Vicus refers to a type of ancient Roman settlement or neighborhood, often characterized by a small community with distinct local customs and markets. These settlements served as hubs for social, economic, and religious activities within larger Roman cities or rural areas. Explore the rest of the article to uncover how vicus shaped everyday life in ancient Rome.
Table of Comparison
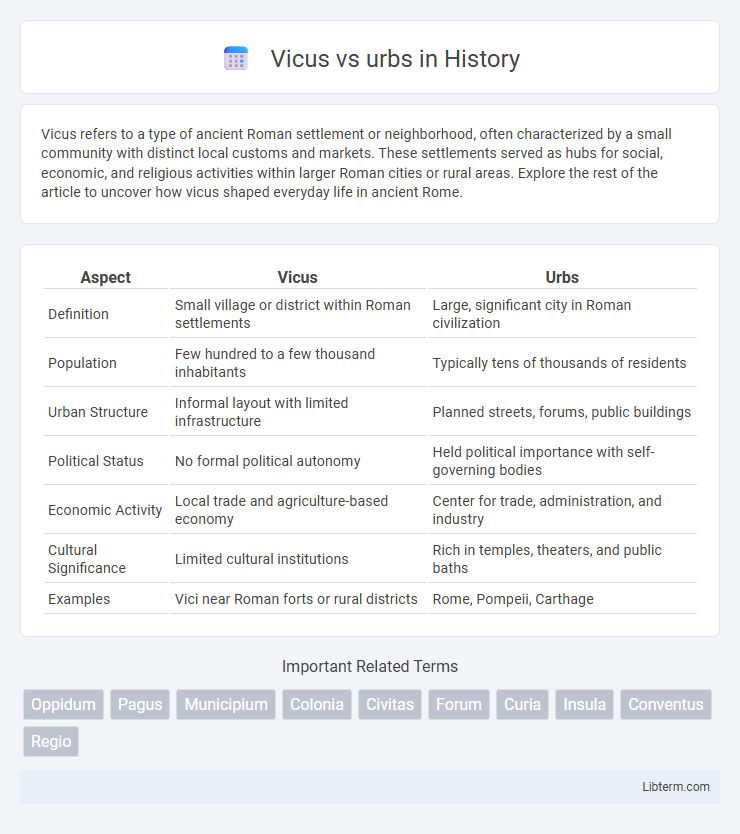
| Aspect | Vicus | Urbs |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Small village or district within Roman settlements | Large, significant city in Roman civilization |
| Population | Few hundred to a few thousand inhabitants | Typically tens of thousands of residents |
| Urban Structure | Informal layout with limited infrastructure | Planned streets, forums, public buildings |
| Political Status | No formal political autonomy | Held political importance with self-governing bodies |
| Economic Activity | Local trade and agriculture-based economy | Center for trade, administration, and industry |
| Cultural Significance | Limited cultural institutions | Rich in temples, theaters, and public baths |
| Examples | Vici near Roman forts or rural districts | Rome, Pompeii, Carthage |
Introduction: Defining Vicus and Urbs
Vicus and Urbs represent distinct forms of settlement in ancient Roman urbanism, with Vicus referring to smaller villages or neighborhoods often situated on the outskirts, while Urbs denotes the larger, formal city center characterized by complex infrastructure and governance. The Vicus typically functioned as a local community hub with limited administrative roles, contrasting with the Urbs, which was the political, economic, and cultural heart of Roman civilization. Understanding the semantic differences between Vicus and Urbs highlights their roles in the spatial and social organization of Roman territory.
Etymology and Historical Context
The term *vicus* originates from Latin, meaning a smaller settlement or neighborhood, often a village or district, while *urbs* denotes a large, formal city with established administrative and political structures in ancient Rome. Historically, a *vicus* functioned as a subdivision within or outside the *urbs*, serving local communities before urban expansion transformed some into significant towns. Understanding the etymology highlights how Roman urban planning distinguished between the organic growth of settlements (*vici*) and the centralized organization of *urbes*.
Geographic Distribution in Ancient Rome
The term "vicus" referred to smaller neighborhood districts or rural settlements situated mainly in the outskirts or less urbanized regions of Ancient Rome, while "urbs" denoted the central, densely populated urban area of the city of Rome itself. Geographic distribution reveals that vici were dispersed throughout the Roman Empire, often serving as local administrative or market centers in both urban peripheries and provincial towns. The urbs concentrated political, religious, and economic activities within Rome's city walls, emphasizing its role as the empire's capital and hub.
Structural and Urban Design Differences
Vicus refers to a small, often rural settlement characterized by organic, irregular street patterns and low-density housing, while urbs denotes a planned city with well-defined grids, systematic zoning, and higher-density infrastructure. Structural design in a vicus emphasizes simplicity and adaptability to terrain, featuring clustered buildings and limited public spaces, whereas an urbs incorporates complex architectural planning, including public forums, aqueducts, and road networks. Urban design differences highlight the vicus' role as a local, community-centric hub versus the urbs' function as a regional center of administration, commerce, and culture.
Social Composition and Population
Vicus and urbs differ significantly in social composition and population size, with vicus representing small rural settlements typically housing interconnected families engaged in agriculture, crafts, or trade. Urban centers or urbs exhibit complex social hierarchies featuring diverse groups such as merchants, artisans, administrators, and elites, supporting a large, densely packed population. Population in a vicus rarely exceeds a few hundred, whereas an urbs accommodates thousands, reflecting advanced infrastructure and economic specialization.
Economic Roles and Functions
Vicus were small rural settlements primarily serving as local trading hubs and artisanal centers, facilitating commerce and agricultural exchange within Roman provinces. Urbs, or cities, functioned as major economic centers with complex infrastructures supporting large-scale trade, manufacturing, administrative activities, and financial markets. The economic roles of vicus emphasized localized production and distribution, whereas urbs controlled broader commercial networks and resource management.
Political Status and Local Governance
Vicus represented a small rural settlement with limited political autonomy, often governed by local magistrates under the authority of a larger urbs or colonia within Roman administrative structure. In contrast, an urbs was a significant urban center with established municipal institutions, including elected magistrates, local senates (curia), and the authority to enact laws, collect taxes, and maintain public services independently. The political status of an urbs granted it greater self-governance and direct interaction with the Roman state, whereas a vicus remained dependent on regional urban authorities for political decisions and administrative oversight.
Daily Life in Vicus versus Urbs
Daily life in a vicus centered on small-scale agriculture, artisanal crafts, and local trade, with residents living in close-knit communities often dependent on nearby urban centers for specialized goods. In contrast, urban life in an urbs featured diverse economic activities, including commerce, administration, and entertainment, supported by complex infrastructure such as aqueducts, forums, and amphitheaters. While vici residents experienced a slower, rural rhythm with limited amenities, urban dwellers enjoyed access to public baths, theaters, and marketplaces, reflecting greater social stratification and cultural opportunities.
Cultural Significance in Roman Society
In Roman society, the distinction between vicus and urbs held deep cultural significance, with the urbs representing the political and religious heart of Rome as the seat of imperial authority and grand architecture. The vicus, by contrast, functioned as smaller, localized communities or neighborhoods that fostered close-knit social interactions and preserved traditional customs within the broader urban framework. This dynamic underscored the complex layers of Roman identity, blending centralized power in the urbs with the diverse, grassroots cultural expressions found in each vicus.
Legacy and Influence on Modern Urban Planning
The distinction between vicus and urbs significantly shapes the legacy of Roman urbanism, where vicus served as rural or suburban settlements and urbs as comprehensive city centers with political, economic, and social functions. This duality influenced modern urban planning by emphasizing hierarchical spatial organization, integrating residential, commercial, and administrative zones into cohesive city designs. Contemporary planners draw on Roman principles of connectivity, infrastructure, and multifunctionality rooted in the vicus-urbs framework to create sustainable and well-structured urban environments.
Vicus Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com