Restorative justice focuses on repairing harm by fostering dialogue and understanding between offenders, victims, and the community. This approach emphasizes accountability, healing, and the reintegration of all parties involved, rather than punishment alone. Discover how restorative justice can transform conflicts and promote lasting peace by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
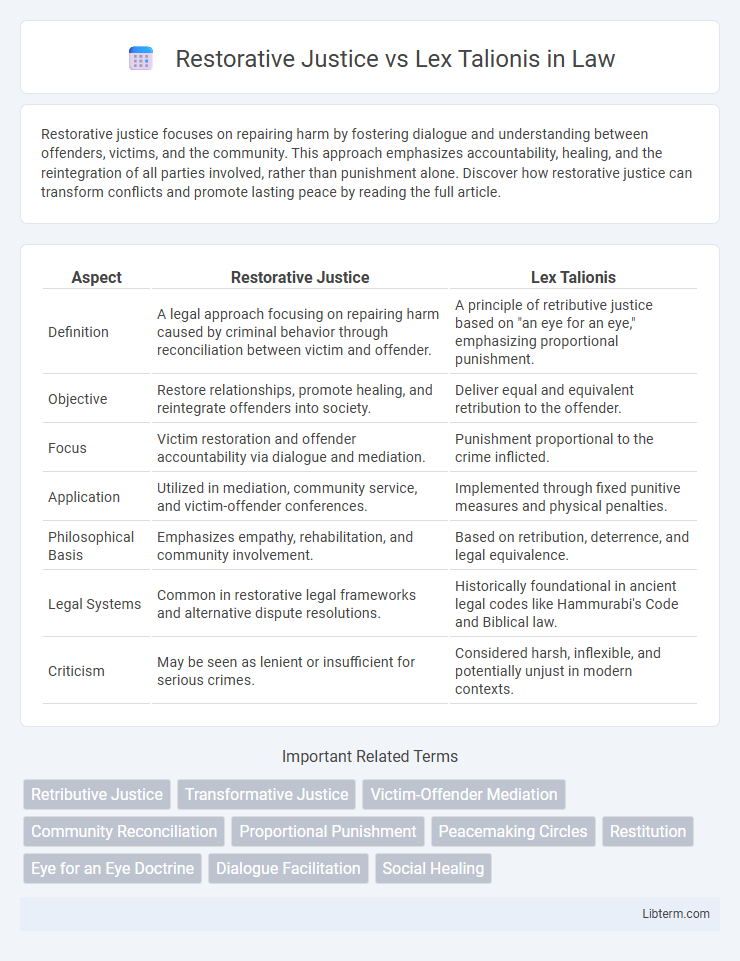
| Aspect | Restorative Justice | Lex Talionis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A legal approach focusing on repairing harm caused by criminal behavior through reconciliation between victim and offender. | A principle of retributive justice based on "an eye for an eye," emphasizing proportional punishment. |
| Objective | Restore relationships, promote healing, and reintegrate offenders into society. | Deliver equal and equivalent retribution to the offender. |
| Focus | Victim restoration and offender accountability via dialogue and mediation. | Punishment proportional to the crime inflicted. |
| Application | Utilized in mediation, community service, and victim-offender conferences. | Implemented through fixed punitive measures and physical penalties. |
| Philosophical Basis | Emphasizes empathy, rehabilitation, and community involvement. | Based on retribution, deterrence, and legal equivalence. |
| Legal Systems | Common in restorative legal frameworks and alternative dispute resolutions. | Historically foundational in ancient legal codes like Hammurabi's Code and Biblical law. |
| Criticism | May be seen as lenient or insufficient for serious crimes. | Considered harsh, inflexible, and potentially unjust in modern contexts. |
Introduction to Restorative Justice and Lex Talionis
Restorative Justice emphasizes repairing harm through reconciliation between offenders and victims, promoting accountability and healing within communities. Lex Talionis, or the law of retaliation, is grounded in the principle of "an eye for an eye," advocating proportional punishment as a means of justice. These contrasting approaches reflect fundamental differences in addressing wrongdoing--Restorative Justice focuses on restoration, while Lex Talionis centers on retribution.
Historical Origins of Restorative Justice
Restorative justice traces its origins to indigenous and traditional societies where community-based conflict resolution emphasized healing and reconciliation rather than punishment. Unlike Lex Talionis, rooted in ancient legal codes like the Code of Hammurabi advocating "an eye for an eye," restorative justice focuses on repairing harm through dialogue and consensus. These practices can be observed in indigenous communities worldwide, including Native American, Maori, and African traditions, making restorative justice a deeply historical and culturally embedded approach.
The Roots of Lex Talionis in Legal Systems
Lex Talionis, rooted in ancient legal systems such as Hammurabi's Code and early Hebrew law, establishes a principle of proportional retribution where the punishment mirrors the offense, embodying the concept of "an eye for an eye." This retributive justice framework prioritizes equilibrium through exact retaliation, influencing many modern legal codes that enforce strict penalties to deter crime and maintain social order. The historical foundation of Lex Talionis contrasts with restorative justice by emphasizing punishment and balance over reconciliation and repair.
Core Principles of Restorative Justice
Restorative Justice centers on repairing harm by involving victims, offenders, and the community in a collaborative process to achieve healing and accountability. It emphasizes dialogue, mutual respect, and restitution rather than punishment, fostering reconciliation and personal growth. In contrast to Lex Talionis, which is based on "an eye for an eye" retributive justice, Restorative Justice prioritizes restoration over retaliation.
Key Tenets of Lex Talionis (“An Eye for an Eye”)
Lex Talionis, or "an eye for an eye," is centered on the principle of retributive justice, emphasizing proportional punishment directly matching the offense committed. It mandates exact equivalence between harm caused and penalty imposed, aiming to deter future transgressions through balanced retaliation. The key tenets prioritize justice through symmetry in punishment, reinforcing social order by ensuring offenders receive penalties that mirror their actions.
Impact on Victims and Offenders: A Comparative Analysis
Restorative Justice prioritizes healing by facilitating dialogue between victims and offenders, often leading to emotional closure and reduced recidivism rates. Lex Talionis, based on the principle of "an eye for an eye," emphasizes proportional punishment that may reinforce victim suffering without addressing offender rehabilitation. Studies indicate that Restorative Justice results in higher victim satisfaction and offenders' reintegration into society compared to the punitive approach of Lex Talionis, which tends to perpetuate cycles of retribution.
Societal Outcomes: Restoration vs. Retribution
Restorative justice emphasizes repairing harm and restoring relationships by involving offenders, victims, and the community in dialogue, which often leads to reduced recidivism and strengthened social cohesion. In contrast, lex talionis, based on the principle of "an eye for an eye," prioritizes retribution and punishment, potentially perpetuating cycles of violence and social division. Societal outcomes of restorative justice show greater long-term benefits in healing and community resilience compared to the punitive focus of retributive justice systems.
Modern Applications and Case Studies
Restorative Justice emphasizes repairing harm through dialogue and community involvement, frequently applied in juvenile justice and conflict resolution programs worldwide, demonstrating reduced recidivism rates. Lex Talionis, or the law of retaliation, remains influential in certain legal systems where proportional punishment is mandated, as seen in some Middle Eastern and tribal societies. Modern case studies reveal Restorative Justice's effectiveness in fostering reconciliation and healing, contrasting with Lex Talionis's focus on retributive justice and deterrence.
Challenges and Criticisms of Both Approaches
Restorative justice faces challenges such as potential retraumatization of victims, imbalance of power in dialogue, and limited applicability in severe crimes, while critics argue that it may lack sufficient deterrence and accountability. Lex Talionis, or the law of retaliation, is criticized for perpetuating cycles of violence, ignoring rehabilitation, and often resulting in disproportionate punishments that fail to address root causes of criminal behavior. Both approaches struggle to balance justice, fairness, and societal healing, raising concerns about effectiveness and ethical implications in modern legal systems.
Future Directions in Justice Reform
Future directions in justice reform emphasize restorative justice as a transformative alternative to lex talionis, focusing on healing and reconciliation rather than retribution. Advances in trauma-informed practices and community-based programs enhance victim-offender mediation, promoting accountability and social harmony. Technology integration and data-driven policy development further support scalable restorative initiatives, aligning justice outcomes with human rights and reducing recidivism rates.
Restorative Justice Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com