A steward plays a vital role in managing resources efficiently, ensuring smooth operations whether on a ship, aircraft, or within an organization. Their responsibilities often include overseeing supplies, coordinating staff, and maintaining safety standards to enhance overall service quality. Discover how understanding the duties of a steward can benefit your experience in various industries by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
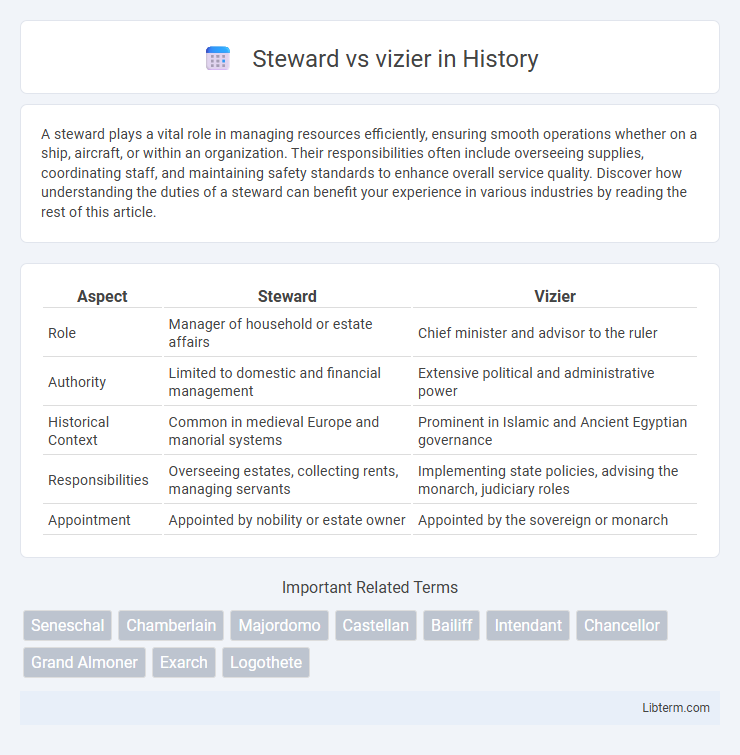
| Aspect | Steward | Vizier |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Manager of household or estate affairs | Chief minister and advisor to the ruler |
| Authority | Limited to domestic and financial management | Extensive political and administrative power |
| Historical Context | Common in medieval Europe and manorial systems | Prominent in Islamic and Ancient Egyptian governance |
| Responsibilities | Overseeing estates, collecting rents, managing servants | Implementing state policies, advising the monarch, judiciary roles |
| Appointment | Appointed by nobility or estate owner | Appointed by the sovereign or monarch |
Introduction to Steward vs Vizier
A steward and a vizier are both high-ranking officials in historical governance, but they differ significantly in terms of roles and authority. A steward typically managed the domestic affairs and estates on behalf of a monarch or noble, focusing on administrative tasks and resource oversight. In contrast, a vizier was often the chief advisor or prime minister in Islamic or Middle Eastern states, wielding extensive political power and influencing state governance and policy decisions.
Historical Origins of Stewards and Viziers
Stewards and viziers both originated as key administrative officials in ancient civilizations, with stewards often emerging in European feudal societies to manage estates and royal households, while viziers appeared in Middle Eastern and North African cultures as high-ranking political advisors and chief ministers. The role of stewards dates back to medieval Europe, where their responsibilities evolved from overseeing domestic affairs to broader administrative duties within noble estates. Viziers trace their lineage to ancient Egypt and the Islamic caliphates, where they held significant authority in governance, often acting as the ruler's principal executive officer.
Roles and Responsibilities: Stewardship Explained
A steward in medieval governance was responsible for managing household affairs and finances, overseeing estate operations, and ensuring resource allocation efficiency. A vizier, primarily in Islamic and Egyptian contexts, held higher political authority, serving as the chief minister who advised the ruler, administered state affairs, and executed governmental policies. While both roles involved management and oversight, the steward focused on domestic and estate management, whereas the vizier functioned as a top-level political advisor and executive.
Viziers: Power and Influence in Ancient Societies
Viziers in ancient societies wielded immense power as chief advisors and administrators, often overseeing the entire bureaucracy and serving as the sovereign's right hand. Their influence extended beyond mere governance to include judicial authority, economic control, and religious duties, making them pivotal figures in state stability and policy implementation. Unlike stewards, whose roles were primarily limited to managing estates or household affairs, viziers operated at the highest level of political hierarchy, shaping laws and directing military campaigns across empires such as Ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia, and the Islamic Caliphates.
Key Differences between Stewards and Viziers
Stewards primarily managed domestic affairs and resources within royal households, acting as estate administrators responsible for budgeting, provisioning, and overseeing servants. Viziers held higher political authority, often serving as the chief advisor to the ruler with broad powers over government policy, judicial matters, and military administration. The key difference lies in the scope of influence: stewards focused on internal household management while viziers exercised extensive state governance and executive duties.
Stewards in European Feudal Systems
Stewards in European feudal systems were crucial officials responsible for managing the household and estates of a noble or monarch, overseeing financial affairs, resource allocation, and administration. Unlike viziers, who typically held expansive political and governmental authority in Islamic states, stewards operated primarily within the domestic and manorial domain. Their role ensured efficient estate management, facilitating wealth accumulation and stability necessary for feudal lordship and governance.
Viziers in Middle Eastern and North African Empires
Viziers held significant power in Middle Eastern and North African empires as chief advisors and administrators, often overseeing state affairs, judiciary, and military operations. Unlike stewards primarily responsible for managing estates or household finances, viziers acted as the ruler's right hand, executing royal decrees and coordinating complex bureaucracy across vast territories. Their role was crucial in ensuring political stability and implementing governance policies in empires such as the Ottoman, Fatimid, and Seljuk dynasties.
Case Studies: Famous Stewards and Viziers
Prominent stewards like Joseph of Egypt managed royal estates and acted as chief administrators under Pharaoh, showcasing the steward's role in resource allocation and governance. In contrast, famous viziers such as Imhotep served as chief ministers in ancient Egypt, overseeing justice, administration, and advisor duties directly under the pharaoh's authority. Case studies of these figures reveal stewards primarily handled household and economic affairs, while viziers conducted higher-level state governance and legal responsibilities.
Impact on Governance and Administration
Stewards and viziers played crucial roles in governance and administration, with stewards often overseeing domestic management and resource allocation within royal households, while viziers held broader authority over state bureaucracy and policy implementation. Viziers typically acted as the chief ministers, directing legal systems, tax collection, and military affairs, thereby shaping centralized administration and long-term state stability. The contrasting scopes of their duties influenced governance structures, where viziers ensured cohesive state control and stewards maintained efficient household management crucial for sustaining royal power.
Legacy and Modern Interpretations
The legacy of stewards and viziers is deeply rooted in their roles as powerful administrative officials in ancient civilizations, with stewards primarily managing estates or households and viziers acting as chief ministers overseeing state affairs. Modern interpretations emphasize the steward's role in responsible resource management and servant leadership, while viziers are often studied as early examples of bureaucratic governance and political influence. Historical texts and contemporary analyses highlight their contributions to administrative systems, influencing modern concepts of public administration and organizational leadership.
Steward Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com