Common mistakes in everyday tasks can lead to unnecessary stress and lost time. Identifying these errors early helps improve efficiency and accuracy in your daily routine. Explore the rest of this article to discover practical tips for avoiding common pitfalls.
Table of Comparison
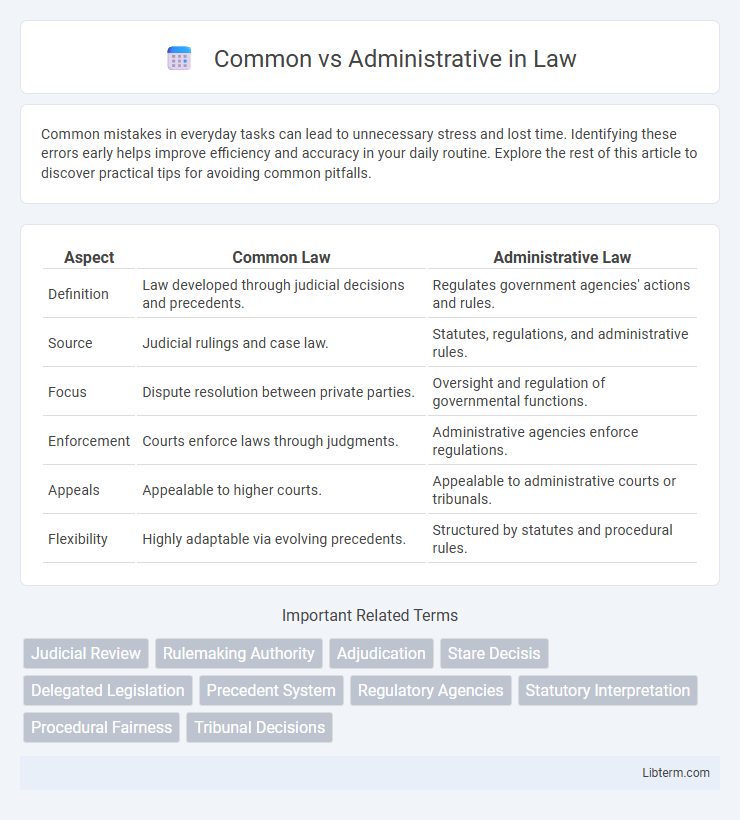
| Aspect | Common Law | Administrative Law |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Law developed through judicial decisions and precedents. | Regulates government agencies' actions and rules. |
| Source | Judicial rulings and case law. | Statutes, regulations, and administrative rules. |
| Focus | Dispute resolution between private parties. | Oversight and regulation of governmental functions. |
| Enforcement | Courts enforce laws through judgments. | Administrative agencies enforce regulations. |
| Appeals | Appealable to higher courts. | Appealable to administrative courts or tribunals. |
| Flexibility | Highly adaptable via evolving precedents. | Structured by statutes and procedural rules. |
Introduction to Common and Administrative Law
Common law is a body of law developed through judicial decisions and precedents established by courts, focusing on case-by-case analysis. Administrative law governs the activities of government agencies, ensuring they act within their legal authority and follow fair procedures. Understanding both systems is essential for navigating legal disputes and regulatory oversight efficiently.
Definition of Common Law
Common law is a legal system developed through judicial decisions and precedents rather than written statutes, emphasizing the role of courts in shaping law over time. It contrasts with administrative law, which governs the actions and regulations of government agencies based on statutory authority. Common law relies on case law interpretation, ensuring consistency and adaptability in legal principles across similar cases.
Definition of Administrative Law
Administrative law governs the activities and decisions of government agencies, ensuring they comply with statutory authority and protect public rights. It establishes frameworks for rulemaking, enforcement, and adjudication within administrative bodies, distinguishing it from common law, which evolves through judicial precedents. This body of law maintains a balance between governmental power and individual freedoms by regulating administrative procedures and actions.
Historical Origins and Development
Common law originated in medieval England, evolving from local customs and judicial decisions, while administrative law developed later as governments expanded and required legal frameworks to regulate public administration. Common law relies heavily on case precedents established by courts, reflecting centuries of legal traditions, whereas administrative law emerged from statutory legislation and executive regulations to address the complexities of modern governance. The historical development of both systems highlights a transition from informal customary practices to formalized legal structures designed to balance judicial authority and administrative efficiency.
Sources of Authority and Legal Principles
Sources of authority in Common law primarily derive from judicial precedents established by court decisions, emphasizing case law and the doctrine of stare decisis. Administrative law rests on statutory statutes, regulations, and executive orders issued by government agencies, rooted in principles of delegation and procedural fairness. Legal principles in Common law prioritize the interpretation of prior judgments, while Administrative law focuses on adherence to legislative mandates and regulatory compliance.
Role of Courts in Common and Administrative Law
Courts in common law primarily interpret and apply legal precedents established through judicial decisions, playing a crucial role in shaping case law and resolving disputes between private parties. In administrative law, courts review government agency actions to ensure legality, fairness, and adherence to statutory mandates, safeguarding individual rights against administrative overreach. This judicial oversight balances the powers of administrative bodies while maintaining the integrity of the legal system.
Key Differences Between Common and Administrative Law
Common law evolves through judicial decisions and precedents, shaping legal principles over time, while administrative law governs the actions and regulations of governmental agencies. Common law addresses disputes between private parties, emphasizing case law and judicial interpretation, whereas administrative law focuses on the enforcement and implementation of statutory regulations by public authorities. Key differences include the sources of law, with common law rooted in court rulings and administrative law grounded in statutes and regulations created by government bodies.
Application and Scope in Legal Systems
Common law applies judicial decisions and precedents to resolve disputes and interpret laws, primarily in countries like the United States and the United Kingdom. Administrative law governs the actions and regulations of government agencies, ensuring legal compliance and protecting public interests within defined administrative frameworks. The scope of common law extends broadly across private and public law, while administrative law specifically oversees governmental functions and regulatory authority.
Impact on Individuals and Government
Common law shapes individual rights by allowing courts to interpret laws based on judicial precedents, directly affecting personal freedoms and obligations. Administrative law governs interactions between individuals and government agencies, ensuring regulations are followed and providing mechanisms for individuals to challenge government decisions. Government operations rely on administrative law to enforce policies and maintain public order, while common law influences legislative development and societal norms.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Common and Administrative Law
Choosing between Common and Administrative Law depends on the nature of the legal issue and the context of its application. Common Law provides a foundation based on judicial precedents ideal for interpreting contracts and resolving private disputes, while Administrative Law governs the actions and decisions of government agencies, ensuring legal compliance and protecting public interests. Understanding their distinct roles helps in determining the appropriate legal framework for effective dispute resolution and regulatory oversight.
Common Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com