Anarchy refers to a state of society without government or hierarchical authority, often associated with political and social disorder. It challenges traditional structures of power, advocating for self-managed, stateless communities based on voluntary cooperation. Explore the article to understand how anarchy influences modern political thought and social movements.
Table of Comparison
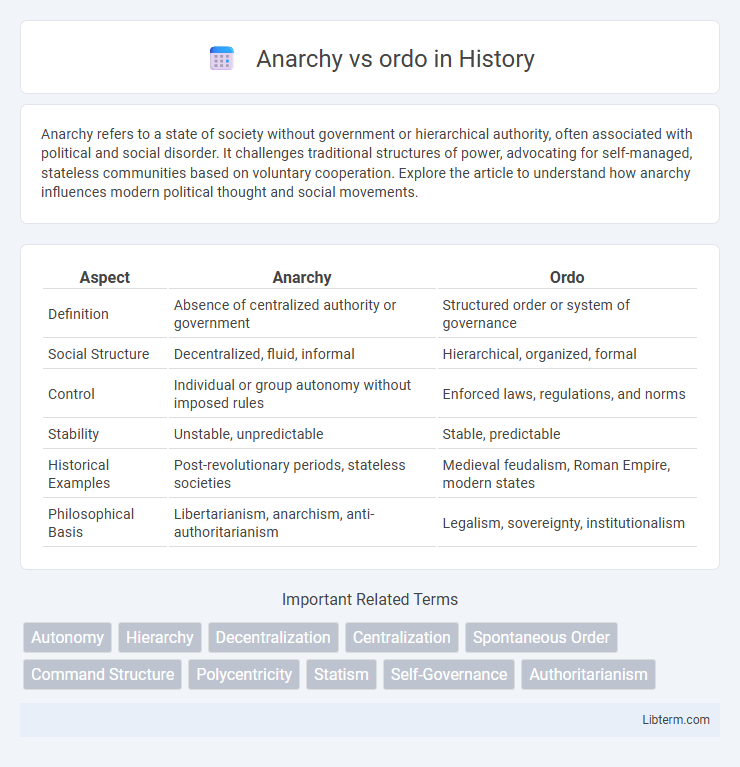
| Aspect | Anarchy | Ordo |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Absence of centralized authority or government | Structured order or system of governance |
| Social Structure | Decentralized, fluid, informal | Hierarchical, organized, formal |
| Control | Individual or group autonomy without imposed rules | Enforced laws, regulations, and norms |
| Stability | Unstable, unpredictable | Stable, predictable |
| Historical Examples | Post-revolutionary periods, stateless societies | Medieval feudalism, Roman Empire, modern states |
| Philosophical Basis | Libertarianism, anarchism, anti-authoritarianism | Legalism, sovereignty, institutionalism |
Introduction to Anarchy and Ordo
Anarchy represents a state of disorder where no governing authority enforces rules, leading to decentralized power and spontaneous social order. Ordo, derived from Latin meaning "order," signifies structured governance and regulated institutions designed to maintain social stability and hierarchy. These contrasting concepts highlight the debate between freedom without control and organized systems enforcing laws and norms.
Defining Anarchy: Core Principles and Concepts
Anarchy is defined by the absence of a centralized authority, emphasizing voluntary cooperation, self-governance, and the rejection of hierarchical structures. Core principles include individual autonomy, mutual aid, and decentralized decision-making, fostering a society based on freedom and equality without imposed order. This contrasts with ordo, which advocates structured governance and legal frameworks to maintain social and economic stability.
Understanding Ordo: Meaning and Historical Context
Ordo refers to a system of order and hierarchy that contrasts sharply with anarchy's lack of centralized control. Historically, Ordo is rooted in medieval and early modern European frameworks where social, political, and religious structures maintained stability and governance. This concept emphasizes authority, rules, and organized institutions as essential for societal coherence and functioning.
Key Philosophies Behind Anarchy
Anarchy centers on the philosophy that rejects all forms of hierarchical authority, advocating for a self-managed society free from centralized government and coercive institutions. Its key principles emphasize voluntary cooperation, mutual aid, and individual autonomy as foundations for social organization. The belief in dismantling state power contrasts sharply with ordo liberalism, which upholds structured legal frameworks to maintain order and economic stability.
The Structure and Ideals of Ordo
Ordo emphasizes a hierarchical structure characterized by clear roles, rules, and authority to maintain social order and stability. It prioritizes institutional frameworks and governance systems that ensure coordination and predictability within society. Central to Ordo is the ideal of organized control to prevent chaos and promote collective well-being through structured regulation.
Anarchy vs Ordo: Social and Political Comparisons
Anarchy and ordo represent contrasting political and social philosophies with anarchy advocating for the absence of hierarchical authority and state control, emphasizing individual freedom and voluntary cooperation. Ordo, rooted in the concept of order, supports structured governance and legal frameworks to maintain social stability and economic regulation. These opposing views reflect debates over the role of the state in balancing freedom with order within societies.
Benefits and Challenges of Embracing Anarchy
Embracing anarchy promotes individual freedom and spontaneous order, allowing self-organization without centralized authority, which can lead to innovative problem-solving and reduced bureaucratic inefficiencies. However, challenges include potential instability, difficulties in maintaining public safety, and the risk of power vacuums that could foster conflict or exploitation. Balancing the benefits of decentralized governance with mechanisms for conflict resolution remains critical to maximizing the advantages of anarchic systems.
Advantages and Limitations of Ordo
Ordo, as a structured system of governance, ensures stability and predictability by establishing clear rules and institutions that regulate social and economic interactions. Its advantages include efficient conflict resolution, protection of property rights, and promotion of cooperation within a community. However, Ordo may face limitations such as rigidity in adapting to rapid societal changes and potential oppression due to centralized authority limiting individual freedoms.
Real-World Examples: Anarchy and Ordo in Practice
Anarchy in practice is often observed in regions experiencing state collapse or weak governance, such as Somalia after 1991, where the absence of a centralized authority led to fragmented rule by warlords and clan militias. Ordo, representing structured order, is exemplified by the European Union, which maintains a complex network of legal frameworks, regulations, and institutions to ensure cooperation, stability, and rule of law among member states. These real-world cases highlight the stark contrast between decentralized chaos and organized governance, impacting economic development, security, and social cohesion.
Conclusion: Balancing Chaos and Order in Society
Balancing chaos and order in society requires integrating the flexibility of anarchy with the stability of ordo to foster resilience and innovation. Effective social systems combine decentralized autonomy with structured governance to adapt to complex challenges while maintaining harmony. Sustainable progress depends on dynamic equilibrium where freedom and regulation coexist, ensuring societal well-being without sacrificing individual agency.
Anarchy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com