Reus is a vibrant city in Catalonia, Spain, known for its rich modernist architecture and as the birthplace of the famous architect Antoni Gaudi. The city offers a unique blend of cultural heritage, historic sites, and contemporary attractions that appeal to travelers and history enthusiasts alike. Discover more about what makes Reus an unforgettable destination by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
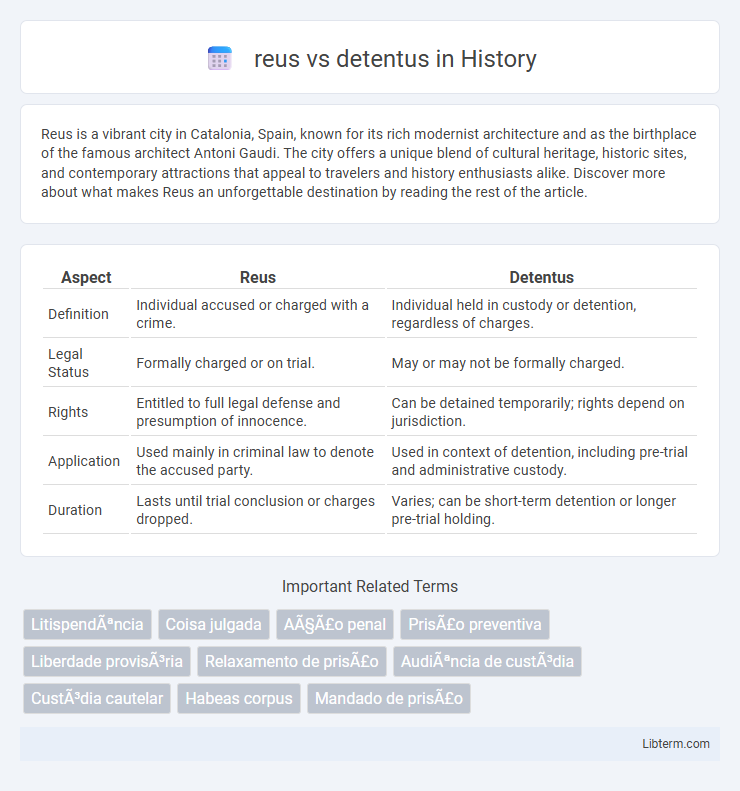
| Aspect | Reus | Detentus |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual accused or charged with a crime. | Individual held in custody or detention, regardless of charges. |
| Legal Status | Formally charged or on trial. | May or may not be formally charged. |
| Rights | Entitled to full legal defense and presumption of innocence. | Can be detained temporarily; rights depend on jurisdiction. |
| Application | Used mainly in criminal law to denote the accused party. | Used in context of detention, including pre-trial and administrative custody. |
| Duration | Lasts until trial conclusion or charges dropped. | Varies; can be short-term detention or longer pre-trial holding. |
Introduction to Reus and Detentus
Reus, in legal terms, refers to the accused or defendant in a criminal case who is alleged to have committed an offense, serving as the central figure subject to prosecution. Detentus denotes a person who is held in detention or custody, often before or during legal proceedings, emphasizing the state of physical restraint. Understanding the distinction between Reus and Detentus is crucial for grasping the responsibilities and rights within criminal law procedures.
Definitions: What Is Reus?
Reus, in legal terminology, refers to the guilty party responsible for committing a crime or offense, emphasizing the individual's active role in the wrongful act. It denotes the person whose conduct aligns with the criminal elements defined by law, distinguishing them from mere suspects or witnesses. Understanding the concept of reus is crucial for determining liability and assigning criminal responsibility in judicial proceedings.
Understanding Detentus
Detentus refers to the status of being lawfully detained or imprisoned, often highlighted in legal contexts to distinguish lawful custody from wrongful detention. Understanding detentus involves recognizing the legal grounds, such as court orders or statutory authority, that justify holding an individual in confinement. This concept is critical in contrasting with "reus," which pertains to a person accused or convicted of a crime, as detentus emphasizes the legality of the physical restraint rather than guilt or innocence.
Legal Distinctions between Reus and Detentus
The legal distinctions between reus and detentus center on the nature of culpability and the context of detention. Reus refers to an individual who is criminally liable for an offense due to intentional wrongdoing or negligence, whereas detentus denotes a person unlawfully detained without personal culpability, often as a result of administrative or procedural errors. Jurisprudence defines reus through the presence of mens rea and actus reus, while detentus emphasizes wrongful restraint lacking criminal intent.
Historical Evolution of Reus and Detentus
Reus, originating from Roman law, evolved as the primary accused party in criminal proceedings, embodying the concept of culpability and responsibility for a crime. Detentus, historically rooted in detention practices, refers to individuals held in custody without formal charges or trial, reflecting evolving legal distinctions between accused persons and detainees. Over time, legal systems have refined the definitions and rights associated with reus and detentus, shaping modern criminal justice frameworks.
Reus in Criminal Proceedings
Reus, in criminal proceedings, refers to the defendant or accused party alleged to have committed a crime, whose guilt must be proven beyond reasonable doubt by the prosecution. The Reus has the right to fair trial, legal representation, and to challenge evidence presented by the detentus, who may be the detainee or person held in custody. The presumption of innocence applies to the Reus until the court establishes culpability through substantive and admissible evidence.
Detentus in the Justice System
Detentus refers to a person who is confined or restrained without formal charges or trial, often raising significant legal and human rights concerns within the justice system. The status of detentus challenges the principles of due process and habeas corpus, highlighting issues of indefinite detention and potential abuses of power. Legal frameworks strive to balance national security and public safety with safeguarding individual rights against unlawful or prolonged detention.
Rights and Responsibilities: Reus vs. Detentus
Reus refers to the accused or defendant in criminal law, bearing the responsibility to respond to charges and defend against prosecution. Detentus, commonly used in civil or administrative contexts, denotes an individual deprived of liberty, emphasizing the rights to challenge unlawful detention and seek due process. The fundamental distinction lies in reus's obligation to address criminal allegations, while detentus holds protections against arbitrary restraint and upholds rights to legal remedies.
Common Misconceptions about Reus and Detentus
Common misconceptions about reus and detentus often confuse their distinct legal roles, with reus specifically referring to the accused in criminal law, while detentus pertains to individuals unlawfully detained without formal charges. People frequently misunderstand that detentus implies guilt, though it strictly denotes a status of detention lacking legal justification. Clarifying these terms ensures accurate legal interpretation and protects against wrongful assumptions in judicial proceedings.
Conclusion: The Significance of Differentiating Reus and Detentus
Differentiating reus and detentus is crucial in legal contexts as it clarifies the roles and responsibilities of defendants versus mere possessors. Reus, as the accused party in criminal proceedings, bears direct liability for the alleged offense, whereas detentus refers to individuals who possess property or custody without criminal intent. Understanding this distinction ensures accurate application of justice and prevents wrongful prosecution or misclassification of involvement in criminal acts.
reus Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com