Duke University stands as a prestigious institution known for its rigorous academic programs and vibrant campus life. Renowned for cutting-edge research and a commitment to innovation, it offers diverse opportunities for personal growth and professional development. Explore the full article to discover how Duke can elevate your educational journey and future career.
Table of Comparison
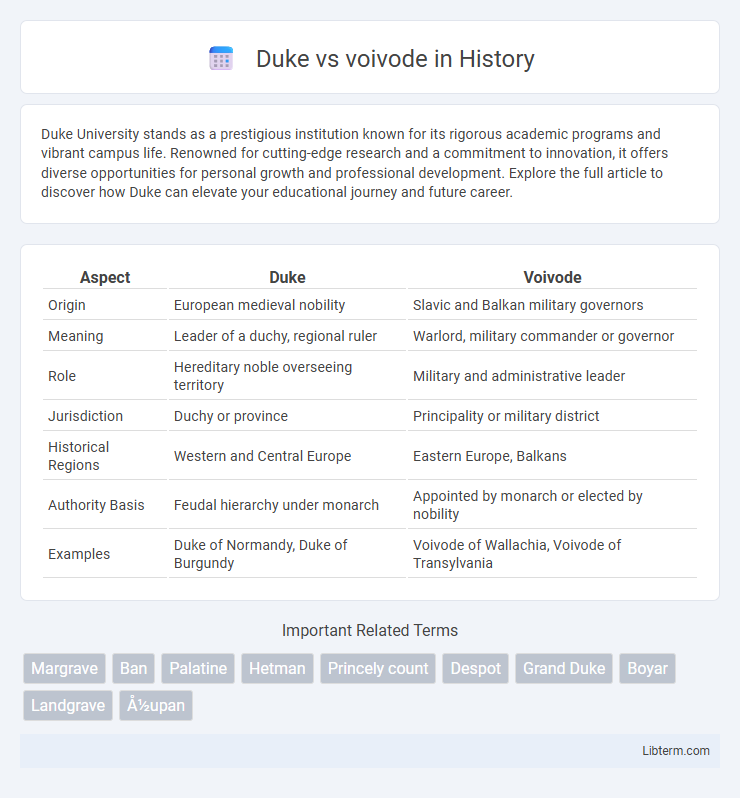
| Aspect | Duke | Voivode |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | European medieval nobility | Slavic and Balkan military governors |
| Meaning | Leader of a duchy, regional ruler | Warlord, military commander or governor |
| Role | Hereditary noble overseeing territory | Military and administrative leader |
| Jurisdiction | Duchy or province | Principality or military district |
| Historical Regions | Western and Central Europe | Eastern Europe, Balkans |
| Authority Basis | Feudal hierarchy under monarch | Appointed by monarch or elected by nobility |
| Examples | Duke of Normandy, Duke of Burgundy | Voivode of Wallachia, Voivode of Transylvania |
Introduction: Understanding Duke and Voivode
A duke is a noble title historically signifying a ruler of a duchy, often recognized within European aristocracy with hereditary or appointed authority. A voivode is a Slavic military leader or provincial governor, commonly associated with Eastern Europe, especially in medieval Poland, Romania, and the Balkans. Both titles denote regional control but differ in cultural origins, governance structures, and military roles.
Etymology: Origins of “Duke” and “Voivode”
The term "Duke" originates from the Latin "dux," meaning "leader" or "commander," historically used in the Roman Empire to denote military commanders and later adopted as a noble title across Europe. "Voivode" derives from the Slavic roots "voi" (meaning "war" or "army") and "voda" (meaning "leader"), signifying a military leader or warlord in Eastern European regions, particularly in medieval Poland, Romania, and the Balkans. Both titles reflect a martial leadership role but emerge from distinct linguistic and cultural traditions that shaped their regional authority and governance.
Historical Contexts: Western vs Eastern Europe
In Western Europe, a duke was a high-ranking noble who ruled a duchy with significant autonomy under a monarchy, often playing a key role in feudal hierarchies during the Middle Ages. In contrast, the voivode in Eastern Europe, particularly in regions like Poland, Hungary, and Romania, was a military leader or provincial governor with both civil and military authority, managing borderlands and defending territories against invasions. While dukes emphasized hereditary nobility and territorial control, voivodeship roles combined military command with administrative governance, reflecting the distinct political and social structures of Eastern European states.
Roles and Functions: Duties of a Duke vs a Voivode
A Duke traditionally governed a duchy, overseeing administrative, military, and judicial responsibilities while acting as a key advisor to the monarch. A Voivode served as a military commander and regional governor, often entrusted with defending border territories and maintaining local order. While Dukes exercised broader civil authority, Voivodes focused more intensively on military leadership and regional defense within feudal hierarchies.
Social Status and Authority
A duke typically held higher social status and greater territorial authority than a voivode, often ruling over a duchy with hereditary rights recognized by a monarchy or empire. Voivodes were military commanders or regional governors with delegated power, commonly appointed by a sovereign to oversee provinces, especially in Eastern Europe. While dukes exercised autonomous or semi-autonomous control with significant political influence, voivodes primarily acted as administrators or military leaders under the authority of a higher ruler.
Military Influence and Leadership
Dukes historically wielded considerable military influence, commanding regional armies and leading troops in battles, which often shaped the political landscape of medieval Europe. Voivodes, particularly in Eastern Europe, served as military governors or warlords tasked with defense and administration of border territories, combining strategic leadership with direct combat roles. Both titles emphasized leadership in warfare, but voivodes typically held responsibilities that blended civil authority with military command, reinforcing their critical role in regional defense.
Governance Structures and Territories
Dukes governed large, semi-autonomous regions within medieval European kingdoms, often holding hereditary titles that combined military, judicial, and administrative powers. Voivodes, primarily found in Eastern Europe, were military governors or regional rulers appointed by monarchs, overseeing provinces called voivodeships with responsibilities including defense and local administration. Unlike dukes, who often inherited their positions, voivodes' authority was typically granted and could be more directly controlled by the central monarchy.
Symbolism and Cultural Significance
The title of Duke traditionally symbolizes regional sovereignty and noble authority within medieval European hierarchy, often linked to military leadership and governance over a duchy. In contrast, the voivode represents a Slavic military commander or provincial governor, embodying both administrative power and warrior ethos, crucial in Eastern European cultural contexts. These titles carry deep cultural significance, reflecting distinct historical identities and the interplay between military duty and political legitimacy in their respective regions.
Modern Usage and Legacy
Duke titles in modern usage often denote hereditary nobility with ceremonial roles across European monarchies, while voivode remains a functional administrative or military position mainly in Eastern Europe, such as Poland and Romania. The legacy of dukes is embedded in the aristocratic hierarchy, influencing contemporary peerage systems and cultural traditions. Voivodeship regions preserve the historical governance structure, maintaining a blend of traditional authority and localized administration.
Key Differences: Duke vs Voivode Compared
Dukes traditionally held hereditary noble titles within Western European feudal systems, governing specific territories with both administrative and military authority tied to royal hierarchy. Voivodes, prevalent in Eastern Europe and Slavic regions, acted as military commanders or provincial governors appointed by central rulers, often blending civil and military responsibilities. The key difference lies in the Duke's typically hereditary status and Western context contrasted with the Voivode's appointed role and Eastern European origin, emphasizing variations in governance and authority structures.
Duke Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com