Khan is a title of Central and South Asian origin historically used to denote a ruler or military leader, symbolizing authority and power. It has evolved over centuries to become a common surname and honorary title in various cultures, reflecting a rich legacy of leadership. Discover how the role and significance of Khan have shaped history and culture in the full article.
Table of Comparison
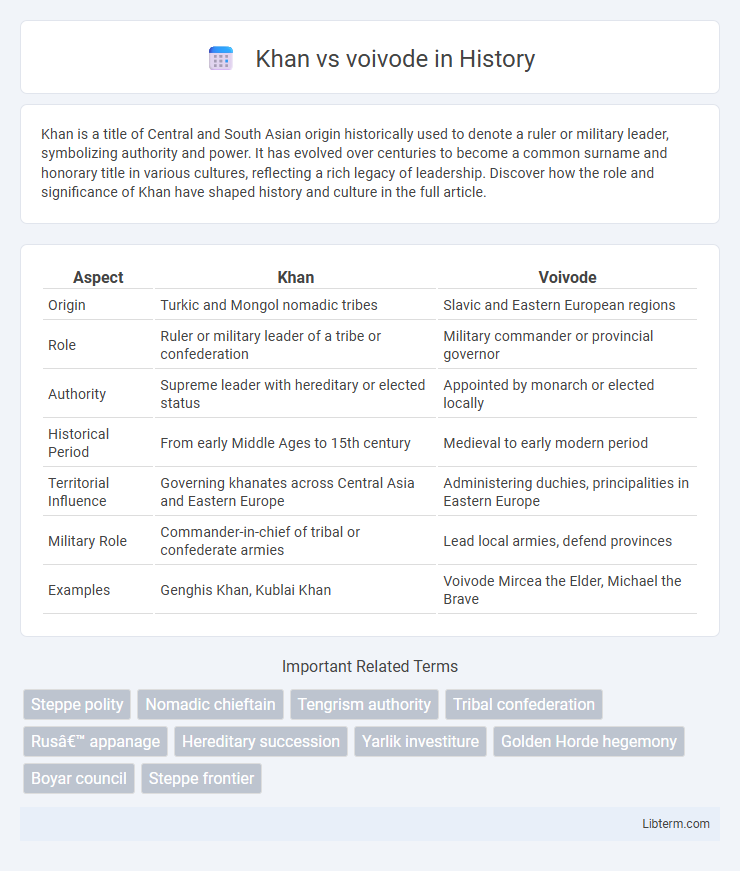
| Aspect | Khan | Voivode |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Turkic and Mongol nomadic tribes | Slavic and Eastern European regions |
| Role | Ruler or military leader of a tribe or confederation | Military commander or provincial governor |
| Authority | Supreme leader with hereditary or elected status | Appointed by monarch or elected locally |
| Historical Period | From early Middle Ages to 15th century | Medieval to early modern period |
| Territorial Influence | Governing khanates across Central Asia and Eastern Europe | Administering duchies, principalities in Eastern Europe |
| Military Role | Commander-in-chief of tribal or confederate armies | Lead local armies, defend provinces |
| Examples | Genghis Khan, Kublai Khan | Voivode Mircea the Elder, Michael the Brave |
Introduction: Understanding Khan and Voivode
Khan and Voivode represent distinct leadership titles rooted in different cultural and historical contexts, with Khan originating in Central Asia and Mongolia as a title for tribal rulers and military commanders. Voivode, primarily used in Eastern Europe and the Balkans, denotes a military leader or provincial governor with authority over a specific region. Understanding the origins and roles of both titles reveals the diverse governance structures and sociopolitical systems across Eurasian history.
Historical Origins of Khan and Voivode
The title "Khan" originated among the Turkic and Mongolic nomadic tribes of Central Asia, signifying a ruler or military leader with supreme authority over a tribe or confederation. In contrast, the term "Voivode" emerged in Eastern Europe, particularly among Slavic and Romanian territories, denoting a military commander or provincial governor appointed to oversee and defend a specific region. Both titles reflect the distinct sociopolitical structures of their respective cultures, with Khans embodying the tribal confederation leadership in steppe societies, while Voivodes represented the feudal or princely governance in medieval Eastern European states.
Etymology: The Meaning Behind the Titles
The title "Khan" originates from the Mongolic and Turkic languages, historically signifying a ruler or military leader in Central Asia and the Mongol Empire, denoting authority and sovereignty. "Voivode" derives from the Slavic root words "voi" (army) and "vod" (to lead), meaning a warlord or military commander primarily used in Eastern Europe. Both titles reflect a strong military connotation, but while "Khan" emphasizes supreme rulership, "Voivode" specifically highlights the role of leading troops into battle.
Regional Contexts: Where Khan and Voivode Ruled
Khans ruled vast territories across Central Asia and Eastern Europe, including the Mongol and Turkic empires, where they exercised supreme authority over nomadic and sedentary populations. Voivodes governed in Eastern Europe, particularly within the medieval principalities of Poland, Wallachia, Moldavia, and the Balkans, overseeing military and administrative functions. The regional context of Khans emphasized expansive, often steppe-based empires, while voivodes operated within more localized, feudal territories in the Slavic and Balkan regions.
Roles and Responsibilities: Comparing Leadership Functions
Khan traditionally serves as a supreme ruler or military leader with authority over vast territories, often tasked with maintaining order, conducting warfare, and overseeing the administration of a khanate. In contrast, a voivode functions primarily as a military commander or governor within a principality, responsible for local defense, enforcement of laws, and managing regional governance under the authority of a sovereign. While both roles involve leadership and strategic decision-making, the Khan's position embodies centralized power across larger domains, whereas the voivode operates within a more defined and subordinate territorial framework.
Military Authority: Khan vs Voivode
The Khan held supreme military authority within the Mongol Empire, commanding vast armies through a centralized and hereditary leadership system that emphasized cavalry tactics and rapid mobility. In contrast, the Voivode, prominent in Eastern European regions like Poland and Wallachia, functioned as a regional military commander appointed by the monarch with responsibilities tied to local defense and administration. While the Khan's power was absolute and expansive, the Voivode's military authority was more localized and often integrated with civil governance.
Societal Influence and Legacy
Khan's leadership established vast nomadic empires that profoundly shaped Central Asian culture, law, and trade routes, influencing the social hierarchy and economic structures across Eurasia. Voivodes, as regional military governors in Eastern Europe and the Balkans, reinforced feudal systems and centralized authority, affecting local governance and societal organization. The legacy of Khans is evident in the enduring cultural integration and military prowess of successor states, while voivodes contributed to the formation of early modern nation-states and administrative traditions.
Power Structures and Succession
Khanate power structures were often centralized, with the khan wielding supreme authority supported by a council of nobles and military leaders, while succession frequently followed a meritocratic or election-based system among royal family members, leading to internal competition. In contrast, voivodes operated within more decentralized feudal systems, holding military and administrative authority granted by a monarch or prince, with succession typically hereditary or appointed by higher nobility, reinforcing localized control. These differing frameworks influenced political stability and continuity, with khanates sometimes experiencing violent succession disputes, whereas voivodeships depended on established noble lineages and royal favor for leadership transitions.
Cultural Representation in History and Folklore
The historical roles of Khans and Voivodes are deeply embedded in the cultural narratives of Central Asia and Eastern Europe, reflecting diverse governance structures and social hierarchies. Khans, often depicted in Mongol and Turkic folklore, symbolize tribal leadership and military prowess, while Voivodes in Slavic traditions represent regional authority and defensemanship. These figures appear prominently in epic poems, legends, and oral histories, illustrating the distinct cultural identities and political dynamics of their respective societies.
Khan and Voivode in Modern Perspectives
Khan and Voivode represent distinct leadership roles with deep historical roots, where Khan typically signifies a tribal or nomadic ruler prominent in Central Asian and Turkic cultures, while Voivode refers to a military commander or governor common in Eastern European and Slavic regions. Modern perspectives analyze Khan as a symbol of centralized tribal authority associated with vast empires like the Mongol Empire, highlighting strategic governance and military prowess. In contrast, the Voivode role is viewed through the lens of localized administrative leadership and feudal military command, reflecting evolving political structures in medieval and modern Eastern Europe.
Khan Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com