Amnesty offers a legal pardon for individuals or groups who have committed offenses, often aimed at promoting reconciliation and social harmony. It serves as a powerful tool for governments to restore peace and facilitate the reintegration of offenders into society. Discover how amnesty can impact your community and the broader implications by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
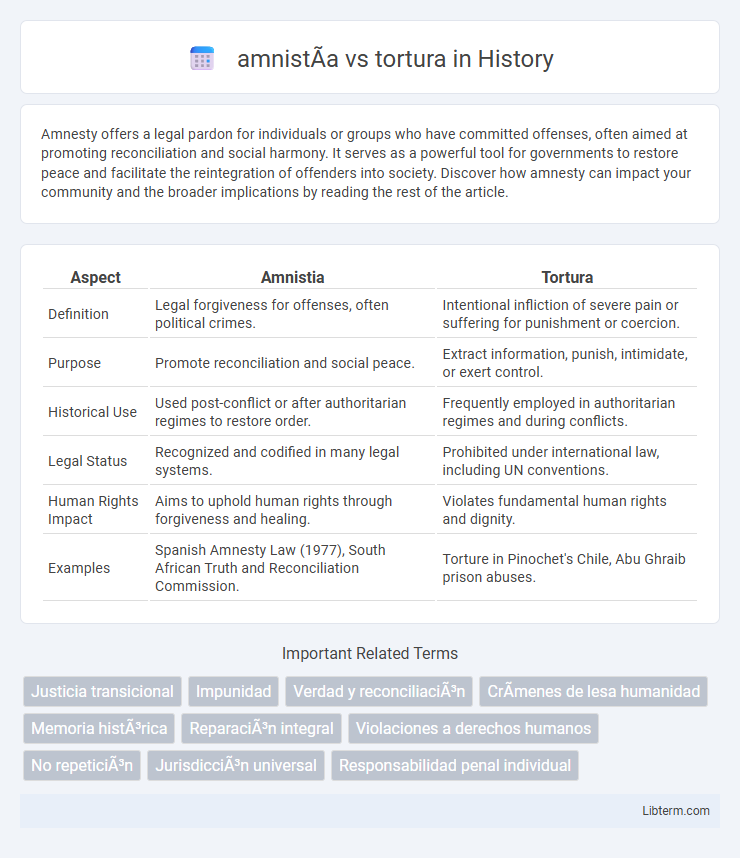
| Aspect | Amnistia | Tortura |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal forgiveness for offenses, often political crimes. | Intentional infliction of severe pain or suffering for punishment or coercion. |
| Purpose | Promote reconciliation and social peace. | Extract information, punish, intimidate, or exert control. |
| Historical Use | Used post-conflict or after authoritarian regimes to restore order. | Frequently employed in authoritarian regimes and during conflicts. |
| Legal Status | Recognized and codified in many legal systems. | Prohibited under international law, including UN conventions. |
| Human Rights Impact | Aims to uphold human rights through forgiveness and healing. | Violates fundamental human rights and dignity. |
| Examples | Spanish Amnesty Law (1977), South African Truth and Reconciliation Commission. | Torture in Pinochet's Chile, Abu Ghraib prison abuses. |
Definición de amnistía: concepto y alcance
Amnistia es una medida legal que implica el perdon y la eliminacion de responsabilidades penales por actos cometidos, generalmente con efectos retroactivos, abarcando delitos especificos dentro de un marco politico o social determinado. Su alcance varia segun la legislacion nacional, pero usualmente excluye crimenes de lesa humanidad como la tortura, que permanecen imprescriptibles y sujetos a sancion internacional. La distincion entre amnistia y tortura es crucial para mantener el cumplimiento de derechos humanos y evitar la impunidad en casos de violaciones graves.
Tortura: formas, consecuencias y legalidad
Tortura abarca diversas formas como la fisica, psicologica y sexual, que causan danos severos y prolongados en las victimas. Las consecuencias incluyen trastornos mentales, danos fisicos permanentes y la destruccion del tejido social y familiar. La legalidad internacional prohibe la tortura bajo la Convencion contra la Tortura de la ONU, con obligaciones claras para los Estados de prevenir, investigar y sancionar estos actos.
Marco legal internacional sobre amnistía y tortura
The international legal framework strictly prohibits amnesty for acts of torture under treaties such as the United Nations Convention Against Torture (UNCAT) and the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court, ensuring that perpetrators are held accountable. Various human rights bodies affirm that amnesty laws cannot shield individuals from prosecution for torture, as such acts constitute crimes against humanity. Judicial precedents reinforce the obligation of states to investigate, prosecute, and punish torture, rejecting any amnesty claims that undermine justice and victims' rights.
Derechos humanos: amnistía y protección contra la tortura
The principle of amnesty must never override the absolute prohibition of torture under international human rights law, as protecting human dignity and preventing cruel, inhuman, or degrading treatment are fundamental. Human rights frameworks prioritize accountability and victim protection, demanding that amnesty laws exclude cases involving torture to ensure justice and compliance with the United Nations Convention Against Torture. Effective legal safeguards and monitoring mechanisms are essential to uphold these rights, promoting both amnesty measures and the unyielding protection against torture without impunity.
Amnistía en casos de violaciones graves: dilemas éticos
Amnistia en casos de violaciones graves plantea dilemas eticos relacionados con la impunidad y la justicia para las victimas, especialmente en contextos de tortura sistematica. La liberacion de responsables mediante amnistias puede contravenir tratados internacionales como la Convencion contra la Tortura, que exige castigo y reparacion efectiva. Estos desafios subrayan la tension entre la busqueda de la paz y el respeto a los derechos humanos fundamentales en procesos de justicia transicional.
Impunidad vs. justicia: el debate sobre la amnistía
The debate on amnesty versus torture centers on the tension between impunity and justice, where amnesty often risks enabling perpetrators to evade accountability for human rights violations such as torture. Legal frameworks and international human rights bodies emphasize that granting amnesty in cases of torture undermines the rule of law and obstructs victims' right to reparations and truth. Ensuring justice requires rejecting amnesty provisions that perpetuate impunity and enforcing robust mechanisms to investigate, prosecute, and punish torture perpetrators.
Víctimas de tortura: acceso a la verdad y reparación
Victims of torture face significant barriers in accessing truth and reparations, with amnesty laws often obstructing justice by granting impunity to perpetrators. Comprehensive truth recovery mechanisms and effective reparation programs are essential to restore dignity and promote healing for torture survivors. International human rights frameworks emphasize the necessity of accountability and redress to uphold victims' rights and prevent recurrence.
Experiencias internacionales: amnistía y procesos de reconciliación
International experiences with amnesty in cases of torture reveal complex challenges where amnesty laws often clash with international human rights norms demanding accountability and justice for victims. Processes of reconciliation, such as those in South Africa's Truth and Reconciliation Commission, show that conditional amnesties tied to full disclosure can facilitate healing while maintaining a commitment to truth. Comparative studies emphasize the necessity of balancing restorative justice mechanisms with victims' rights to memory and reparations to prevent impunity and promote long-term societal peace.
El papel de la sociedad civil ante la amnistía y la tortura
La sociedad civil juega un papel crucial en la defensa de los derechos humanos al denunciar la tortura y exigir la no aplicacion de amnistias que protejan a los responsables. Movimientos sociales, ONGs y organismos internacionales impulsan mecanismos de justicia transicional que aseguren la reparacion y la verdad. La presion colectiva contribuye a la implementacion de politicas que previenen la impunidad y fortalecen el Estado de derecho.
Alternativas a la amnistía: justicia transicional y garantías de no repetición
Justice transitional mechanisms offer effective alternatives to amnesty by prioritizing truth, accountability, and reparations for torture victims, ensuring comprehensive redress. Guarantees of non-repetition include institutional reforms, legal safeguards, and education programs designed to prevent future human rights violations. These alternatives strengthen democratic institutions and promote long-term societal healing without compromising justice.
amnistía Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com