Civil engineering shapes the infrastructure that supports modern society, including roads, bridges, and water systems essential for daily life. Advances in sustainable materials and innovative design techniques are revolutionizing the field to create more durable and eco-friendly structures. Discover how these developments can impact Your community by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
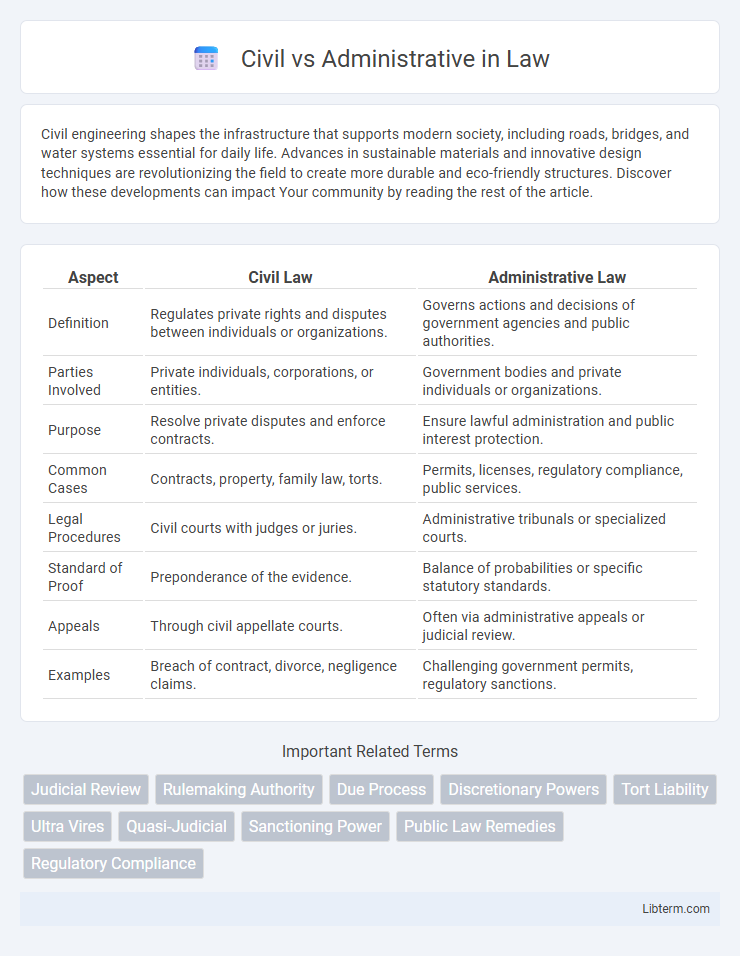
| Aspect | Civil Law | Administrative Law |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Regulates private rights and disputes between individuals or organizations. | Governs actions and decisions of government agencies and public authorities. |
| Parties Involved | Private individuals, corporations, or entities. | Government bodies and private individuals or organizations. |
| Purpose | Resolve private disputes and enforce contracts. | Ensure lawful administration and public interest protection. |
| Common Cases | Contracts, property, family law, torts. | Permits, licenses, regulatory compliance, public services. |
| Legal Procedures | Civil courts with judges or juries. | Administrative tribunals or specialized courts. |
| Standard of Proof | Preponderance of the evidence. | Balance of probabilities or specific statutory standards. |
| Appeals | Through civil appellate courts. | Often via administrative appeals or judicial review. |
| Examples | Breach of contract, divorce, negligence claims. | Challenging government permits, regulatory sanctions. |
Introduction to Civil and Administrative Law
Civil law governs disputes between private parties involving rights, obligations, and liabilities, such as contracts, property, and family matters. Administrative law regulates the actions and decisions of government agencies, ensuring legality, fairness, and accountability in public administration. Understanding both fields is essential for navigating legal frameworks in private and public sectors.
Defining Civil Law: Key Concepts
Civil law governs private rights and disputes between individuals or organizations, including contracts, property, and torts. It establishes the legal framework for compensation or restitution rather than punishment. This system contrasts with administrative law, which oversees the actions and regulations of government agencies.
Understanding Administrative Law: Core Principles
Administrative law governs the activities of government agencies and ensures their decisions comply with legal standards, focusing on fairness, accountability, and transparency. Core principles include the rule of law, due process, and the right to a fair hearing, which protect individuals from arbitrary administrative actions. Understanding the distinction between civil law, which deals with disputes between private parties, and administrative law is essential for navigating regulatory frameworks and challenging governmental decisions.
Major Differences Between Civil and Administrative Law
Civil law governs disputes between private parties involving rights, obligations, and damages, while administrative law regulates the actions and decisions of government agencies to ensure legality and fairness. Civil law cases often result in compensation or specific performance, whereas administrative law cases typically involve the review or enforcement of government regulations and policies. Key differences include the parties involved, types of remedies sought, and the procedural frameworks governing each legal domain.
Types of Cases Handled in Civil vs Administrative Courts
Civil courts primarily handle disputes involving contracts, property, torts, family law, and personal injury claims, focusing on private rights and remedies. Administrative courts oversee cases related to government regulations, including licensing, social security, immigration, tax disputes, and challenges to administrative decisions. The distinction ensures that civil courts address interpersonal conflicts, whereas administrative courts manage issues arising from public administration and regulatory enforcement.
Roles of Judges and Officials in Civil and Administrative Proceedings
In civil proceedings, judges primarily resolve disputes between private parties by interpreting laws and assessing evidence to issue binding judgments on matters such as contracts, property, and torts. Administrative proceedings involve officials or administrative judges who enforce regulatory compliance, adjudicate disputes related to government agencies, and ensure due process under administrative law. While civil judges maintain judicial impartiality, administrative officials often combine investigative and adjudicative roles to implement public policies and regulatory frameworks.
Procedural Steps: Civil Lawsuits vs Administrative Hearings
Civil lawsuits involve formal pleadings, discovery, and trial phases where parties present evidence before a judge or jury. Administrative hearings typically require filing a complaint or petition with the agency, followed by an informal investigation and a hearing conducted by an administrative law judge. Unlike civil courts, administrative proceedings emphasize agency rules and often allow for less formal evidence and faster resolutions.
Remedies and Outcomes in Civil and Administrative Cases
Civil cases typically seek remedies such as monetary damages, injunctions, or specific performance to resolve disputes between private parties. Administrative cases often result in outcomes like fines, license suspensions, or agency orders aimed at enforcing regulatory compliance. The remedies in civil cases focus on compensating harm or enforcing contracts, whereas administrative remedies emphasize regulatory enforcement and public interest protection.
Examples of Civil and Administrative Disputes
Civil disputes commonly involve issues such as contract breaches, property disputes, and family law matters including divorce and child custody. Administrative disputes frequently center on challenges to government regulations, licensing decisions, or benefits determinations like social security or immigration appeals. Courts handling civil cases include civil courts, whereas administrative tribunals or specialized agencies typically resolve administrative disputes.
Importance of Distinguishing Civil from Administrative Law
Distinguishing civil law from administrative law is crucial for understanding their distinct roles in the legal system; civil law primarily governs private disputes between individuals or organizations, such as contracts and torts, whereas administrative law regulates the activities of government agencies and ensures lawful public administration. This separation helps ensure appropriate legal procedures and remedies are applied, protecting individual rights in civil cases while maintaining government accountability in administrative matters. Proper classification guides legal practitioners, courts, and citizens in navigating jurisdictional boundaries and accessing specialized tribunals or courts efficiently.
Civil Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com