding and infection, but tonsillotomy typically preserves more tonsillar tissue, reducing complications associated with full tonsil removal.
Understanding Uvulectomy: Definition and Purpose
Uvulectomy involves the surgical removal of the uvula to treat conditions such as snoring and obstructive sleep apnea by reducing airway obstruction. This procedure differs from tonsillotomy, which entails partial removal of the tonsils primarily to alleviate recurrent tonsillitis or sleep-disordered breathing. Understanding uvulectomy's purpose highlights its role in improving airway function while minimizing impact on immune tissue, unlike the more extensive tonsil tissue removal in tonsillotomy.
What is Tonsillotomy? Key Facts
Tonsillotomy is a surgical procedure that involves partial removal of the tonsils, primarily indicated for treating obstructive sleep apnea and recurrent tonsillitis while preserving tonsil tissue to reduce recovery time and complications. This minimally invasive technique contrasts with tonsillectomy, which completely removes the tonsils, often leading to more postoperative pain and bleeding. Tonsillotomy maintains some immune function of the tonsils, making it a preferred option for children with obstructive airway symptoms.
Indications for Uvulectomy: Who Needs It?
Uvulectomy is primarily indicated for patients experiencing chronic uvular inflammation, recurrent uvular edema, or obstructive sleep apnea caused by uvular hypertrophy. Those with frequent gag reflexes or persistent snoring related to uvular anomalies may also benefit from the procedure. Unlike tonsillotomy, which targets partial removal of tonsillar tissue to reduce tonsillar hypertrophy and recurrent tonsillitis, uvulectomy specifically addresses issues involving the uvula to improve airway function and comfort.
Indications for Tonsillotomy: Ideal Candidates
Ideal candidates for tonsillotomy include children and adults experiencing recurrent tonsillitis, obstructive sleep apnea, or significant tonsillar hypertrophy causing airway obstruction. Tonsillotomy is preferred for patients needing symptom relief while preserving some tonsillar tissue to reduce postoperative pain and bleeding risks. This procedure suits individuals with moderate tonsillar enlargement without active infection or malignancy.
Surgical Techniques: Uvulectomy vs Tonsillotomy
Uvulectomy involves the surgical removal of the uvula, typically using laser or electrocautery methods to minimize bleeding and ensure precise excision. Tonsillotomy, also known as partial tonsillectomy, employs techniques such as coblation, microdebrider, or radiofrequency ablation to remove only a portion of the tonsillar tissue, preserving the tonsillar capsule. Both procedures differ significantly in tissue removal extent and tool selection, impacting recovery time and postoperative pain levels.
Risks and Complications: Comparing Both Procedures
Uvulectomy carries risks such as bleeding, infection, and potential airway obstruction due to swelling, while tonsillotomy, a partial removal of tonsillar tissue, generally has a lower risk of severe bleeding and postoperative pain compared to tonsillectomy. Tonsillotomy may result in recurrence of tonsillar hypertrophy or infection since some tissue remains, whereas uvulectomy complications are primarily localized but can impact swallowing and speech. Careful patient selection and postoperative monitoring are crucial for minimizing complications in both procedures.
Recovery and Aftercare: What to Expect
Recovery after uvulectomy generally involves mild throat discomfort and a faster healing process, typically resolving within a week with proper hydration and pain management. Tonsillotomy recovery may take longer, often up to two weeks, with increased risk of bleeding and soreness requiring careful monitoring and throat rest. Both procedures necessitate avoidance of irritating foods and strenuous activity to promote healing and minimize complications.
Outcomes and Effectiveness: Uvulectomy vs Tonsillotomy
Uvulectomy primarily targets the uvula to reduce snoring and improve airway obstruction, showing moderate effectiveness in symptom relief but limited impact on overall airway patency compared to tonsillotomy. Tonsillotomy, which involves partial removal of tonsillar tissue, demonstrates higher success rates in reducing obstructive sleep apnea symptoms and improving breathing by minimizing tonsillar obstruction while preserving immune function. Clinical outcomes suggest tonsillotomy offers superior long-term efficacy and fewer complications related to postoperative pain and bleeding compared to uvulectomy.
Choosing the Right Procedure: Factors to Consider
Choosing between uvulectomy and tonsillotomy depends on factors such as the severity of symptoms, underlying medical conditions, and the specific anatomical issues present. Uvulectomy primarily targets elongated or inflamed uvulas causing snoring or discomfort, while tonsillotomy focuses on partial tonsil removal to relieve obstruction or recurrent infections. Patient age, recovery time, and potential complications should be carefully evaluated with an ENT specialist to determine the most suitable procedure.
Uvulectomy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com