Canonry offers a unique blend of historical significance and architectural beauty, often serving as residences for clergy within cathedral precincts. These estates provide insight into ecclesiastical life and the church's influence on local communities through the centuries. Explore the rest of the article to discover how canonries continue to shape cultural heritage today.
Table of Comparison
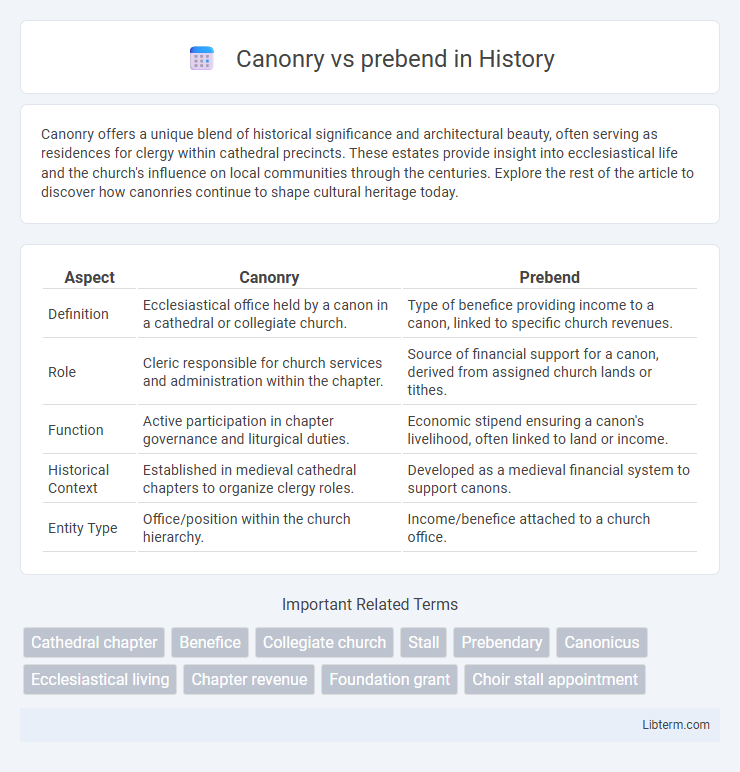
| Aspect | Canonry | Prebend |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ecclesiastical office held by a canon in a cathedral or collegiate church. | Type of benefice providing income to a canon, linked to specific church revenues. |
| Role | Cleric responsible for church services and administration within the chapter. | Source of financial support for a canon, derived from assigned church lands or tithes. |
| Function | Active participation in chapter governance and liturgical duties. | Economic stipend ensuring a canon's livelihood, often linked to land or income. |
| Historical Context | Established in medieval cathedral chapters to organize clergy roles. | Developed as a medieval financial system to support canons. |
| Entity Type | Office/position within the church hierarchy. | Income/benefice attached to a church office. |
Introduction to Canonry and Prebend
Canonry refers to the position held by a canon, a clergy member serving in a cathedral or collegiate church, often tied to specific duties and responsibilities within the ecclesiastical chapter. A prebend is the stipend or income assigned to a canon, derived from designated church revenues or estates, enabling the canon to sustain their clerical role. Understanding the relationship between canonry and prebend highlights the organizational and financial structures underpinning medieval and early modern church governance.
Historical Origins of Canonry and Prebend
Canonries originated in the early medieval church as positions held by clergy attached to a cathedral or collegiate church, serving both liturgical and administrative functions. Prebends developed concurrently as a form of income assigned to canons, derived from specific estates or revenues to support their ecclesiastical duties. The historical distinction lies in canonry representing the office or role within the church, while prebend refers to the financial endowment enabling the canon's sustenance.
Definition and Legal Basis of Canonry
A canonry is a specific ecclesiastical office held by a canon within a cathedral or collegiate church, defined by its entitlement to a prebend, which is the stipend or property allocated for the canon's maintenance. The legal basis of a canonry is grounded in canon law and ecclesiastical statutes that regulate the rights, duties, and revenue distribution tied to the office, ensuring clerical support and church governance. Unlike a prebend itself, which refers primarily to the benefice or income, the canonry encompasses both the role of the cleric and the attached prebendal rights.
Definition and Legal Basis of Prebend
A canonry refers to a position held by a canon within a cathedral or collegiate church, involving specific duties and rights, whereas a prebend is the stipend or income assigned to a canon, often derived from church revenues. The legal basis of a prebend is rooted in ecclesiastical law, which allocates a portion of church property revenues to support a canon's livelihood and enable them to perform their religious functions. Prebendal endowments are typically documented in church statutes or charters, ensuring financial provision tied to specific ecclesiastical roles or offices.
Key Differences Between Canonry and Prebend
A canonry refers to a position held by a canon, a clergy member attached to a cathedral or collegiate church, responsible for religious duties and administration. A prebend is the stipend or income granted to a canon, sourced from church revenues or estates, to support their office. The key difference lies in canonry being the office or role, while prebend denotes the financial endowment associated with that role.
Roles and Responsibilities of Canons
Canons serve as senior clergy members in a cathedral or collegiate church, responsible for maintaining the daily worship and administration of church affairs, while prebends primarily refer to the financial endowments granted to these clergy members. The role of canons includes participating in chapter meetings, overseeing liturgical functions, and managing the cathedral's property and charitable activities. Unlike prebendaries, who simply receive income from their prebend, canons hold specific duties aimed at sustaining the spiritual and organizational integrity of the ecclesiastical institution.
Financial Aspects: Canonry vs Prebend
A canonry typically provides a fixed stipend or income derived from the revenues of a cathedral or collegiate church, ensuring stable financial support for the canon's duties. In contrast, a prebend is a specific type of benefice linked to designated church lands or properties, generating revenue that funds the prebendary's stipend, often varying with the income from those assets. Financially, canonries offer more predictable earnings through established allocations, while prebends depend on the fluctuating income of assigned estates or tithes.
Importance in Ecclesiastical Hierarchy
Canonries and prebends are distinct yet interconnected roles within the ecclesiastical hierarchy, with canonries representing the office held by clergy attached to a cathedral or collegiate church. Prebends refer to the financial endowments or revenue granted to a canon, ensuring their economic support and enabling them to fulfill their liturgical and administrative duties. The importance of these roles lies in maintaining the organizational structure and governance of the church, reinforcing clerical responsibilities, and sustaining ecclesiastical influence through the allocation of prebendal income.
Modern Usage and Relevance
Canonries and prebends, historically linked to ecclesiastical benefices, now primarily serve symbolic or honorary roles within modern Anglican and Catholic cathedrals. Canonries often denote positions held by clergy entitled to participate in cathedral governance, while prebends represent the financial stipends once attached to these offices, largely replaced by salaried roles. Contemporary relevance lies in preserving ecclesiastical heritage and supporting clergy duties through established endowments or canonical titles.
Conclusion: Canonry vs Prebend Compared
A canonry and a prebend both represent ecclesiastical benefices granting income to clergy, yet a canonry typically involves a permanent position within a cathedral chapter, while a prebend refers specifically to the stipend derived from church revenues assigned to a canon. Canonries often entail corporate responsibilities and participation in cathedral governance, whereas prebends are primarily financial endowments supporting clerical duties. Understanding the distinction clarifies ecclesiastical structures and the distribution of clerical incomes in historical and contemporary church administration.
Canonry Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com