A judgment debtor is an individual or entity ordered by a court to pay a specific amount to the judgment creditor following a lawsuit. The judgment creditor is the party awarded the money, entitled to collect the debt through legal means such as wage garnishment or property liens. Explore the rest of the article to understand your rights and options when dealing with judgment debtor and creditor issues.
Table of Comparison
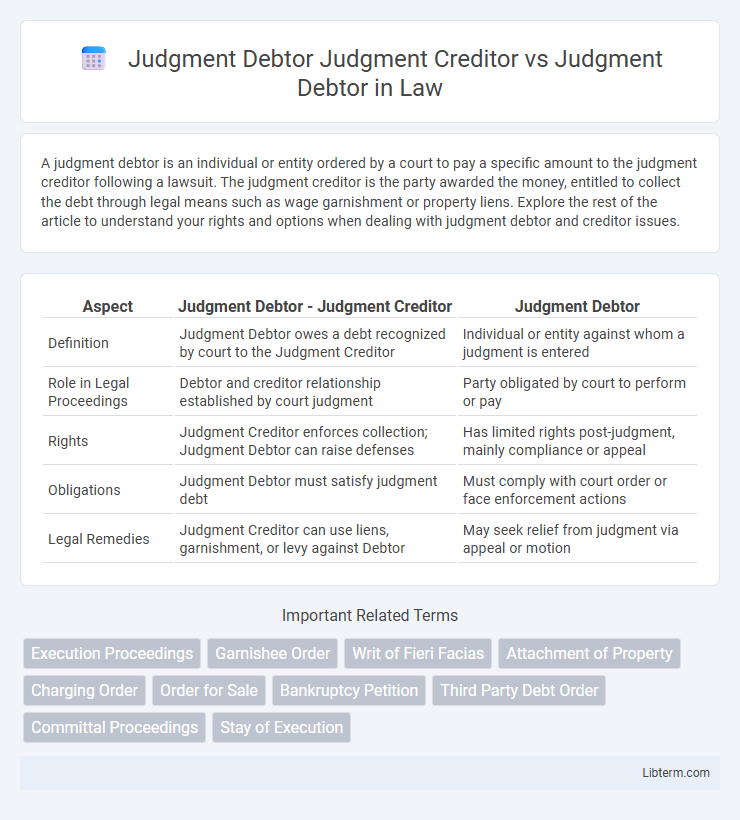
| Aspect | Judgment Debtor - Judgment Creditor | Judgment Debtor |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Judgment Debtor owes a debt recognized by court to the Judgment Creditor | Individual or entity against whom a judgment is entered |
| Role in Legal Proceedings | Debtor and creditor relationship established by court judgment | Party obligated by court to perform or pay |
| Rights | Judgment Creditor enforces collection; Judgment Debtor can raise defenses | Has limited rights post-judgment, mainly compliance or appeal |
| Obligations | Judgment Debtor must satisfy judgment debt | Must comply with court order or face enforcement actions |
| Legal Remedies | Judgment Creditor can use liens, garnishment, or levy against Debtor | May seek relief from judgment via appeal or motion |
Understanding Judgment Debtor and Judgment Creditor
A judgment creditor is an individual or entity that has obtained a legal judgment against another party, the judgment debtor, who owes a debt or obligation as determined by the court. Understanding the roles helps clarify that the judgment debtor must satisfy the debt, often through payment or asset transfer, while the judgment creditor has the legal right to enforce the judgment to recover the owed amount. Enforcement mechanisms may include wage garnishment, liens, or bank levies to ensure compliance with the court's judgment.
Key Legal Definitions
A Judgment Creditor is an individual or entity that has obtained a court order requiring the Judgment Debtor to pay a debt or fulfill an obligation. The Judgment Debtor is the party legally obligated to satisfy the judgment, often through monetary payment or asset transfer. Distinguishing between these roles is crucial in enforcement actions, as the creditor seeks to collect the debt while the debtor must comply with the court's directive.
Roles and Responsibilities of a Judgment Creditor
A Judgment Creditor holds the legal right to enforce a court's judgment by collecting the awarded debt from the Judgment Debtor, often through methods like wage garnishment, bank levies, or property liens. The Judgment Creditor must initiate enforcement actions within the statutory period and ensure all collection efforts comply with relevant laws to avoid liability. Their primary responsibility is to actively pursue the debt recovery while adhering to ethical and legal standards, ensuring the Judgment Debtor's rights are respected during enforcement.
Rights and Obligations of a Judgment Debtor
A Judgment Debtor is legally obligated to satisfy the debt or damages ordered by the court, which may include payment of money, property transfer, or compliance with specific court mandates. The Judgment Debtor's rights typically include protection from unlawful seizure and the ability to negotiate payment terms, while their obligations encompass full compliance with the judgment to avoid enforcement actions such as wage garnishment or asset liens. Distinct from the Judgment Creditor, who enforces the judgment, the Judgment Debtor must adhere to all court-imposed duties and maintain transparency about asset disclosures during enforcement proceedings.
Judgment Creditor vs Judgment Debtor: Core Differences
Judgment Creditor vs Judgment Debtor centers on the legal roles and responsibilities in court-ordered debt recovery, where the judgment creditor holds the right to collect a debt after winning a lawsuit, while the judgment debtor is the individual or entity obligated to pay the debt. The judgment creditor initiates enforcement actions such as wage garnishment or asset seizure, whereas the judgment debtor must comply with court orders to settle the owed amount. Understanding these distinctions is critical in post-judgment procedures and debt collection enforcement under civil law.
Legal Processes Following a Judgment
Judgment creditor obtains legal rights to enforce the court's decision, including garnishment, liens, or seizure of assets against the judgment debtor to satisfy the debt. The judgment debtor faces obligations to comply with payment schedules or risk enforcement actions such as wage garnishment or property liens. Courts monitor these legal processes to ensure fair execution of judgments and may intervene if the debtor fails to meet court-ordered payment obligations.
Enforcement of Judgments Against the Debtor
Enforcement of judgments against the judgment debtor involves legal actions initiated by the judgment creditor to recover the awarded amount through methods such as wage garnishment, bank account levies, or property liens. The judgment debtor is obligated to satisfy the judgment, and failure to comply can result in court-ordered enforcement measures like asset seizure or contempt of court penalties. Effective enforcement ensures that the creditor's rights are upheld and the debtor fulfills their financial obligations as determined by the court.
Defenses Available to Judgment Debtors
Judgment debtors facing claims from judgment creditors can invoke several defenses such as challenging the validity of the original judgment, proving payment or satisfaction of the debt, or demonstrating procedural errors during enforcement. Statutory exemptions may protect certain assets from seizure, while jurisdictional disputes can also serve as defenses against creditor claims. Effective use of these defenses requires understanding applicable state laws and court rules governing judgment enforcement and debtor protections.
Common Disputes Between Creditors and Debtors
Common disputes between judgment creditors and judgment debtors often arise over the enforcement of court orders, including unpaid debts, asset garnishment, and lien placements. Judgment creditors seek to collect the amount awarded by the court, while judgment debtors may contest the debt validity, claim exemptions, or negotiate payment plans. Conflicts frequently occur around the interpretation of judgment terms, debtor asset disclosures, and the methods used for debt recovery.
Resolving Judgment Debt: Negotiation and Settlement
Negotiation and settlement play crucial roles in resolving judgment debt between judgment creditors and judgment debtors by facilitating mutually agreeable payment plans or lump-sum settlements that avoid prolonged litigation. Judgment creditors often leverage negotiation to recover assets efficiently while judgment debtors seek settlements to reduce financial burdens and prevent enforcement actions like wage garnishments or property liens. Effective communication and legal counsel optimize outcomes, ensuring compliance with court orders and preserving financial stability for both parties.
Judgment Debtor Judgment Creditor Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com