The Guardian offers comprehensive news coverage with a focus on in-depth analysis and global perspectives. Its commitment to unbiased reporting and diverse viewpoints makes it a trusted source for staying informed on current events. Discover how The Guardian can enhance your understanding by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
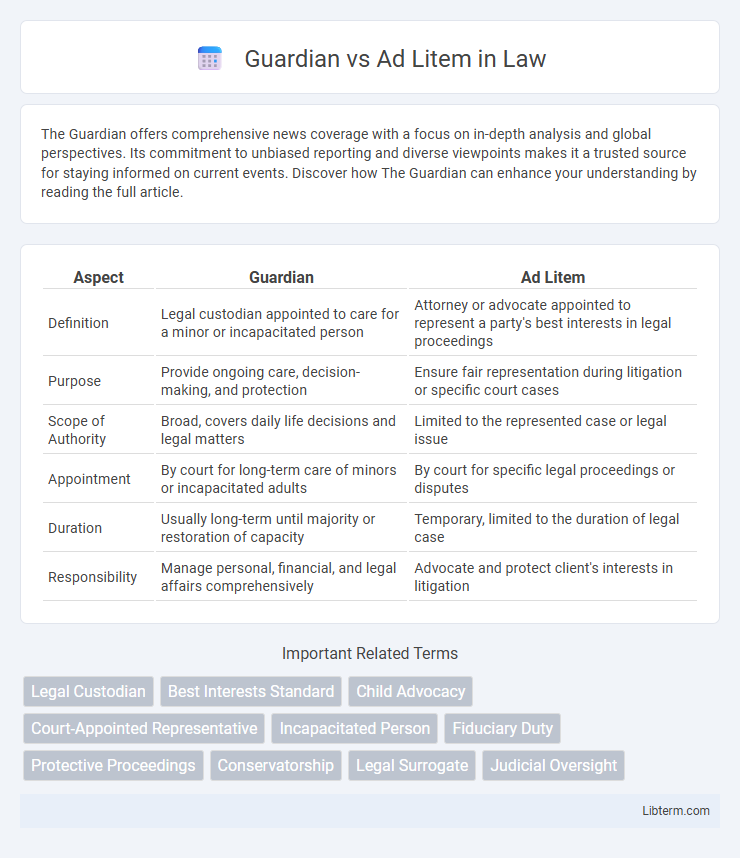
| Aspect | Guardian | Ad Litem |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal custodian appointed to care for a minor or incapacitated person | Attorney or advocate appointed to represent a party's best interests in legal proceedings |
| Purpose | Provide ongoing care, decision-making, and protection | Ensure fair representation during litigation or specific court cases |
| Scope of Authority | Broad, covers daily life decisions and legal matters | Limited to the represented case or legal issue |
| Appointment | By court for long-term care of minors or incapacitated adults | By court for specific legal proceedings or disputes |
| Duration | Usually long-term until majority or restoration of capacity | Temporary, limited to the duration of legal case |
| Responsibility | Manage personal, financial, and legal affairs comprehensively | Advocate and protect client's interests in litigation |
Guardian vs Ad Litem: Key Differences Explained
A guardian is a legally appointed individual responsible for making decisions and managing the personal and financial affairs of a minor or incapacitated adult, while an ad litem is a court-appointed advocate who represents the best interests of a child or incapacitated party specifically during legal proceedings. Guardians have ongoing authority over the ward's daily life, including healthcare and education, whereas ad litems provide recommendations to the court without permanent decision-making power. Key differences include the scope of authority, duration of appointment, and the primary role: guardians provide care and management, while ad litems serve as objective advocates in legal cases.
Understanding the Role of a Guardian
A Guardian is legally appointed to manage the personal, medical, and financial affairs of a minor or incapacitated individual, ensuring their well-being and decisions align with their best interests. Unlike a Guardian ad Litem, who only represents a child's interests during specific legal proceedings, a Guardian has ongoing responsibility and authority. Understanding the Guardian's role involves recognizing their duty to protect, support, and make long-term decisions for those unable to do so themselves.
What Is an Ad Litem?
An Ad Litem is a court-appointed advocate who represents the best interests of a child or incapacitated person during legal proceedings. Unlike a Guardian, whose role involves making long-term decisions about personal and financial matters, an Ad Litem's responsibility is limited to providing objective recommendations based on an investigation. Courts rely on Ad Litems to offer impartial insights that help resolve custody, welfare, or guardianship disputes.
Appointment Process: Guardian vs Ad Litem
The appointment process for a Guardian involves a court petition where the judge evaluates the individual's capacity and best interests before granting decision-making authority. In contrast, an Ad Litem is appointed specifically for representing a child's or incapacitated person's interests during legal proceedings, often without requiring full guardianship rights. Courts typically select Guardians through a more comprehensive vetting process, while Ad Litems are appointed for concise, case-specific advocacy.
Legal Responsibilities of a Guardian
A Guardian holds the legal responsibility to make personal, financial, and healthcare decisions for a ward who is unable to manage their own affairs due to incapacity. This includes managing assets, paying bills, ensuring proper medical care, and advocating for the ward's best interests in legal matters. Unlike a Guardian ad Litem, whose role is limited to representing a minor or incapacitated person during a specific court case, a Guardian's duties are ongoing and encompass comprehensive care and protection.
Duties and Authority of an Ad Litem
An Ad Litem is appointed by the court to represent the best interests of a minor or incapacitated individual during legal proceedings, with duties including investigation, reporting, and recommending outcomes to the court. Their authority is limited to the scope defined by the court order, ensuring the represented party's rights and welfare are protected without making permanent decisions. Unlike a Guardian, an Ad Litem does not manage personal or financial affairs but serves solely as a legal advocate in the case at hand.
When Is a Guardian Needed?
A guardian is needed when an individual, such as a minor or an incapacitated adult, cannot manage their personal or financial affairs safely and effectively. Courts typically appoint a guardian after determining that the person lacks the capacity to make informed decisions due to age, disability, or mental health issues. Guardians have ongoing responsibilities, including making healthcare, educational, and financial decisions to protect the ward's best interests.
When Is an Ad Litem Appointed?
An Ad Litem is appointed by the court specifically during legal proceedings to represent the best interests of a minor or incapacitated person when their rights or welfare are directly at stake. This appointment occurs in cases such as custody disputes, abuse allegations, or complex family law matters requiring independent advocacy. Unlike a Guardian who manages daily affairs, an Ad Litem serves solely for the duration and scope of the litigation to ensure fair representation.
Pros and Cons: Guardian vs Ad Litem
A guardian assumes full legal responsibility for a minor or incapacitated person, providing comprehensive decision-making in health, education, and finances, which ensures stability but may limit the ward's autonomy and requires court supervision. An ad litem serves as a court-appointed advocate specifically for legal proceedings, offering expert representation in the child's best interests without assuming long-term authority, which allows for focused advocacy but may lack continuity or holistic care. Choosing between a guardian and an ad litem depends on the need for ongoing care versus temporary legal advocacy, highlighting trade-offs between control, oversight, and specialized representation.
Choosing the Right Legal Advocate for Minors
Selecting the right legal advocate for minors involves understanding the distinct roles of a guardian and an ad litem. A guardian manages the child's personal and financial affairs, while an ad litem represents the child's best interests in court proceedings. Evaluating the case's specific needs ensures the appointment of a professional who can effectively safeguard the minor's welfare and legal rights.
Guardian Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com