An interlocutory remedy provides temporary relief during ongoing litigation to prevent harm before a final judgment is reached, maintaining the status quo and protecting parties' rights. Common examples include temporary injunctions and restraining orders that address urgent issues immediately. Explore the rest of the article to understand how interlocutory remedies can influence the outcome of your case.
Table of Comparison
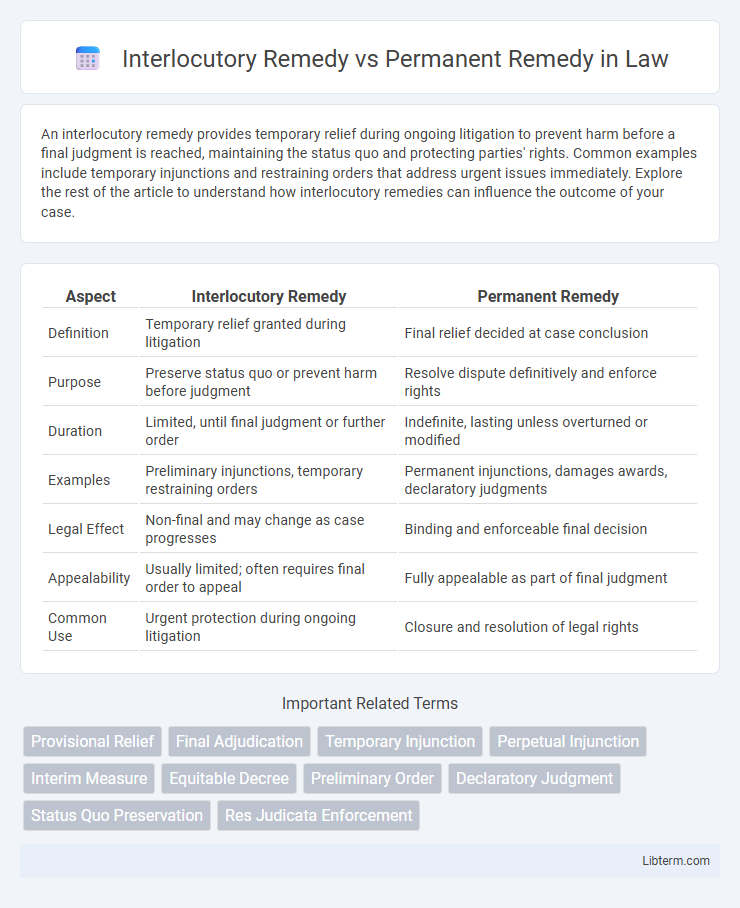
| Aspect | Interlocutory Remedy | Permanent Remedy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temporary relief granted during litigation | Final relief decided at case conclusion |
| Purpose | Preserve status quo or prevent harm before judgment | Resolve dispute definitively and enforce rights |
| Duration | Limited, until final judgment or further order | Indefinite, lasting unless overturned or modified |
| Examples | Preliminary injunctions, temporary restraining orders | Permanent injunctions, damages awards, declaratory judgments |
| Legal Effect | Non-final and may change as case progresses | Binding and enforceable final decision |
| Appealability | Usually limited; often requires final order to appeal | Fully appealable as part of final judgment |
| Common Use | Urgent protection during ongoing litigation | Closure and resolution of legal rights |
Introduction to Legal Remedies
Legal remedies are judicial orders that aim to enforce a right or redress a harm, categorized into interlocutory and permanent remedies based on their duration and purpose. Interlocutory remedies provide temporary relief or preserve the status quo during litigation, such as preliminary injunctions or temporary restraining orders. Permanent remedies, including damages or permanent injunctions, conclusively resolve disputes by fully addressing the rights and obligations of the parties involved.
Defining Interlocutory Remedies
Interlocutory remedies are temporary court orders granted during the pendency of a lawsuit to preserve the status quo and prevent irreparable harm before the final judgment. These remedies include injunctions, temporary restraining orders, and preliminary injunctions, designed to provide immediate relief without determining the ultimate rights of the parties. Unlike permanent remedies, interlocutory remedies do not resolve the substantive issues but ensure fair process and protect the interests of parties pending trial.
Understanding Permanent Remedies
Permanent remedies provide final legal relief that resolves the underlying dispute by enforcing rights or compensating for harm, often through damages, injunctions, or declaratory judgments. Unlike interlocutory remedies, which offer temporary or provisional relief during litigation, permanent remedies are granted after a full trial or settlement and aim to restore parties to their rightful position. Courts base permanent remedies on detailed evidence and legal principles to ensure lasting resolution and prevent future harm.
Key Differences: Interlocutory vs Permanent Remedies
Interlocutory remedies are temporary court orders granted during the course of litigation to preserve the status quo or prevent harm until a final decision is made, whereas permanent remedies provide a final resolution to the dispute after full adjudication. Interlocutory remedies typically include injunctions, temporary restraining orders, and protective orders, designed to maintain fairness and prevent irreversible damage. Permanent remedies involve final judgments such as damages, specific performance, or declaratory relief that conclusively determine the rights and obligations of the parties.
Legal Grounds for Granting Interlocutory Remedies
Interlocutory remedies are granted based on the necessity to prevent irreparable harm or preserve the status quo pending a final decision, emphasizing urgency and the balance of convenience. Courts consider factors such as a prima facie case, the likelihood of success on the merits, and the potential for serious and immediate damage that cannot be adequately remedied by damages alone. Permanent remedies, by contrast, are awarded after determining the substantive rights of parties in a final judgment, focusing on complete and lasting resolution of the dispute.
Criteria for Awarding Permanent Remedies
Permanent remedies are awarded based on the establishment of a clear legal right and the failure of monetary damages to provide adequate relief. Courts require that the plaintiff demonstrate irreparable harm, the inadequacy of legal remedies, and a favorable balance of equities before granting a permanent injunction or specific performance. The criteria emphasize the necessity for finality and fairness in preventing ongoing or future violations of rights.
Common Examples of Interlocutory Remedies
Common examples of interlocutory remedies include temporary restraining orders, preliminary injunctions, and interlocutory mandatory injunctions, which provide immediate relief pending a final decision. These remedies aim to preserve the status quo, prevent irreparable harm, and ensure fairness during ongoing litigation. Unlike permanent remedies that offer final resolution, interlocutory remedies are provisional and typically issued on a temporary basis.
Typical Cases Involving Permanent Remedies
Permanent remedies commonly arise in cases involving breaches of contract, property disputes, and intellectual property infringement where court orders compel long-term compliance or restitution. Cases like injunctions in trademark infringement or specific performance in real estate transactions exemplify typical scenarios requiring permanent remedies to enforce rights or prevent ongoing harm. Courts grant these remedies after thorough consideration of evidence and the inadequacy of monetary damages to address irreparable injury.
Impacts on Parties: Temporary vs Long-Term Relief
Interlocutory remedies provide temporary relief to parties, preserving the status quo and preventing irreparable harm during ongoing litigation, ensuring immediate but short-term protection. Permanent remedies, granted after a full hearing, deliver final relief, resolving the dispute conclusively and imposing long-term obligations or rights on the parties involved. The impact on parties differs significantly, with interlocutory remedies offering provisional protections and permanent remedies establishing definitive legal outcomes.
Conclusion: Choosing the Appropriate Remedy
Choosing the appropriate remedy depends on the case's urgency and long-term objectives; interlocutory remedies provide temporary relief to maintain the status quo during litigation, while permanent remedies offer final resolution and enforcement. Courts carefully evaluate factors such as potential harm, likelihood of success, and public interest before deciding which remedy best serves justice. Effective legal strategy hinges on aligning the chosen remedy with the specific circumstances and desired outcomes of the dispute.
Interlocutory Remedy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com