Records serve as vital documents that capture important information, transactions, or events for future reference and accountability. Proper management and organization of records enable efficient retrieval and ensure compliance with legal and regulatory requirements. Discover how effective records management can enhance your productivity and safeguard your data throughout this article.
Table of Comparison
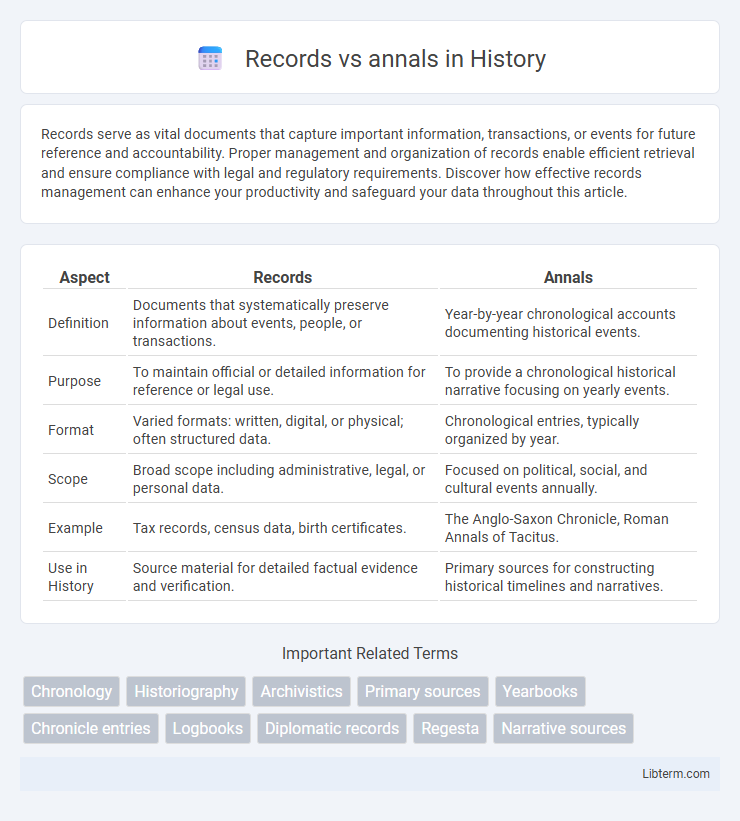
| Aspect | Records | Annals |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Documents that systematically preserve information about events, people, or transactions. | Year-by-year chronological accounts documenting historical events. |
| Purpose | To maintain official or detailed information for reference or legal use. | To provide a chronological historical narrative focusing on yearly events. |
| Format | Varied formats: written, digital, or physical; often structured data. | Chronological entries, typically organized by year. |
| Scope | Broad scope including administrative, legal, or personal data. | Focused on political, social, and cultural events annually. |
| Example | Tax records, census data, birth certificates. | The Anglo-Saxon Chronicle, Roman Annals of Tacitus. |
| Use in History | Source material for detailed factual evidence and verification. | Primary sources for constructing historical timelines and narratives. |
Introduction to Records and Annals
Records serve as official documents that capture detailed, organized information about events, transactions, or activities, often maintained for legal, administrative, or historical purposes. Annals, in contrast, are chronological accounts that record events year by year, focusing on historical occurrences with less emphasis on comprehensive detail. Understanding the distinction between records and annals is essential for historians and archivists in evaluating the reliability, context, and scope of information preserved over time.
Defining Records
Records are documented evidence of specific events, transactions, or facts maintained for accuracy and legal purposes, often including items like birth certificates, financial statements, and official correspondence. They serve as primary sources that verify information and support accountability in various fields such as business, law, and history. Unlike annals, which provide chronological narratives, records emphasize precise documentation and retrieval for reference and verification.
Understanding Annals
Annals are chronological records of events, typically arranged year by year, emphasizing historical accuracy and continuous documentation. Unlike general records, which may include varied types of documents or data entries, annals specifically serve as systematic yearly accounts often maintained by institutions or historians. Understanding annals involves recognizing their role in preserving a sequential timeline that aids in tracing historical developments and contextualizing events within broader narratives.
Key Differences Between Records and Annals
Records are systematic collections of documented information, often detailed and varied in format, serving administrative, legal, or personal purposes. Annals specifically denote chronological yearly entries focused on historical events, maintaining a strict temporal order with concise notations. The key differences lie in purpose, structure, and content depth: records encompass broad documentation with diverse uses, while annals provide a synthesized, date-based historical narrative.
Historical Significance of Records
Records serve as primary sources containing detailed, contemporaneous accounts of events, indispensable for verifying historical facts and understanding societal contexts. Unlike annals, which are chronological summaries often lacking depth, records provide comprehensive data such as official documents, letters, and eyewitness testimonies critical to accurate historiography. The historical significance of records lies in their ability to preserve authentic, granular information that forms the foundation for research, legal evidence, and cultural heritage.
The Role of Annals in History
Annals play a critical role in history by providing a chronological, year-by-year account of events, which helps historians trace the development and context of significant occurrences over time. Unlike general records, annals emphasize temporal sequencing and continuity, making them essential for understanding the evolution of societies, political regimes, and cultural shifts. Their structured format facilitates precise dating and cross-referencing, contributing invaluable insights into historical research and historiography.
Structure and Format Comparison
Records typically present information in a detailed, itemized format organized chronologically or thematically, designed for quick reference or legal documentation. Annals follow a strict chronological sequence, often year-by-year, emphasizing a linear historical narrative without extensive elaboration. The structure of records prioritizes comprehensive data capture, while annals emphasize time-based storytelling with minimal interpretative content.
Uses in Modern Research
Records provide detailed, contemporaneous documentation essential for quantitative data analysis and verifying specific events in modern research, while annals offer chronological summaries beneficial for understanding historical context and tracing developments over time. Researchers utilize records for precise fact-checking and primary source evidence, whereas annals assist in identifying long-term trends and constructing narratives within historical studies. Combining both sources enhances accuracy and depth in multidisciplinary investigations, especially in fields like history, archaeology, and social sciences.
Famous Examples of Records and Annals
Famous examples of records include the Magna Carta, a foundational legal document establishing rights in 1215, and the Dead Sea Scrolls, ancient manuscripts offering invaluable biblical texts. Notable annals feature the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle, a detailed yearly record of early English history, and the Annals of Tacitus, which provide a comprehensive Roman Empire historical timeline. These documents serve distinct purposes: records often capture specific events or transactions, while annals systematically document events in chronological order.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Records and Annals
Choosing between records and annals depends on the desired level of detail and purpose; records offer precise, factual documentation ideal for legal or administrative use, while annals provide a chronological narrative suited for historical analysis. Records prioritize accuracy and specificity, often including exact dates and data, making them essential for verification. Annals emphasize context and continuity, allowing for a broader understanding of events over time.
Records Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com