Globalization has transformed economies by fostering interconnected markets and enabling seamless exchange of goods, services, and information across borders. It drives innovation, cultural exchange, and economic growth, yet also presents challenges such as inequality and environmental impact. Explore the rest of this article to understand how globalization shapes your world and the opportunities it creates.
Table of Comparison
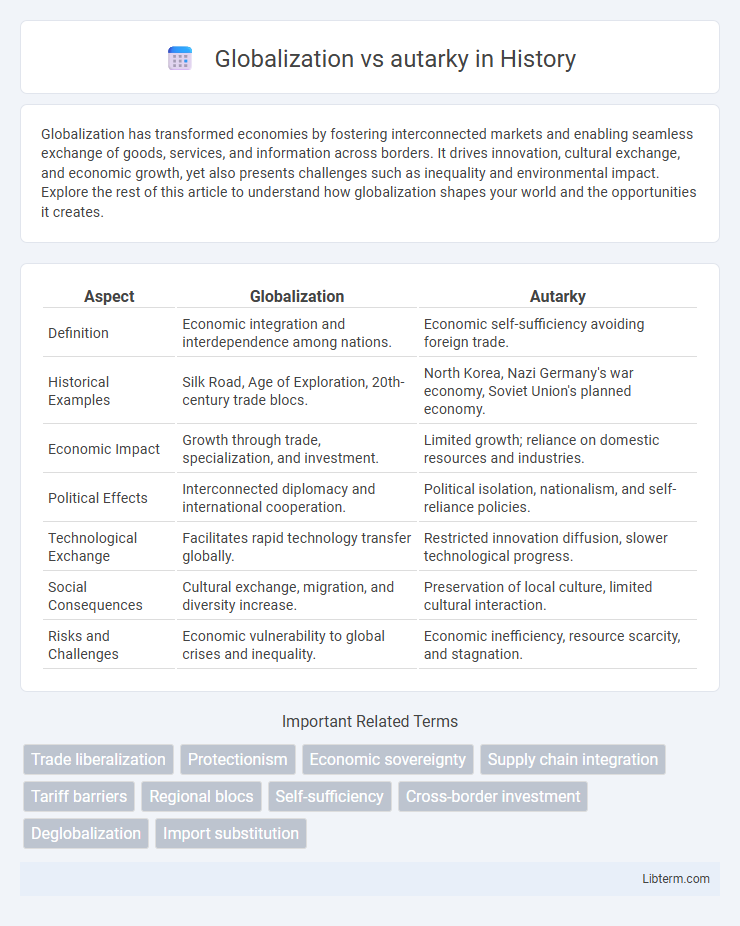
| Aspect | Globalization | Autarky |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Economic integration and interdependence among nations. | Economic self-sufficiency avoiding foreign trade. |
| Historical Examples | Silk Road, Age of Exploration, 20th-century trade blocs. | North Korea, Nazi Germany's war economy, Soviet Union's planned economy. |
| Economic Impact | Growth through trade, specialization, and investment. | Limited growth; reliance on domestic resources and industries. |
| Political Effects | Interconnected diplomacy and international cooperation. | Political isolation, nationalism, and self-reliance policies. |
| Technological Exchange | Facilitates rapid technology transfer globally. | Restricted innovation diffusion, slower technological progress. |
| Social Consequences | Cultural exchange, migration, and diversity increase. | Preservation of local culture, limited cultural interaction. |
| Risks and Challenges | Economic vulnerability to global crises and inequality. | Economic inefficiency, resource scarcity, and stagnation. |
Understanding Globalization: Definition and Key Features
Globalization refers to the increasing interconnectedness and interdependence of countries through the exchange of goods, services, information, and capital across borders. Key features include the expansion of international trade, the rise of multinational corporations, advancements in communication technology, and the integration of financial markets. This phenomenon contrasts with autarky, where a nation prioritizes economic self-sufficiency and limits external trade and investment.
What is Autarky? Principles and Historical Context
Autarky refers to an economic system where a country aims for self-sufficiency by minimizing reliance on international trade and imports. The principles of autarky emphasize domestic production, control over resources, and economic independence to protect against external shocks and preserve national sovereignty. Historically, autarky has been pursued during periods of conflict or economic isolation, such as Nazi Germany in the 1930s or North Korea's ongoing policy, reflecting efforts to shield economies from global market fluctuations and geopolitical pressures.
Economic Impacts: Globalization vs Autarky
Globalization fosters economic growth through increased trade, investment, and technology transfer, enhancing productivity and consumer choice by integrating markets worldwide. Autarky limits economic expansion by isolating domestic economies, reducing economies of scale, innovation, and resource allocation efficiency. Countries embracing globalization typically experience higher GDP growth and standards of living compared to those pursuing autarkic policies.
Trade Policies: Open Markets vs Self-Sufficiency
Trade policies under globalization emphasize open markets to enhance economic efficiency, promote competition, and increase consumer choices through reduced tariffs and trade barriers. Autarky prioritizes self-sufficiency by minimizing reliance on international trade, aiming to protect domestic industries and control economic stability despite potential inefficiencies and higher costs. The debate between open markets and self-sufficiency hinges on balancing economic growth with national security and resilience against global market fluctuations.
Innovation and Technology Transfer: Comparative Analysis
Globalization accelerates innovation and technology transfer by fostering international collaboration, enabling firms to access diverse markets and cutting-edge research across borders. Autarky limits these opportunities, resulting in slower technological advancement due to restricted knowledge exchange and reduced economies of scale. Comparative analysis shows countries engaged in globalization exhibit higher rates of patent filings, increased R&D investment, and faster diffusion of technological breakthroughs compared to autarkic economies.
Social and Cultural Effects: Integration vs Isolation
Globalization fosters social and cultural integration by enabling cross-cultural exchanges, increasing diversity, and promoting mutual understanding among nations. Autarky, characterized by economic and cultural isolation, limits exposure to external influences, often leading to homogeneity and stagnation in social development. The contrast between globalization and autarky profoundly impacts the evolution of cultural identities and societal cohesion worldwide.
Environmental Considerations in Globalization and Autarky
Globalization often leads to increased resource consumption and carbon emissions due to expanded production and transportation networks, intensifying environmental degradation. In contrast, autarky minimizes ecological footprints by localizing resource use and production, reducing dependency on long-distance trade and associated emissions. However, autarkic systems may lack access to advanced green technologies, potentially limiting environmental innovation and efficiency gains available through global collaboration.
Political Stability and Geopolitical Influence
Political stability often strengthens under globalization as interconnected economies promote cooperation and reduce the likelihood of conflicts, while autarky can lead to isolation that may increase internal political tensions due to economic inefficiencies and resource constraints. Geopolitically, globalization enhances a nation's influence through alliances, trade networks, and soft power, whereas autarky limits a country's reach and leverage on the global stage by restricting diplomatic and economic engagement. Nations adopting globalization tend to benefit from collective security arrangements and multilateral institutions that stabilize regional and global political environments.
Case Studies: Successes and Failures of Both Models
Case studies reveal that globalization fosters economic growth and innovation, as seen in South Korea's transformation into a technological powerhouse through export-driven policies, while autarky struggles with inefficiency and limited market access, exemplified by North Korea's stagnant economy. Conversely, some autarkic policies, like India's pre-1991 economic strategy, initially promoted self-reliance but ultimately hindered competitiveness and growth. These examples highlight that globalization typically enhances prosperity and integration, whereas autarky often results in economic isolation and slower development.
Future Trends: Navigating Between Globalization and Autarky
Future trends indicate a nuanced balance between globalization and autarky, driven by geopolitical shifts, technological advancements, and supply chain resilience priorities. Countries may adopt selective decoupling strategies to safeguard critical industries while maintaining global trade flows for efficiency and innovation. Emerging regional trade agreements and digital trade platforms will likely shape this dynamic, emphasizing adaptability in economic policies and international cooperation.
Globalization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com