Prince was an iconic musician known for his extraordinary talent, blending genres like funk, rock, and pop to create a unique sound. His influence reshaped the music industry, inspiring countless artists with his innovative style and dynamic performances. Discover more about Prince's legacy and impact by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
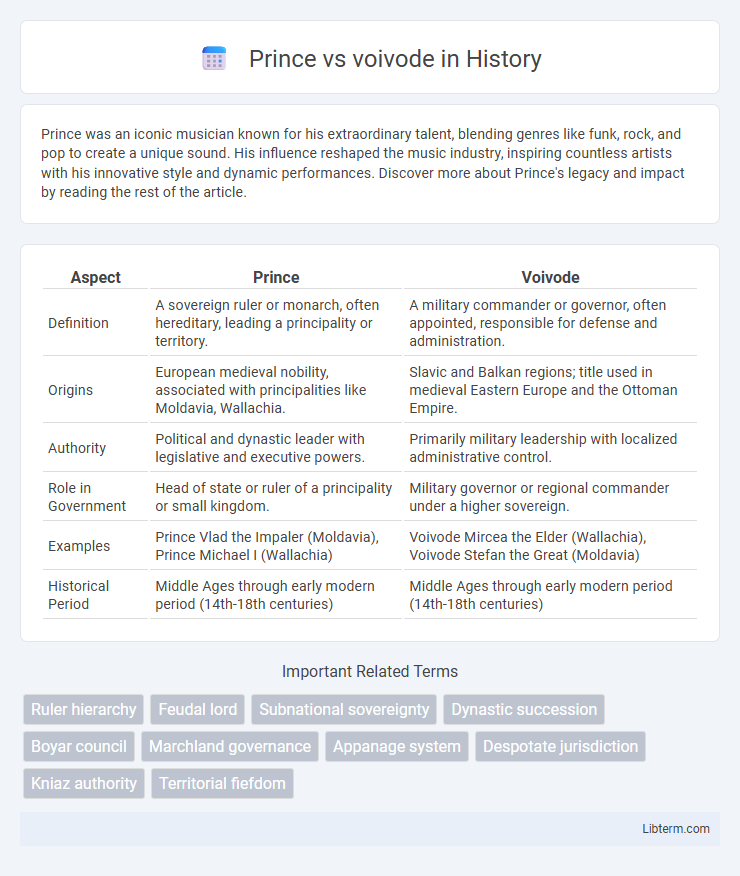
| Aspect | Prince | Voivode |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A sovereign ruler or monarch, often hereditary, leading a principality or territory. | A military commander or governor, often appointed, responsible for defense and administration. |
| Origins | European medieval nobility, associated with principalities like Moldavia, Wallachia. | Slavic and Balkan regions; title used in medieval Eastern Europe and the Ottoman Empire. |
| Authority | Political and dynastic leader with legislative and executive powers. | Primarily military leadership with localized administrative control. |
| Role in Government | Head of state or ruler of a principality or small kingdom. | Military governor or regional commander under a higher sovereign. |
| Examples | Prince Vlad the Impaler (Moldavia), Prince Michael I (Wallachia) | Voivode Mircea the Elder (Wallachia), Voivode Stefan the Great (Moldavia) |
| Historical Period | Middle Ages through early modern period (14th-18th centuries) | Middle Ages through early modern period (14th-18th centuries) |
Introduction: Understanding "Prince" and "Voivode
The term "Prince" historically refers to a hereditary monarch or ruler, often associated with sovereignty over a principality or kingdom, symbolizing centralized authority and dynastic leadership. In contrast, a "Voivode" denotes a military commander or regional governor, particularly in Eastern Europe, responsible for administrative control and defense within a specific territory. Understanding the nuances between a Prince's ruling sovereignty and a Voivode's military-administrative role clarifies the diverse governance structures in medieval and early modern societies.
Historical Origins of the Titles
The titles "Prince" and "Voivode" both originated in medieval Europe, yet they signify distinct roles rooted in different cultural and political contexts. "Prince" stems from the Latin "princeps," meaning "first citizen," often denoting sovereign rulers or high-ranking nobility in Western and Central Europe. In contrast, "Voivode" derives from Slavic origins, combining "voi" (war) and "voda" (leader), initially referring to military commanders or regional governors in Eastern European territories such as Poland, Romania, and the Balkans.
Etymology and Linguistic Roots
The title "Prince" originates from the Latin term "princeps," meaning "first" or "chief," reflecting its usage in Western European aristocracy to denote sovereign or high-ranking nobles. In contrast, "Voivode" derives from the Slavic roots "voi" (army) and "voda" (leader), literally translating to "army leader," and was historically used in Eastern European and Balkan regions to signify a military commander or regional ruler. These linguistic origins highlight distinct cultural and administrative roles embedded in the titles, with "Prince" emphasizing noble precedence and "Voivode" underscoring martial authority.
Geographic Regions and Usage
Prince is a title often used in Western and Central European regions, particularly in countries like Germany, Russia, and Italy, signifying a sovereign ruler or a member of royalty. Voivode, historically rooted in Eastern European areas such as Poland, Romania, and the Balkans, refers to a military leader or provincial governor. Geographic distinctions between these titles highlight the varying administrative and cultural roles within medieval and early modern European governance systems.
Political Authority and Power Structures
Prince typically refers to a hereditary ruler with centralized political authority over a principality, often inheriting power through dynastic succession. Voivode historically denotes a military leader or governor appointed by a monarch, responsible for regional control and administration within a broader realm. The power structure of a prince is often autonomous and sovereign, while a voivode operates within a hierarchical system under the authority of a king or higher sovereign.
Roles in Medieval Governance
The prince in medieval governance typically held centralized authority, overseeing the administration, military command, and diplomatic relations within a principality or kingdom. The voivode functioned as a provincial governor or military leader appointed by the prince or monarch, responsible for local defense, justice enforcement, and implementation of royal policies in territories like Wallachia, Moldavia, and Transylvania. Both roles were crucial for maintaining feudal order, with the prince setting broad strategic directives and the voivode executing regional governance and military operations.
Military Responsibilities of Princes vs Voivodes
Princes held supreme military authority as commanders-in-chief, responsible for organizing armies, leading troops into battle, and overseeing the defense of the realm. Voivodes acted as regional military governors, managing local garrisons, enforcing martial law, and coordinating military logistics within their territories. While princes formulated strategic campaigns and national defense policies, voivodes implemented these directives on a provincial level, ensuring military readiness and maintaining order.
Notable Figures: Famous Princes and Voivodes
Notable historical figures include Prince Vladimir the Great of Kievan Rus, who centralized power and Christianized the region, and Voivode Vlad the Impaler of Wallachia, known for his military leadership and resistance against the Ottoman Empire. Prince Alexander Nevsky also stands out for defending Russian lands against invasions and fostering diplomatic relations with the Mongol Empire. Voivode Mihai Viteazul is recognized for briefly uniting Wallachia, Transylvania, and Moldavia under his rule, marking a significant moment in Romanian history.
Evolution of the Titles Over Time
The title "Prince" originally denoted a sovereign ruler of a principality, often hereditary and linked to Western European nobility, while "Voivode" referred to a military leader or governor in Eastern European and Slavic regions, evolving into a territorial ruler or regional governor. Over time, the Prince title became more associated with dynastic prestige and centralized authority in medieval Europe, whereas the Voivode's role shifted from military commander to a more administrative and political figure within principalities like Wallachia and Moldavia. By the early modern period, Princes frequently held higher status in European nobility hierarchies, while Voivodes often acted as appointed leaders, reflecting differing evolutions shaped by regional governance structures and cultural influences.
Legacy and Modern Relevance
Princes, historically sovereign rulers of principalities, shaped the political and cultural landscapes of medieval Europe, while voivodes served as regional military governors or nobles in Eastern Europe, particularly within Slavic territories. The legacy of princes is evident in the formation of nation-states and royal dynasties, whereas voivodes contributed to the administrative and military organization of emerging states like Wallachia and Transylvania. In modern contexts, princely titles persist symbolically within constitutional monarchies, whereas the term voivode endures in regional historical identity and occasional administrative nomenclature, reflecting their entrenched cultural and political significance.
Prince Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com