The formation of a kingdom represents a pivotal stage in political organization, characterized by centralized authority under a monarch. Understanding the historical evolution and governance structures of kingdoms reveals insights into cultural development and social hierarchies. Explore the article to uncover how kingdoms have shaped civilizations and what their legacy means for your perspective on power and society.
Table of Comparison
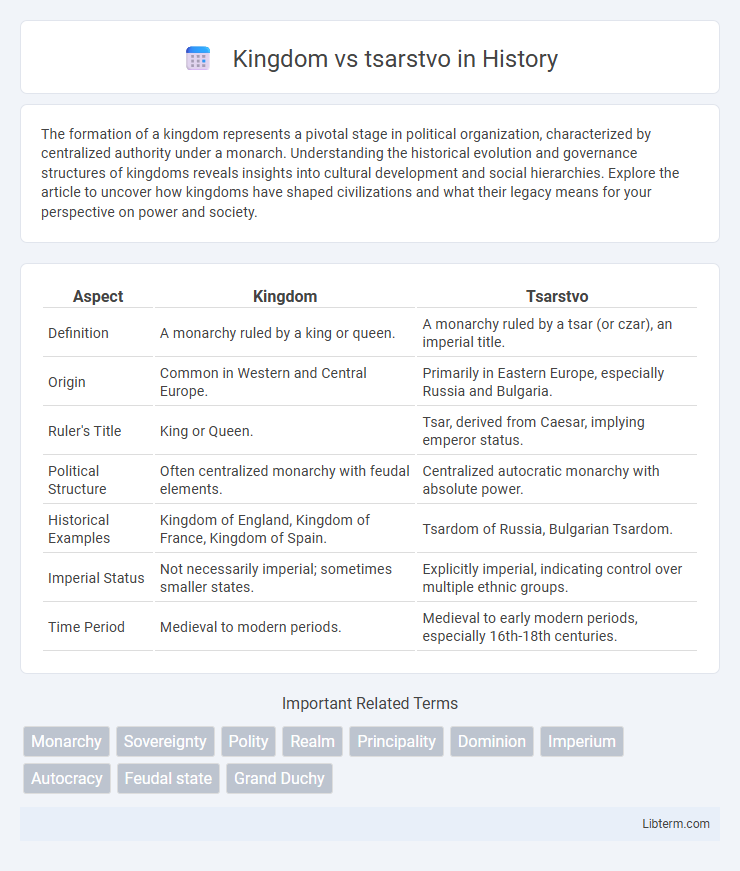
| Aspect | Kingdom | Tsarstvo |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A monarchy ruled by a king or queen. | A monarchy ruled by a tsar (or czar), an imperial title. |
| Origin | Common in Western and Central Europe. | Primarily in Eastern Europe, especially Russia and Bulgaria. |
| Ruler's Title | King or Queen. | Tsar, derived from Caesar, implying emperor status. |
| Political Structure | Often centralized monarchy with feudal elements. | Centralized autocratic monarchy with absolute power. |
| Historical Examples | Kingdom of England, Kingdom of France, Kingdom of Spain. | Tsardom of Russia, Bulgarian Tsardom. |
| Imperial Status | Not necessarily imperial; sometimes smaller states. | Explicitly imperial, indicating control over multiple ethnic groups. |
| Time Period | Medieval to modern periods. | Medieval to early modern periods, especially 16th-18th centuries. |
Defining "Kingdom" and "Tsarstvo": Etymology and Origins
A "Kingdom" derives from the Old English "cyningdom," meaning the domain ruled by a king, rooted in Germanic traditions emphasizing hereditary monarchy and territorial governance. The term "Tsarstvo" comes from the Slavic word "tsar," itself originating from the Latin "Caesar," signifying imperial authority and often associated with Eastern European and Russian realms. Both terms denote sovereign states but reflect distinct cultural and historical lineages shaping their political and linguistic identities.
Historical Evolution of Kingdoms and Tsarstva
Kingdoms originated in early medieval Europe as centralized states ruled by monarchs, evolving through feudal systems and dynastic succession. Tsarstva, notably in Russia and Eastern Europe, developed from principalities under Byzantine and Mongol influences, with the title "tsar" symbolizing imperial authority linked to Roman and Orthodox traditions. The historical evolution of kingdoms and tsarstva reflects distinct political, cultural, and religious trajectories shaping their governance and territorial expansion.
Geographical Context: Where Kingdoms and Tsarstva Flourished
Kingdoms predominantly flourished in Western and Central Europe, with notable examples including the Kingdom of England, Kingdom of France, and Kingdom of Spain. Tsarstva, or tsardoms, were primarily established in Eastern Europe and Northern Eurasia, particularly within the territories of Russia and Bulgaria. The distinct geographical contexts reflect the differing cultural, political, and historical developments shaping these forms of monarchy.
Political Structure: Hierarchy and Governance
Kingdoms typically feature a centralized monarchy led by a king or queen, with a clear, hereditary hierarchy involving nobles, lords, and vassals who govern distinct territories under the monarch's authority. Tsarstvo, a term often associated with Russian autocracy, denotes an imperial governance system where the tsar wields absolute power, combining executive, legislative, and judicial functions with limited aristocratic delegation. The political structure in a tsarstvo emphasizes centralized control with fewer intermediary governing bodies compared to the often more decentralized feudal hierarchy seen in kingdoms.
Roles and Titles: Kings vs. Tsars
Kings traditionally serve as sovereign rulers of kingdoms, often inheriting their position by birthright within a hereditary monarchy, and their authority is frequently linked to divine right or constitutional frameworks depending on the region. Tsars were Autocratic emperors mainly in Russia and Bulgaria, symbolizing supreme power with both political and religious authority, derived from the Byzantine tradition and the concept of Orthodox Christian leadership. The title of Tsar connotes a higher imperial status compared to kings, implying broader territorial control and absolute governance over a diverse empire.
Religion and Cultural Influence in Kingdoms and Tsarstva
Kingdoms often aligned their religious institutions closely with the monarchy, using religion to legitimize royal authority and unify diverse populations under a common faith, such as Christianity in medieval European kingdoms. Tsarstva, particularly in Russia, integrated the Orthodox Church deeply into state governance, making the tsar both a political and spiritual leader, which reinforced a unique cultural identity distinct from Western Europe. This intertwining of religion and culture in tsarstva shaped social norms, art, and law, creating a centralized, theocratic influence that permeated all aspects of life.
Notable Examples: Famous Kingdoms and Tsarstva in History
Notable examples of kingdoms include the Kingdom of England, the Kingdom of France, and the Kingdom of Spain, each known for their influential monarchies and role in shaping European history. Famous tsarstva (tsardoms) include the Tsardom of Russia, which evolved into the Russian Empire, and the Tsardom of Bulgaria, recognized for their autocratic rulers titled tsars. The distinction lies in the cultural and political origins, with kingdoms commonly found in Western Europe and tsarstva in Eastern Europe and Russia.
Kingdom vs. Tsarstvo: Key Differences and Similarities
Kingdom and Tsarstvo both denote sovereign states ruled by monarchs, but Kingdom typically refers to Western European monarchies led by kings or queens, while Tsarstvo is a Slavic term specifically associated with Russian or Eastern European empires ruled by a tsar. Key differences include cultural and historical contexts, with Kingdoms often rooted in feudal traditions and Tsarstvo linked to autocratic rule and Orthodox Christianity. Similarities involve centralized royal authority, hereditary leadership, and the significance of monarchical titles in legitimizing power and governance.
Impact on Modern States and Contemporary Terminology
The distinction between "Kingdom" and "Tsarstvo" highlights different historical legacies that shape modern states, with kingdoms often linked to Western European monarchies influencing parliamentary democracy development, while Tsarstvo relates primarily to Russian and Slavic autocratic traditions affecting centralized state governance. Contemporary terminology reflects these roots: "kingdom" remains prevalent in constitutional monarchies such as the United Kingdom and Saudi Arabia, whereas "tsarstvo" is less commonly used but informs Russia's imperial history and cultural identity. This semantic differentiation influences modern political narratives and national identity constructions in post-monarchical societies.
Legacy and Symbolism: Kingdoms and Tsarstva in Today's World
Kingdoms evoke a legacy of medieval European monarchies that symbolize unity, heritage, and centralized sovereignty, often reflected in constitutional monarchies like the United Kingdom. Tsarstva, rooted in Eastern Slavic traditions such as the Russian Empire, carry symbolism tied to autocratic power, Orthodox Christianity, and imperial expansion. In today's world, kingdoms primarily represent historical continuity and national identity, while tsarstva underscore a complex legacy of cultural influence and political authority.
Kingdom Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com